At its core, Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process that uses a catalyst—typically a metal surface—to efficiently break down precursor gases and assemble them into highly ordered, high-quality materials. While it is a type of thermal CVD, the addition of the catalyst is the critical factor that enables the synthesis of advanced materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes by lowering reaction temperatures and directing atomic-level growth.
The true advantage of catalytic CVD is not just in forming a thin film, but in using the catalyst as a template to actively guide the growth of a material with a precise, controlled structure that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with heat alone.
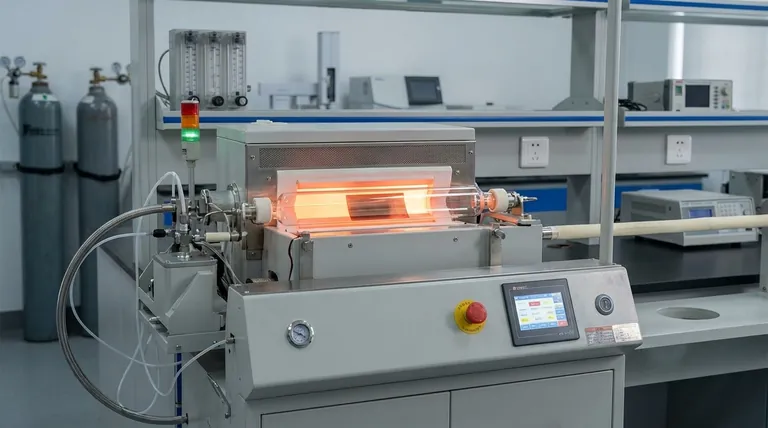

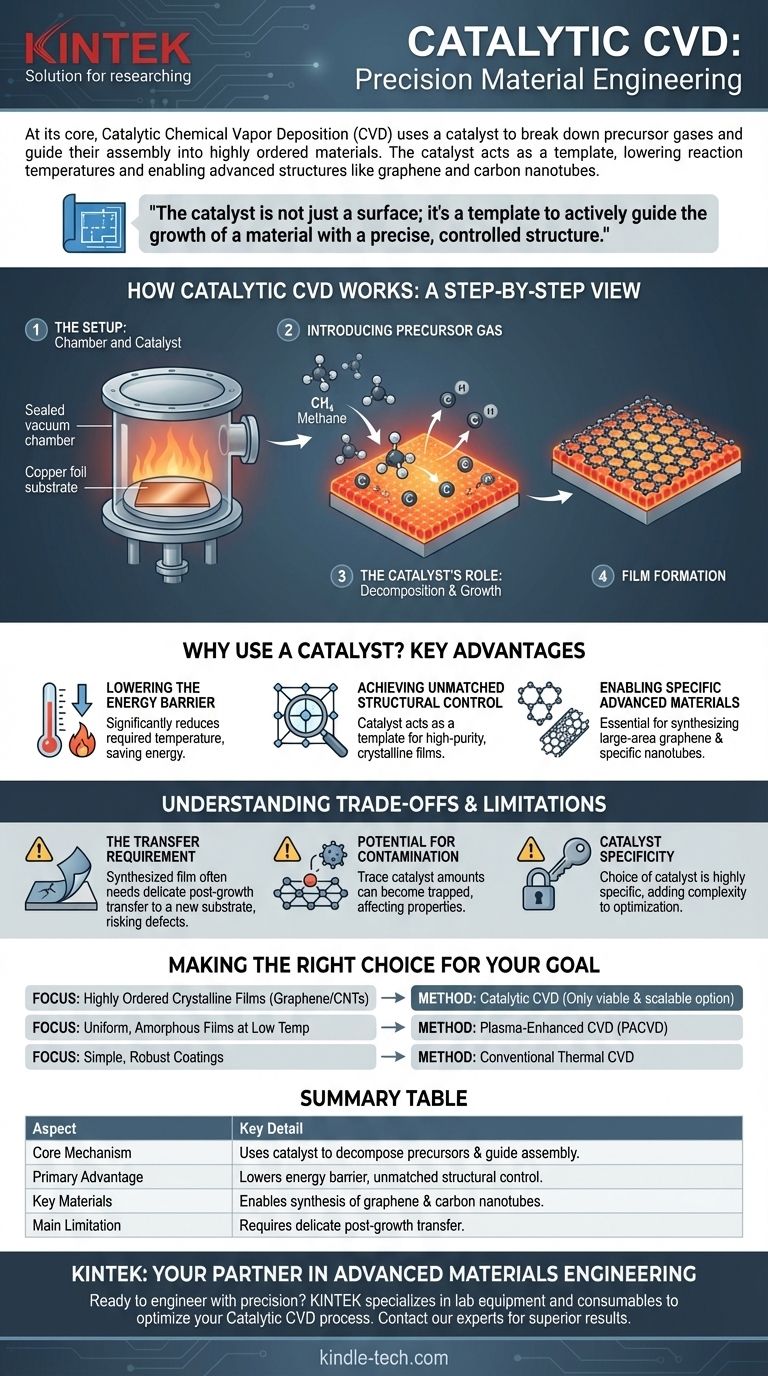
How Catalytic CVD Works: A Step-by-Step View
To understand catalytic CVD, it is best to visualize it as a precise, atomic-scale construction process happening inside a controlled environment. The synthesis of graphene on a copper foil is the classic example.
The Setup: Chamber and Catalyst
The process begins with placing a catalyst substrate, such as a thin foil of copper or nickel, inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is sealed and heated to a specific target temperature, typically several hundred degrees Celsius.
Introducing the Precursor Gas
A precursor gas, which contains the atoms needed for the final material (e.g., a carbon-containing gas like methane for graphene), is then introduced into the hot chamber at a controlled flow rate.
The Catalyst's Role: Decomposition and Growth
This is the key step. When the precursor gas molecules collide with the hot catalyst surface, the catalyst helps break them apart into their constituent atoms (e.g., methane breaks into carbon and hydrogen). These carbon atoms then dissolve into or diffuse across the catalyst surface.
Film Formation
As the surface becomes saturated with carbon atoms, they begin to link together, using the underlying crystal structure of the catalyst as a guide. This directed process allows them to form a highly ordered, continuous film, such as a single atomic layer of graphene, across the entire catalyst surface.
Why Use a Catalyst? The Key Advantages
The addition of a catalyst transforms the CVD process, offering benefits that go far beyond simple deposition.
Lowering the Energy Barrier
The most significant advantage is a dramatic reduction in the temperature required for the chemical reaction. The catalyst provides an alternative, lower-energy pathway for the precursor to decompose, saving energy and making the process compatible with a wider range of equipment.
Achieving Unmatched Structural Control
The catalyst surface is not a passive bystander; it acts as a template for growth. This templating effect is what allows for the synthesis of high-purity, single-crystal, or large-grain polycrystalline films with properties that are superior to materials made by other methods.
Enabling Specific Advanced Materials
For certain materials, catalysis is not just an advantage—it is a necessity. Large-area, high-quality graphene and specific types of carbon nanotubes cannot be effectively synthesized without the guiding role of a catalyst.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, catalytic CVD is not without its challenges. Objectivity requires acknowledging its practical limitations.
The Transfer Requirement
For many electronics applications, the synthesized film (like graphene) is needed on an insulating or transparent substrate, not the metal catalyst it was grown on. This necessitates a delicate post-growth transfer process, which can introduce wrinkles, tears, and defects, compromising the material's perfect structure.
Potential for Contamination
Although CVD is known for producing high-purity materials, trace amounts of the catalyst can sometimes get trapped in the film during growth. This contamination can negatively impact the material's electrical or chemical properties.
Catalyst Specificity
The choice of catalyst is highly specific to the desired material and its intended structure. Finding the right catalyst, optimizing its preparation, and managing its cost can add significant complexity to the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the material you need and its final application.
- If your primary focus is large-area, highly ordered crystalline films (like graphene or carbon nanotubes): Catalytic CVD is often the only viable and scalable method to achieve the required structural perfection.
- If your primary focus is depositing uniform, amorphous films at very low temperatures on sensitive substrates: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PACVD), which uses energy from plasma instead of high heat, may be a better choice.
- If your primary focus is a simple, robust coating where atomic-level structure is not the main concern: Conventional thermal CVD or other variants could be more straightforward and cost-effective.
Understanding the fundamental role of the catalyst is the key to moving beyond simple film deposition and into the realm of true materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Uses a catalyst to decompose precursor gases and guide atomic assembly. |
| Primary Advantage | Lowers energy barrier and provides unmatched structural control. |
| Key Materials | Enables synthesis of graphene and carbon nanotubes. |
| Main Limitation | Often requires a delicate post-growth transfer process. |
Ready to engineer advanced materials with precision? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge research and development. Our expertise in deposition technologies can help you optimize your catalytic CVD process for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right solutions for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















