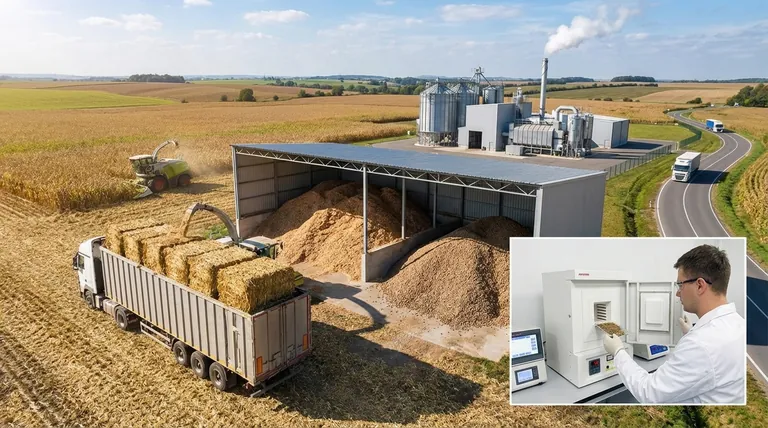
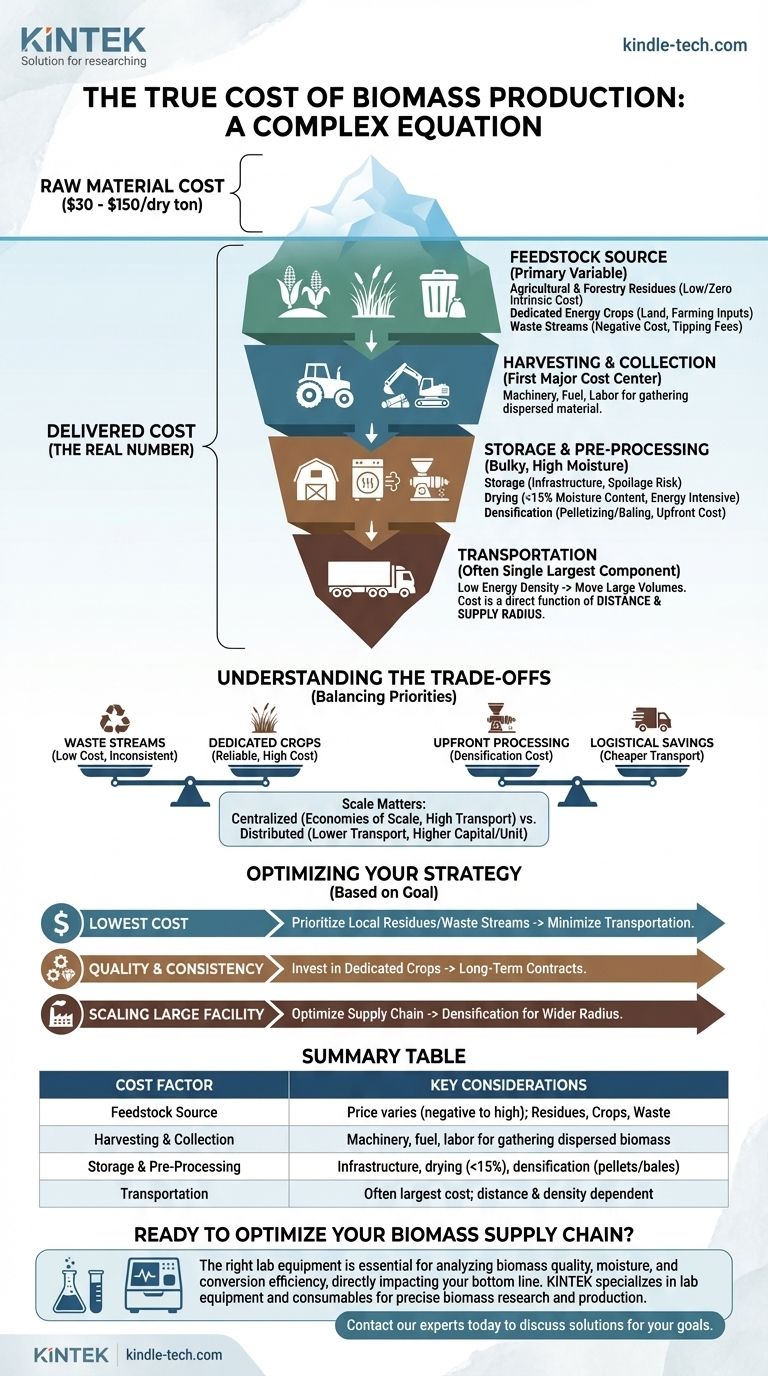
Ultimately, the cost of biomass production is not a single figure but a complex equation driven by source, location, and logistics. While costs can range from as low as $30 to over $150 per dry ton, the most important number is the final "delivered cost" at the processing facility. This figure is determined less by the raw material itself and more by the complex supply chain required to get it from the field to the factory gate.
The true cost of biomass is not the price of the raw material, but the total "delivered cost" to your facility. This figure is dominated by logistics—collection, storage, and especially transportation—making your supply chain design the single most critical factor in economic viability.

Deconstructing the "Delivered Cost" of Biomass
The final price per ton is an aggregation of costs incurred at every step of the supply chain. Understanding these components is essential for any realistic economic assessment.
Factor 1: The Feedstock Source
The type of biomass is the primary variable.
- Agricultural & Forestry Residues: Materials like corn stover, wheat straw, or logging residues have a very low or even zero intrinsic cost. The cost is almost entirely in their collection and aggregation.
- Dedicated Energy Crops: Plants like switchgrass, miscanthus, or poplar are grown specifically for energy. Their cost includes land use (lease or purchase), farming inputs (fertilizer, water, labor), and harvesting.
- Waste Streams: Municipal solid waste (MSW) or food processing waste can have a negative cost, where you are paid a "tipping fee" to take the material. However, these streams often require significant investment in sorting and cleaning.
Factor 2: Harvesting and Collection
This is the first major cost center. It involves the machinery, fuel, and labor required to gather the dispersed biomass material from a field or forest. For residues, this step can account for a significant portion of the total cost.
Factor 3: Storage and Pre-Processing
Biomass is bulky, has high moisture, and can degrade over time.
- Storage: Proper storage is necessary to ensure a year-round supply for a facility and to prevent spoilage, which represents a direct financial loss. This requires space and infrastructure like barns or covered pads.
- Drying: Most conversion technologies require biomass with low moisture content (typically <15%). The energy and equipment used for drying add a significant cost.
- Densification: Processes like pelletizing or bailing increase the density of the biomass. While this adds an upfront processing cost, it dramatically reduces downstream transportation and handling costs.
Factor 4: Transportation
Transportation is frequently the single largest component of the delivered biomass cost. Because biomass has low energy density, you have to move large volumes to get a meaningful amount of energy. Costs are a direct function of distance, defining the viable "supply radius" around a processing facility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a biomass strategy involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" approach; the optimal choice depends on your specific goals and constraints.
Waste Streams vs. Dedicated Crops
Waste streams offer a potentially very low-cost feedstock, but their supply can be inconsistent and the quality variable. Dedicated energy crops provide a reliable, high-quality supply but come at a much higher production cost and compete for agricultural land.
Upfront Processing vs. Logistical Savings
Investing in densification (like pelletizing) adds a significant cost at the front of the supply chain. However, the resulting pellets are far cheaper to transport and easier to handle, which can lead to major savings for facilities that draw from a wide geographic area. For small facilities with a very local supply, this extra step may not be economical.
Scale: Centralized vs. Distributed Models
A large, centralized biorefinery benefits from immense economies of scale in the conversion process, making its per-unit production cost lower. However, it requires a massive and expensive logistical network to feed it. A smaller, distributed model may have higher capital costs per unit of output but can be placed closer to the biomass source, drastically cutting transportation expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal biomass strategy depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible feedstock cost: Prioritize agricultural residues or organic waste streams located very close to your facility to minimize transportation.
- If your primary focus is supply consistency and quality for industrial use: Invest in dedicated energy crops through long-term contracts with growers, despite higher production costs.
- If your primary focus is scaling a large industrial facility: Your project's success hinges on optimizing the supply chain, likely requiring densification to manage transportation costs over a wider radius.
Ultimately, mastering biomass economics means shifting your focus from the cost of the material itself to the cost of moving it.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Source | Agricultural residues, dedicated crops, or waste streams. Price varies from negative (tipping fees) to high. |
| Harvesting & Collection | Machinery, fuel, and labor for gathering dispersed biomass. |
| Storage & Pre-Processing | Infrastructure for storage, drying (<15% moisture), and densification (pelletizing/baling). |
| Transportation | Often the largest cost; determined by distance and biomass density. |
Ready to Optimize Your Biomass Supply Chain?
Navigating the complexities of biomass costs—from sourcing the right feedstock to designing an efficient logistics network—is critical for your project's economic viability. The right lab equipment is essential for analyzing biomass quality, moisture content, and conversion efficiency, directly impacting your bottom line.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of biomass research and production facilities. We provide the reliable tools you need to test, validate, and optimize your processes, helping you control costs and ensure quality from the field to the final product.
Let's build a more efficient and cost-effective future for biomass together. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the method of determining ash? Choose the Right Ashing Method for Your Lab
- What are the different types of ashing analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What are the environmental impacts of metal processing? A Guide to Sustainability and Solutions
- How do you determine the ash content of a plant sample? A Step-by-Step Guide to Mineral Analysis
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and induction furnace? Choosing the Right Heat Source for Your Lab



















