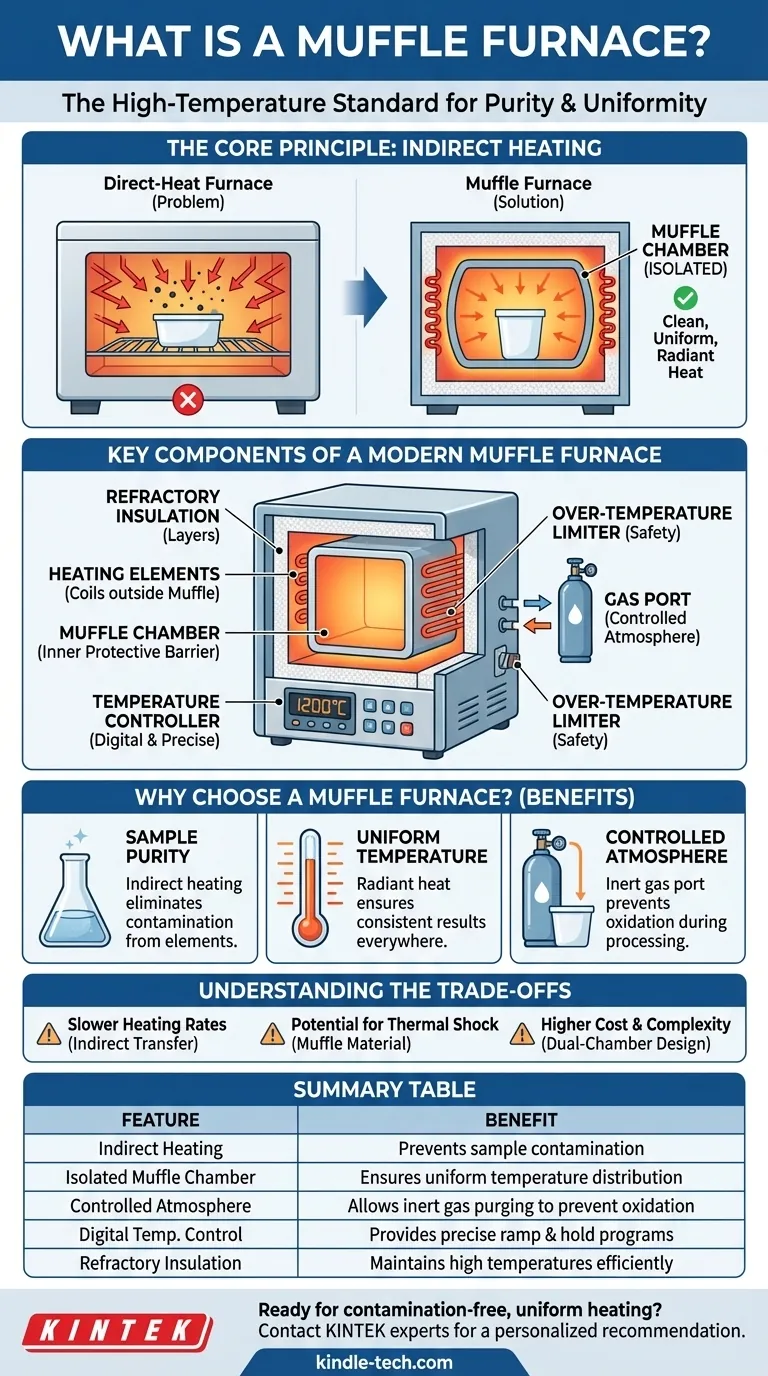
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats its contents without direct exposure to the heating elements. Its defining feature is an internal chamber, or "muffle," which acts as a protective barrier. This design isolates the sample, preventing contamination and ensuring highly uniform heat distribution for applications in research and materials processing.
The core problem with direct-heat furnaces is the risk of sample contamination and uneven temperatures. A muffle furnace solves this by using an isolated inner chamber that radiates clean, uniform heat, making it the standard for precision high-temperature work.

The Core Principle: Indirect Heating
The entire concept of the muffle furnace is built around separating the heat source from the material being heated. This principle of indirect heating is what distinguishes it from simpler kilns or ovens.
What is the "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is the heart of the furnace. It is a box-like or barrel-shaped chamber made of high-temperature refractory materials. This chamber sits inside the main furnace body.
How It Works
Heating elements are positioned on the outside of the muffle chamber. These elements heat the muffle's walls to the desired temperature. The muffle then radiates that thermal energy inward, heating the sample or load placed inside it evenly from all sides.
The Benefit of Isolation
This isolation is the furnace's primary advantage. By preventing direct contact, it ensures that no byproducts from the heating elements (like flaking oxides) can fall onto and contaminate the sample. This is critical in scientific analysis, metallurgy, and advanced materials development.
Key Components of a Modern Muffle Furnace
While the concept is straightforward, modern muffle furnaces incorporate several key components to ensure safety, precision, and versatility.
Heating Elements
These are typically robust electric resistance coils located between the outer insulation and the exterior of the muffle chamber. They are designed for long life at extreme temperatures.
Refractory Insulation
The furnace is constructed with layers of high-performance insulating material. This ensures the furnace can reach and maintain temperatures that can exceed 2000°C while keeping the exterior relatively cool and minimizing energy waste.
Temperature Controller and Safety Systems
Modern units use sophisticated digital controllers to precisely manage temperature ramps and holds. They also include critical safety features like an over-temperature limiter, which automatically shuts down the furnace to protect both the equipment and the valuable load inside.
Controlled Atmosphere Capabilities
Many muffle furnaces include a gas port. This allows users to purge the chamber and introduce non-flammable protective gases, such as nitrogen or argon. This creates an inert atmosphere, preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace design comes with inherent trade-offs that are important to understand.
Slower Heating Rates
Because heat is transferred indirectly—from the elements, through the muffle wall, and then to the sample—the overall time to reach a target temperature can be longer than in a direct-fired furnace. This is the price paid for uniformity and purity.
Potential for Thermal Shock
The refractory muffle chamber, while durable, can be susceptible to cracking if heated or cooled too rapidly. Modern controllers are programmed to manage these rates carefully, but it remains a physical limitation of the materials.
Higher Cost and Complexity
The dual-chamber construction, advanced controls, and high-grade refractory materials make muffle furnaces more complex and generally more expensive than simpler ovens or kilns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your technical requirements for purity, uniformity, and atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: A muffle furnace is non-negotiable, as it eliminates contamination from the heat source.
- If your primary focus is temperature uniformity: The radiant heat provided by the muffle design delivers exceptionally even temperature distribution, which is critical for consistent material treatment.
- If your primary focus is processing in an inert atmosphere: A muffle furnace with a gas port is the standard tool for preventing oxidation during high-temperature work.
By understanding its core function of providing clean, indirect heat, you can confidently decide when a muffle furnace is the correct tool for your objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Indirect Heating | Prevents sample contamination from heating elements |
| Isolated Muffle Chamber | Ensures uniform temperature distribution |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Allows inert gas purging to prevent oxidation |
| Digital Temperature Control | Provides precise ramp and hold programs |
| Refractory Insulation | Maintains high temperatures efficiently and safely |
Ready to achieve contamination-free, uniform heating for your lab work?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance muffle furnaces designed for researchers and materials scientists who demand precision and purity. Our furnaces deliver the clean, indirect heating you need for applications like ash content determination, heat treatment, and materials testing.
Let us help you select the perfect muffle furnace for your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are furnaces usually made of? A Guide to Materials for Extreme Temperatures
- What are the four steps to the heat treating process? Master the 3 Core Stages for Superior Results
- What is the precaution for muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Lab Excellence
- What is melt loss? The Ultimate Guide to Reducing Metal Loss in High-Temp Processing
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing



















