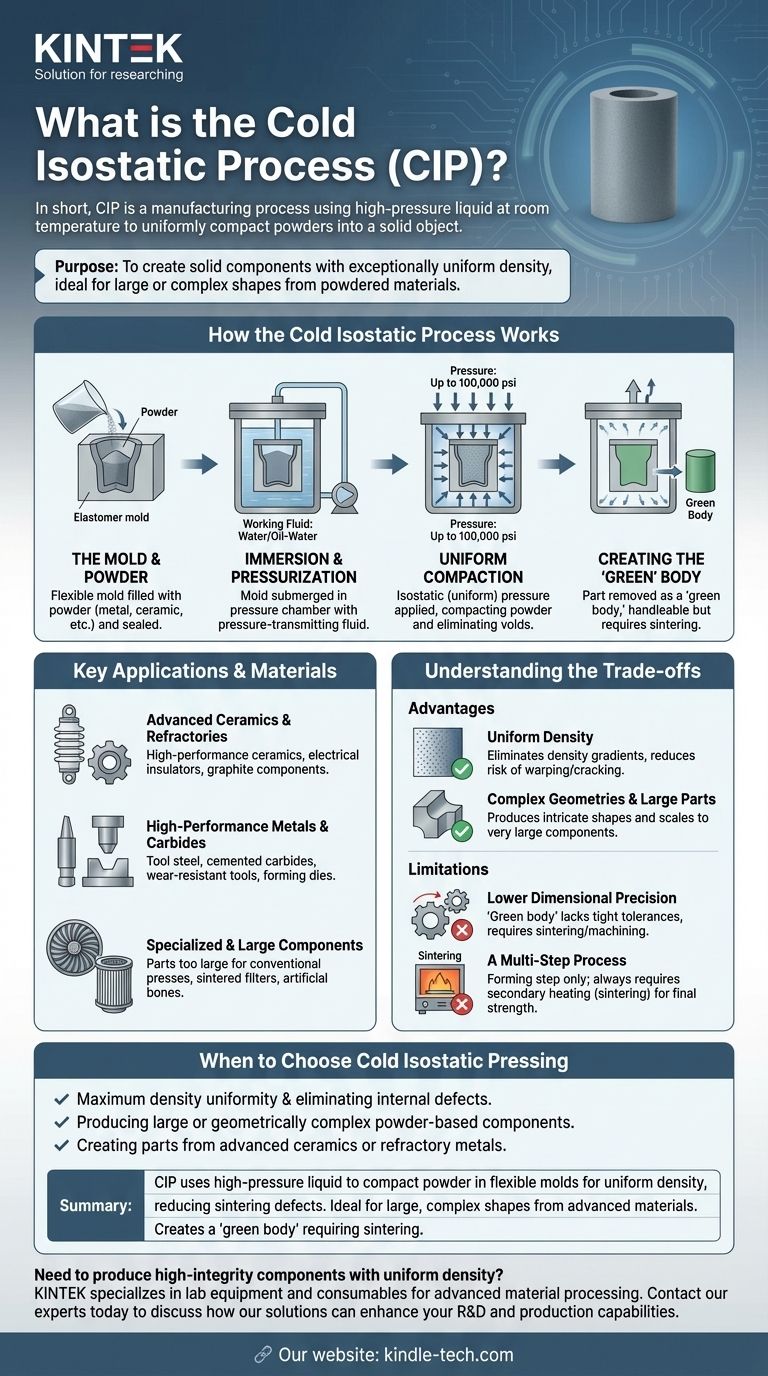
In short, cold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a manufacturing process that uses a high-pressure liquid at room temperature to uniformly compact powders into a solid object. The powder is placed in a flexible mold, which is then submerged in the liquid inside a pressure chamber. By applying intense, equal pressure from all directions, the powder particles are forced together into a cohesive, handleable part known as a "green body."
The fundamental purpose of cold isostatic pressing is to create solid components with exceptionally uniform density from powdered materials. It is the go-to method for forming large or complex shapes that cannot be made effectively with traditional directional pressing techniques.
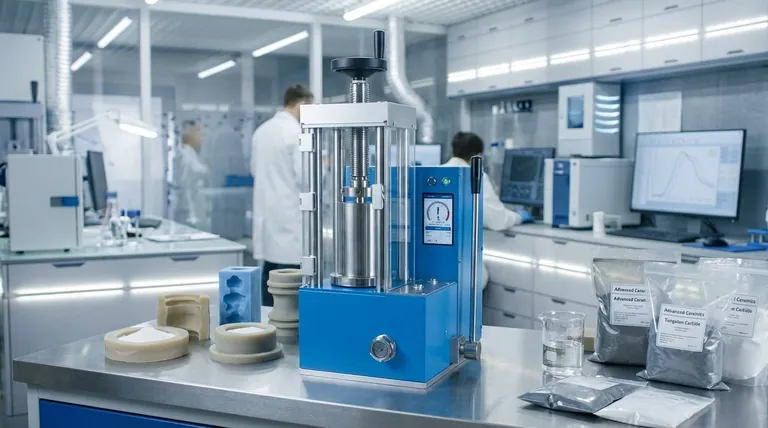

How the Cold Isostatic Process Works
The CIP method is a straightforward yet powerful application of fluid dynamics and material science. It transforms loose powder into a solid form through four distinct steps.
Step 1: The Mold and Powder
The process begins by filling a flexible, typically elastomer mold with the desired powder. This could be a metal, ceramic, or composite material. The mold is then sealed to protect the powder from the pressurizing liquid.
Step 2: Immersion and Pressurization
The sealed mold is placed inside a robust pressure chamber. This chamber is filled with a working fluid—often water with a corrosion inhibitor or an oil-water mixture—which acts as the pressure-transmitting medium.
Step 3: Uniform Compaction
An external pump pressurizes the fluid within the chamber, with pressures potentially reaching as high as 100,000 psi. Because the pressure is exerted by a liquid, it is applied equally on all surfaces of the mold. This isostatic (uniform) pressure compacts the powder particles together, eliminating voids and increasing density.
Step 4: Creating the 'Green' Body
After a set time, the pressure is released, and the part is removed from the chamber. The result is a solid component, referred to as a "green body." This part is solid enough to be handled but has not yet reached its final strength; the particles are held together by mechanical interlocking, not metallurgical bonds. It requires a subsequent heating process, like sintering, to achieve its final properties.
Key Applications and Materials
CIP is essential for producing components where uniform density is critical for performance. It is used across a wide range of industries for specialized materials.
Advanced Ceramics and Refractories
This process is ideal for consolidating high-performance ceramic powders like silicon nitride, silicon carbide, and boron carbide. It is also used for producing electrical insulators and graphite components where internal defects must be minimized.
High-Performance Metals and Carbides
CIP is commonly used to form parts from tool steel, cemented carbides, and other high-melting-point metals. These materials often become wear-resistant tools, metal forming dies, or other industrial components requiring high structural integrity.
Specialized and Large Components
The method is uniquely suited for parts that are too large to fit in conventional uniaxial presses. It is also used for niche applications like creating sintered filters, artificial bones, and other complex shapes that benefit from uniform compaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing process, cold isostatic pressing has distinct advantages and limitations that define its ideal use cases.
Advantage: Uniform Density
The primary benefit of CIP is its ability to produce parts with highly uniform density. Isostatic pressure eliminates the density gradients common in uniaxial (top-down) pressing, which drastically reduces the risk of warping or cracking during the final sintering stage.
Advantage: Complex Geometries and Large Parts
Because the pressure conforms to the shape of the flexible mold, CIP can produce complex and intricate shapes. It also offers excellent scalability for producing very large components that would be impossible to make with traditional hard tooling.
Limitation: Lower Dimensional Precision
The as-pressed "green body" from a CIP process does not have tight dimensional tolerances. The flexibility of the mold and the nature of powder compaction mean that final precision must be achieved through sintering and any necessary final machining.
Limitation: A Multi-Step Process
It is critical to remember that CIP is a forming step, not a finishing one. The resulting green body always requires a secondary thermal process (sintering) to fuse the particles and develop the material's final mechanical properties and strength.
When to Choose Cold Isostatic Pressing
Your choice to use CIP should be driven by the final requirements for your component's material properties, size, and shape.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density uniformity and eliminating internal defects: CIP is the ideal choice, as isostatic pressure prevents the density gradients common in other methods.
- If your primary focus is producing large or geometrically complex powder-based components: CIP offers a scalability and shape flexibility that traditional die pressing cannot match.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from advanced ceramics or refractory metals: CIP is a standard and reliable method for ensuring these high-performance materials are consolidated without introducing stress or flaws.
Ultimately, cold isostatic pressing is a critical tool for creating high-integrity components from powders when uniformity is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses high-pressure liquid at room temperature to compact powder in a flexible mold. |
| Key Benefit | Achieves exceptionally uniform density, reducing warping/cracking in sintering. |
| Ideal For | Large, complex shapes from advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and carbides. |
| Output | Creates a handleable "green body" that requires sintering for final strength. |
Need to produce high-integrity components with uniform density?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, including solutions for powder compaction and sintering. Our expertise can help you achieve the precise material properties and complex geometries your laboratory requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your R&D and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- How does a cold isostatic press contribute to the formation of TZC molybdenum alloy green bodies? Key Densification Tips
- What is the cold CIP process? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Powdered Parts
- What advantages does CIP equipment offer for W-TiC composites? Achieve High-Density, Defect-Free Materials
- What are the advantages of using a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP)? Achieve High Density in Ceramic Pellets



















