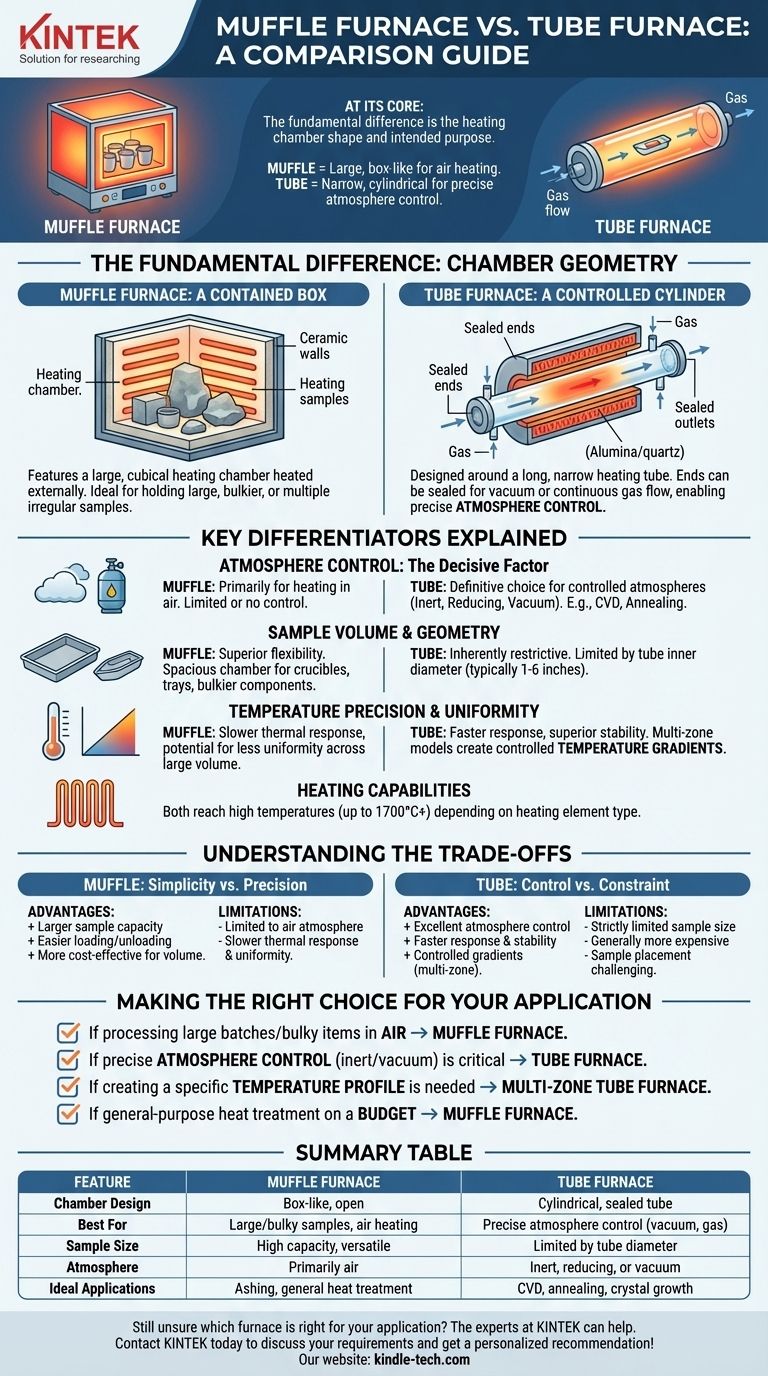
At its core, the difference between a muffle furnace and a tube furnace comes down to the shape of their heating chamber and, consequently, their intended purpose. A muffle furnace has a large, box-like chamber for heating samples in air, while a tube furnace uses a narrow, cylindrical tube that allows for precise control over the gas atmosphere. This fundamental design difference dictates their respective strengths and applications.
The choice is a function of your primary goal. Select a muffle furnace for processing larger, bulkier samples where atmosphere control is not critical. Choose a tube furnace when you require precise control over the gaseous environment and temperature profile for smaller samples.

The Fundamental Difference: Chamber Geometry
The most significant distinction between these two types of furnaces is their physical design. This single factor influences nearly every other aspect of their performance, from sample capacity to atmospheric control.
The Muffle Furnace: A Contained Box
Think of a muffle furnace as a high-performance oven. It features a large, cubical heating chamber, often made of a refractory ceramic material, that is heated externally.
This design makes it exceptionally well-suited for holding large or irregularly shaped samples. It's also ideal for processing multiple samples at once, such as in ashing or general heat-treating applications.
The Tube Furnace: A Controlled Cylinder
A tube furnace, by contrast, is designed around a long, narrow heating tube, typically made of alumina, quartz, or silicon carbide. Heating elements surround this tube, creating a concentrated and uniform hot zone.
The key advantage is that the ends of the tube can be sealed. This allows for the creation of a vacuum or the continuous flow of specific gases, providing precise atmosphere control that is impossible to achieve in a standard muffle furnace.
Key Differentiators Explained
While both furnaces heat materials to high temperatures, their suitability for a given task depends on several key factors stemming from their design.
Atmosphere Control: The Decisive Factor
This is the most critical point of distinction. Tube furnaces are the definitive choice for applications requiring a controlled atmosphere.
By sealing the ends and introducing gas inlets and outlets, you can perform processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), annealing in an inert (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) or reducing (e.g., Hydrogen) atmosphere.
Muffle furnaces are designed primarily for heating in air. While some can be modified with a gas port, they are not sealed and cannot provide the purity or control of a dedicated tube furnace.
Sample Volume and Geometry
A muffle furnace offers superior flexibility for sample size. Its spacious chamber can accommodate crucibles, trays of powders, or bulky components that would never fit inside a processing tube.
A tube furnace is inherently restrictive. The maximum size of your sample is limited by the inner diameter of the work tube, which typically ranges from 1 to 6 inches.
Temperature Precision and Uniformity
Due to their smaller thermal mass and contained volume, tube furnaces often provide more rapid heating/cooling rates and more precise temperature control.
Furthermore, multi-zone tube furnaces, which have several independent heating elements along the tube, are unparalleled for creating controlled temperature gradients. This is essential for processes like crystal growth or specialized chemical synthesis.
Heating Capabilities
Both furnace types can reach similar maximum temperatures, often up to 1700°C or higher. The specific temperature range is determined by the type of heating element used, such as Kanthal wire, silicon carbide (SiC) rods, or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces involves balancing capability against constraint. Neither is universally "better"; they are simply different tools for different jobs.
The Muffle Furnace: Simplicity vs. Precision
Advantages:
- Significantly larger sample capacity.
- Easier to load and unload diverse sample types.
- Generally more cost-effective for a given heating volume.
Limitations:
- Effectively limited to heating in an air atmosphere.
- Slower thermal response and potentially less temperature uniformity across the large chamber.
The Tube Furnace: Control vs. Constraint
Advantages:
- Excellent, precise control over the gas atmosphere.
- Often faster thermal response and superior temperature stability.
- Ability to create controlled temperature gradients with multi-zone models.
Limitations:
- Strictly limited sample size and geometry.
- Generally more expensive, especially models with gas handling and multi-zone control.
- Sample placement can be more challenging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, focus on the non-negotiable requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is processing large batches or bulky items in air: A muffle furnace is the practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control (inert gas, vacuum, reactive gases): A tube furnace is the only appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific temperature profile along your sample: A multi-zone tube furnace is required.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment on a budget: A muffle furnace offers the best combination of versatility and value.
Your final decision will be guided by the unique demands of your specific material and experimental goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Design | Box-like, open chamber | Cylindrical, sealed tube |
| Best For | Large/bulky samples, heating in air | Precise atmosphere control (vacuum, gas) |
| Sample Size | High capacity, versatile geometry | Limited by tube diameter (1-6 inches typical) |
| Atmosphere | Primarily air | Inert, reducing, or vacuum environments |
| Ideal Applications | Ashing, general heat treatment, calcination | CVD, annealing, crystal growth, chemical synthesis |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK can help you select the perfect lab furnace for your specific needs. Whether you require the high-volume capacity of a muffle furnace or the precise atmosphere control of a tube furnace, we have the equipment and expertise to support your laboratory's success.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your high-temperature processing requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- What is the introduction of muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a chamber furnace? Understand the Key Distinctions for Your Lab
- What is the alternative to a laboratory oven? Find the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition



















