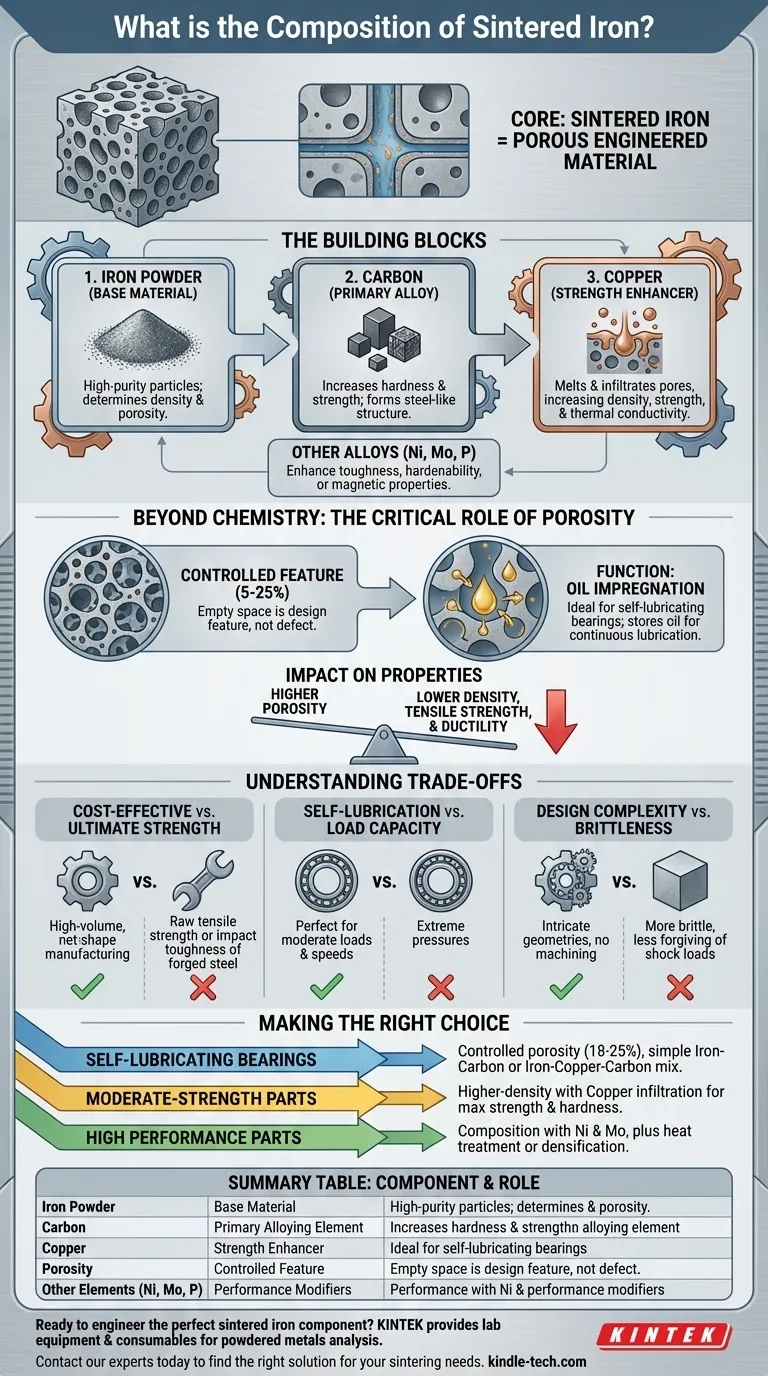
At its core, sintered iron is a porous material made primarily from iron powder. Its composition is defined not just by the base iron, but by the intentional addition of alloying elements—most commonly carbon and copper—and the carefully controlled level of porosity that remains after the manufacturing process.
The key takeaway is that "sintered iron" is not a single substance but a family of engineered materials. Its composition is a deliberate balance of metallic elements and controlled porosity, tailored to achieve specific properties like self-lubrication or cost-effective strength for complex parts.

The Building Blocks of Sintered Iron
The unique properties of a sintered iron part come from a combination of its base metal, specific additives, and its unique internal structure.
The Foundation: Iron Powder
The process begins with a base of high-purity iron powder. The size and shape of these powder particles are critical, as they directly influence the final density and porosity of the finished component.
The Primary Alloying Element: Carbon
Much like in traditional steelmaking, carbon (typically added as graphite powder) is the most critical alloying element. During the high-temperature sintering process, carbon diffuses into the iron particles, transforming the material into a steel-like structure. This dramatically increases its hardness and strength.
Enhancing Strength: Copper
Copper is the second most common alloying addition. As the part is heated, the copper melts and infiltrates the network of pores between the iron particles. This process, known as infiltration, significantly increases the material's density, strength, and thermal conductivity.
Other Key Alloying Elements
Depending on the performance requirements, other elements may be added to the initial powder mix:
- Nickel and Molybdenum: These are used to improve toughness, fatigue strength, and the material's ability to be heat-treated (hardenability).
- Phosphorus: A small amount of phosphorus can be added to improve the magnetic properties for soft magnetic applications, like in solenoids or sensors.
Beyond Chemistry: The Critical Role of Porosity
You cannot understand the composition of sintered iron without understanding the role of its internal pores. Unlike in cast or wrought metals where porosity is a defect, in sintered materials, it is a design feature.
Porosity as a Controlled Feature
The empty space between the initial powder particles is not entirely eliminated during compaction and sintering. The final percentage of porosity (typically ranging from 5% to 25%) is a controlled variable that defines the part's characteristics.
The Function of Pores: Oil Impregnation
This network of interconnected pores is the reason sintered iron is ideal for self-lubricating bearings. The part can be impregnated with oil, which is stored in the pores. During operation, heat and motion draw the oil out to the surface, providing continuous lubrication.
The Impact on Mechanical Properties
Porosity directly impacts the part's physical properties. A higher level of porosity results in a lower density, which in turn reduces the material's tensile strength and ductility compared to a solid, fully dense metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing sintered iron involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. Its benefits are significant, but they come with limitations.
Cost-Effectiveness vs. Ultimate Strength
Sintered parts are extremely cost-effective for high-volume production of complex shapes, as they require little to no machining (net-shape manufacturing). However, they cannot typically match the raw tensile strength or impact toughness of a forged steel component.
Self-Lubrication vs. Load Capacity
The porosity that enables self-lubrication is also what limits the material's strength. Sintered bearings are perfect for moderate loads and speeds, but they may fail under the extreme pressures that a solid bronze or roller bearing could handle.
Design Complexity vs. Brittleness
Powder metallurgy allows for the creation of intricate geometries that would be difficult or expensive to machine. The trade-off is that the inherent porosity can make the material more brittle and less forgiving of shock loads than a comparable wrought material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "correct" composition depends entirely on the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is self-lubricating bearings: Choose a composition with controlled, interconnected porosity (18-25%), typically a simple iron-carbon or iron-copper-carbon mix.
- If your primary focus is moderate-strength structural parts: Opt for a higher-density composition with copper infiltration to maximize strength and hardness while retaining cost benefits.
- If your primary focus is higher performance and fatigue resistance: Specify a composition including nickel and molybdenum, and consider secondary operations like heat treatment or densification.
Ultimately, understanding the composition of sintered iron is about seeing it as an engineered system, where elements and structure work together to deliver specific performance advantages.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sintered Iron | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Powder | Base Material | High-purity particles; determines final density and porosity. |
| Carbon (Graphite) | Primary Alloying Element | Increases hardness and strength by forming a steel-like structure. |
| Copper | Strength Enhancer | Melts and infiltrates pores, increasing density, strength, and thermal conductivity. |
| Porosity | Controlled Feature | Network of pores (5-25%) enabling self-lubrication via oil impregnation. |
| Other Elements (Ni, Mo, P) | Performance Modifiers | Enhance toughness, hardenability, or magnetic properties for specific applications. |
Ready to engineer the perfect sintered iron component for your application?
The precise balance of iron, alloys, and porosity is key to achieving the properties you need, whether for self-lubricating bearings, cost-effective structural parts, or high-performance components. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for developing and analyzing powdered metals.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory's sintering and materials testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory orbital shaker play in silane coupling? Enhance Self-Assembled Monolayer Uniformity
- What is rotary extraction? Master the Art of Gentle Solvent Removal for Pure Concentrates
- What are the methods of oil sludge treatment? A Guide to Recovery, Disposal & Cost
- What are the stages of an electric arc furnace? The Complete Tap-to-Tap Cycle Explained
- Can CBD be distilled? A Guide to High-Purity CBD Concentrate Production
- What indicates the purity of precious metals? The Definitive Guide to Hallmarks and Assay Marks
- How does the tip effect influence Al2O3 reinforcement in PCAS? Master Morphological Control for Stronger Composites
- How thick is gold coating for SEM? Achieve Perfect Conductivity Without Masking Details



















