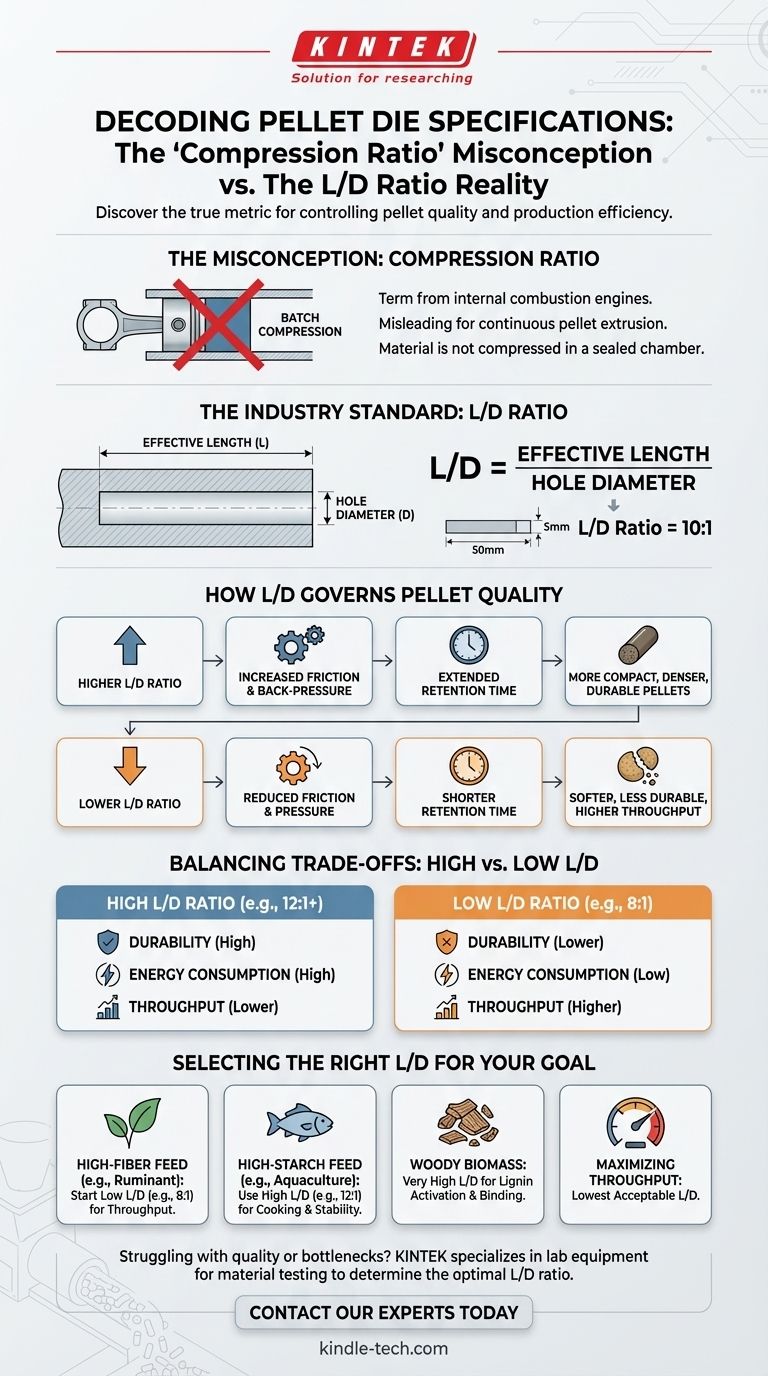
In the context of industrial pelleting, the term "compression ratio" is not a standard industry specification for a pellet die. The critical parameter you are likely seeking is the L/D ratio, which is the ratio of the effective length of the die hole to its diameter. This ratio is the single most important design factor that determines the amount of pressure, friction, and retention time applied to the raw material as it is forced through the die.
The term "compression ratio" can be misleading when applied to pellet dies. The crucial metric that governs pellet quality and production efficiency is the L/D ratio (effective length divided by hole diameter), which dictates the pressure, friction, and retention time applied to the material.

Deconstructing the "Compression Ratio" Misconception
The confusion often arises because "compression ratio" is a familiar term from internal combustion engines, where it describes the ratio of cylinder volumes. However, an industrial pellet mill operates on a principle of continuous extrusion, not batch compression, making a different metric necessary.
Why the Term is Confusing
In a pellet die, material is not compressed into a final volume within a sealed chamber. Instead, it is continuously forced through multiple small channels or holes.
The key action is the friction and resistance the material experiences as it travels through the length of these holes. This process generates the pressure and heat needed to form a dense, durable pellet.
Introducing the Correct Metric: The L/D Ratio
The industry-standard metric for this function is the L/D ratio. It is calculated with a simple formula:
L/D = Effective Length / Hole Diameter
The effective length (L) is the portion of the die hole where compression and formation actually occur. The hole diameter (D) is the final diameter of the pellet. A die with a 50mm effective length and a 5mm hole has an L/D ratio of 10:1.
How the L/D Ratio Governs Pellet Quality
Understanding the L/D ratio is fundamental to controlling the final product. A higher or lower ratio directly changes the forces exerted on the material, leading to different pellet characteristics.
The Role of Friction and Pressure
A higher L/D ratio means the material travels through a longer channel relative to its diameter. This increases the friction and back-pressure, resulting in a more compact and denser pellet.
Conversely, a lower L/D ratio provides a shorter path. This reduces friction and pressure, which is suitable for materials that are easier to compress or require less processing.
Impact on Pellet Durability
The pressure generated by a high L/D ratio is critical for creating durable pellets. This compaction forces particles together, reducing voids and creating strong intermolecular bonds. For materials like wood, this pressure and associated heat activates natural lignins that act as a binder.
Retention Time and Heat Generation
A longer effective length (higher L/D) also increases the retention time—the duration the material spends under intense pressure inside the die hole. This extended time generates more frictional heat, which can be beneficial for cooking starches in animal feed, improving digestibility and pellet integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an L/D ratio is a balancing act between pellet quality, energy consumption, and production rate. There is no single "best" ratio; the optimal choice depends entirely on the raw material and the desired outcome.
High L/D Ratios: Durability vs. Throughput
Choosing a high L/D ratio (e.g., 12:1 or higher) produces very durable, dense pellets. However, it requires significantly more energy to push material through the die.
This increased resistance can lower the overall production rate (throughput) and increase the risk of die blockages, especially with difficult materials.
Low L/D Ratios: Efficiency vs. Quality
A low L/D ratio (e.g., 8:1 or lower) allows for higher throughput and lower energy consumption. The die is easier to run and less prone to plugging.
The primary drawback is the potential for poor pellet quality. The pellets may be soft, crumble easily (creating fines), and lack the durability required for handling and transport.
The Influence of Raw Materials
The characteristics of your feed formulation are paramount.
- Fibrous materials (like alfalfa or high-fiber feed) are naturally resistant to compression and may require a lower L/D ratio to prevent blockages.
- High-starch materials (like poultry or aquaculture feed) benefit from a higher L/D ratio to ensure proper cooking (gelatinization) and binding.
- Oily or high-fat materials act as lubricants, reducing friction. A higher L/D ratio is often needed to compensate and generate enough pressure for a firm pellet.
Selecting the Right L/D Ratio for Your Goal
Your choice of die specification should be a deliberate decision based on your production objectives and raw material characteristics.
- If your primary focus is high-fiber feed (e.g., ruminant): Start with a lower L/D ratio (e.g., 8:1) to facilitate throughput and prevent plugging.
- If your primary focus is high-starch feed (e.g., aquaculture): Use a higher L/D ratio (e.g., 12:1) to achieve the necessary cooking and water stability.
- If your primary focus is woody biomass: A very high L/D ratio is often required to generate the heat and pressure needed to activate lignin as a natural binder.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: Choose the lowest L/D ratio that produces a pellet of minimally acceptable quality for your application.
Ultimately, mastering the L/D ratio transforms pelleting from a brute-force process into a precisely controlled manufacturing operation.
Summary Table:
| L/D Ratio | Typical Application | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Low (e.g., 8:1) | High-fiber feeds (ruminant) | Higher throughput, lower energy use, but softer pellets |
| High (e.g., 12:1+) | High-starch feeds (aquaculture), biomass | Denser, more durable pellets, better cooking/starch gelatinization |
Struggling with pellet quality or production bottlenecks? The right die specification is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and process development, helping you precisely determine the optimal L/D ratio for your specific raw materials and production goals. Contact our experts today to optimize your pelleting process for superior durability and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
- Why is KBr used as a mulling agent in IR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What roles do high-strength graphite dies and graphite paper play in SPS of B4C? Enhance Your Sintering Precision
- Why are tungsten carbide (WC) molds required for hot-pressing battery materials? Ensure Density and Precision
- Are there different types of silicone molds? A Guide to Tin-Cure vs. Platinum-Cure
- What is the function of graphite molds during hot pressing of Tantalum Carbide? Optimize Your TaC Ceramic Densification
- Why is compression molding important? Unmatched Strength for Large, Durable Parts



















