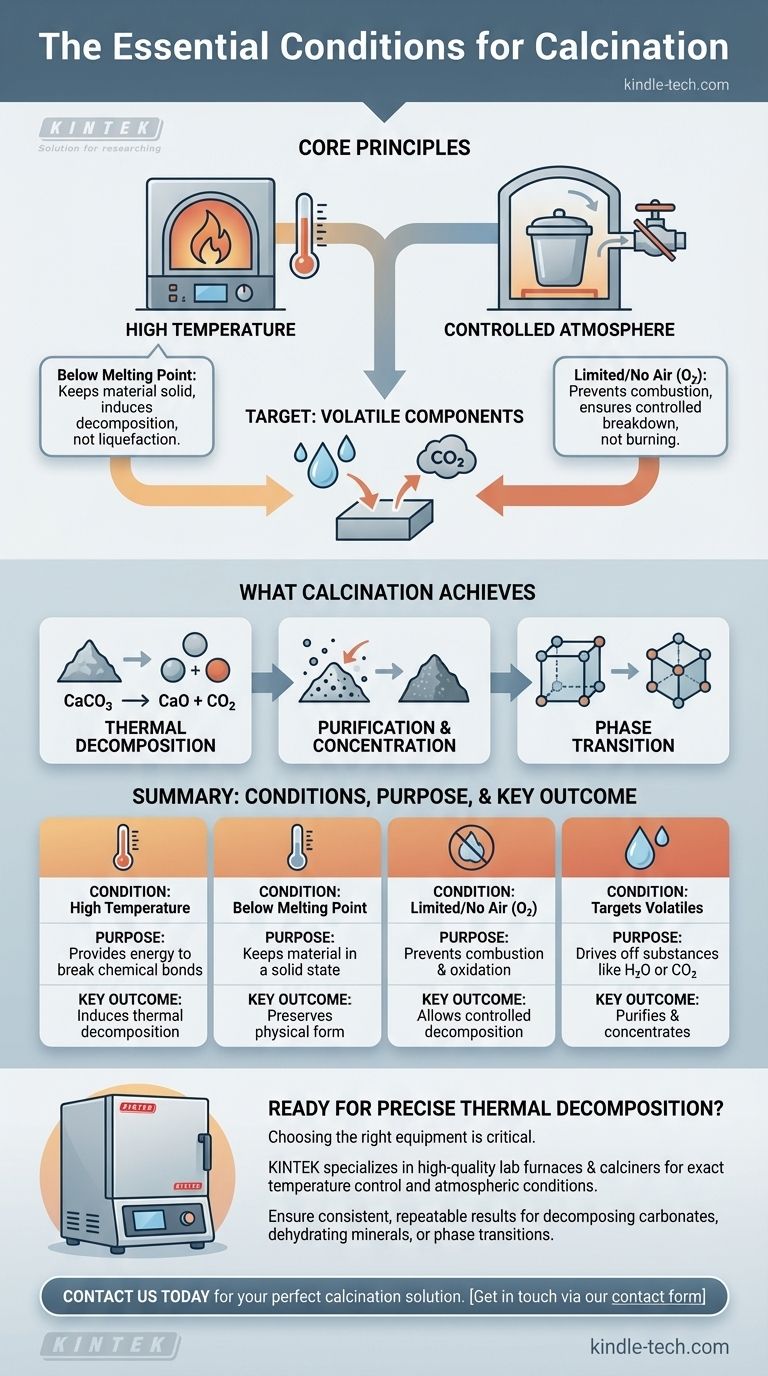
The essential condition for calcination is heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in an environment with a limited supply or complete absence of air. This specific set of conditions is not for burning the material, but for inducing thermal decomposition, driving off volatile substances like water or carbon dioxide, or triggering a change in the material's physical form.
The core principle of calcination is to use heat to break down a substance, not to burn it. Controlling the atmosphere by limiting or eliminating air is the critical factor that prevents combustion and allows for this controlled decomposition.

The Core Principles of Calcination
To understand calcination, we must look at its two defining parameters: heat and atmosphere. Each serves a distinct and critical purpose in achieving the desired chemical or physical change.
The Role of High Temperature
The primary driver of the process is heat. Applying a high temperature provides the necessary thermal energy to break chemical bonds within the solid material.
However, this temperature must be carefully controlled to remain below the substance's melting point. The goal is to alter a solid, not to liquefy it, which would fundamentally change the nature of the process and the end product.
Why the Atmosphere is Controlled
The most defining condition of calcination is the absence or limited supply of air (specifically, oxygen). This is what distinguishes it from other heat-treatment processes like roasting.
By restricting oxygen, you prevent combustion. The objective is to decompose the material through heat alone, causing components to be released as gas, rather than to have it react with oxygen in a burning process.
The Target: Volatile Components
Calcination specifically targets the removal of volatile fractions from a substance. These are components that can be turned into gas and driven off by heat.
Common examples include removing absorbed moisture (H₂O) or chemically bound water from hydrates, and driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂) from carbonate ores like limestone.
What Calcination Aims to Achieve
The specific conditions of calcination are designed to produce several key outcomes, primarily in the fields of metallurgy and materials science.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common goal. Heat is used to break down a compound into simpler substances. The classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate).
When heated, the calcium carbonate decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind the solid lime.
Purification and Concentration
By driving off volatile impurities like water and carbon dioxide, the remaining solid becomes more concentrated in the desired element or compound. This is a crucial step in preparing ores for further processing.
Phase Transition
In some applications, the heat from calcination is used not to decompose a material but to change its crystalline structure, or phase. This can alter the material's physical properties, such as its hardness or reactivity, making it suitable for specific industrial uses.
The Equipment: Calciners and Furnaces
This process is conducted in specialized, high-temperature reactors. A calciner is a purpose-built piece of equipment, often a rotating cylinder, that allows for precise control over both temperature and the internal atmosphere, ensuring the conditions for calcination are met.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the required conditions allows you to determine when calcination is the appropriate industrial process.
- If your primary focus is decomposing a carbonate ore: Calcination is the correct method to drive off carbon dioxide and produce a metal oxide.
- If your primary focus is removing water from a hydrated mineral: The process effectively dehydrates the material, concentrating the desired compound.
- If your primary focus is to fully oxidize a substance (like a sulfide ore): Calcination is the wrong choice; you would need roasting, which involves heating in an excess of air.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about the precise application of heat in a controlled atmosphere to achieve a specific chemical or physical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Purpose | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperature | Provides energy to break chemical bonds | Induces thermal decomposition |
| Temperature Below Melting Point | Keeps the material in a solid state | Preserves the physical form of the product |
| Limited or No Air (O₂) | Prevents combustion and oxidation | Allows for controlled decomposition, not burning |
| Targets Volatile Components | Drives off substances like H₂O or CO₂ | Purifies and concentrates the solid material |
Ready to achieve precise thermal decomposition in your lab?
Choosing the right equipment is critical for successful calcination. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and calciners that provide the exact temperature control and atmospheric conditions your processes demand.
Whether you are decomposing carbonates, dehydrating minerals, or studying phase transitions, our reliable equipment ensures consistent, repeatable results.
Contact us today to find the perfect calcination solution for your laboratory needs. Get in touch via our contact form and let our experts help you enhance your material processing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the risks of using a muffle furnace? Mitigate Thermal, Material, and Operational Hazards
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- What is the difference between sintering and vitrification? Key Thermal Process Distinctions
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- What is the role of muffle furnace in fluid mechanics? A Key Tool for Material Preparation



















