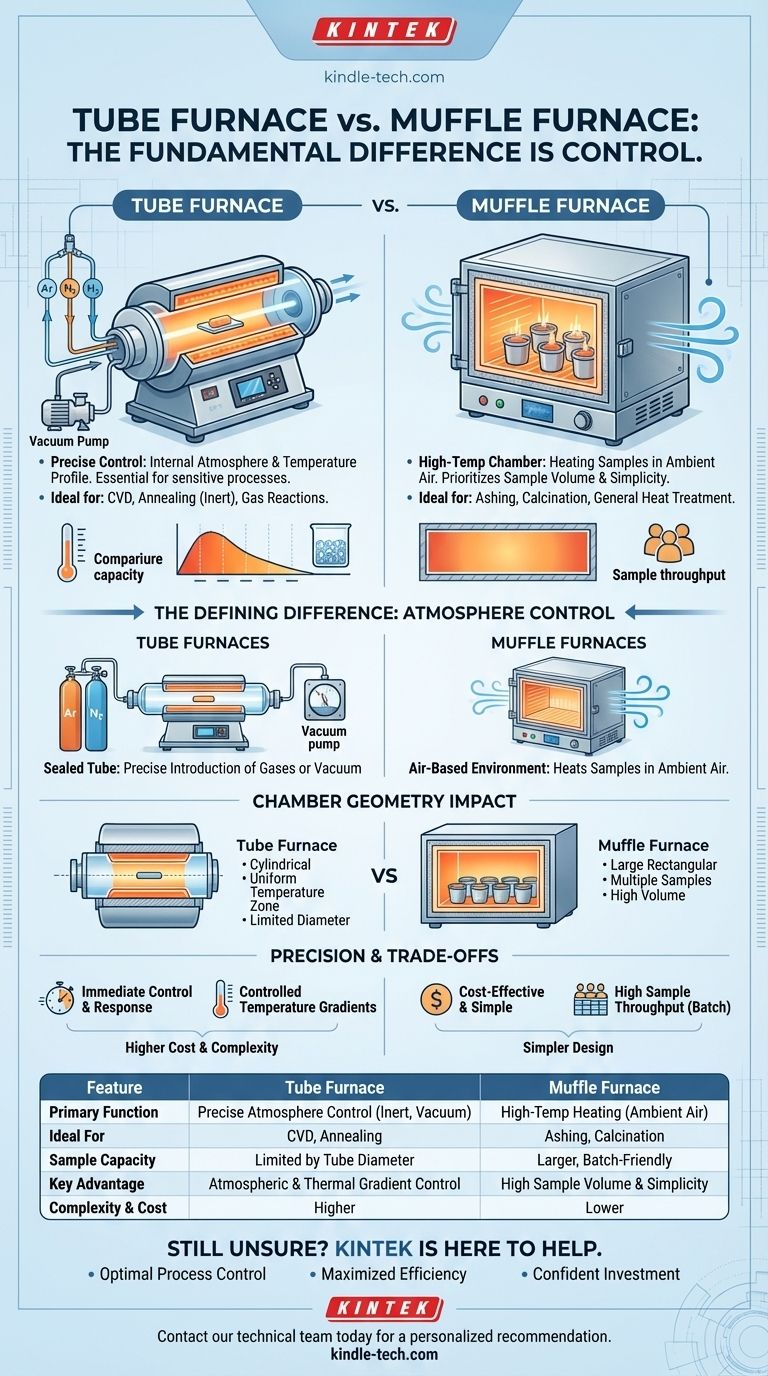
The fundamental difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace is control. A tube furnace is engineered for precise control over the internal atmosphere and temperature profile, making it essential for sensitive processes. In contrast, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed for heating samples in ambient air, prioritizing sample volume and simplicity.
Your choice is not about which furnace is "better," but which tool provides the correct environment for your work. Select a tube furnace when you need to control the gas atmosphere; choose a muffle furnace for straightforward heating of larger samples in air.
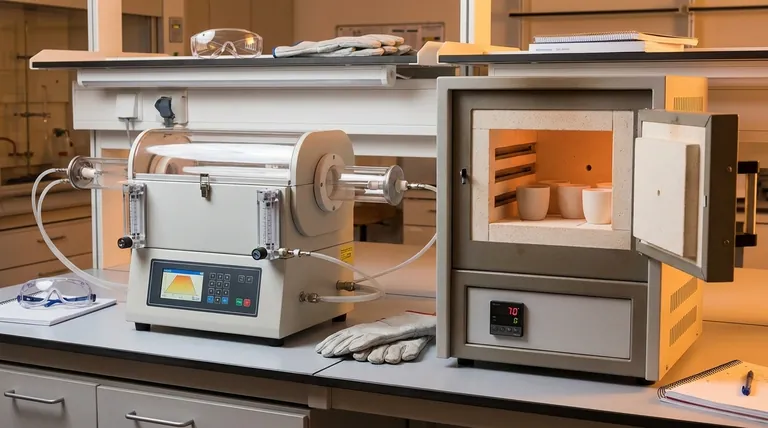

The Defining Difference: Atmosphere Control
The most critical distinction is how each furnace manages the environment around the sample. This capability dictates the types of applications for which each is suited.
How Tube Furnaces Manage Atmospheres
A tube furnace uses a sealed cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz, that passes through the heating element.
This design allows for the precise introduction of gases or the application of a vacuum. It is the standard for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), annealing in inert environments (like argon or nitrogen), or reactions that require a specific gaseous reactant.
The Muffle Furnace's Air-Based Environment
A muffle furnace is essentially a highly insulated box with a heating chamber. Its primary function is to heat samples in ambient air.
This makes it ideal for applications like ashing, calcination, or general heat treatments where an air atmosphere is acceptable or desired. While some models can be adapted for inert gas purging, it is not their core design principle.
Chamber Geometry and Its Impact
The physical shape and size of the heating zone directly influence sample placement and process uniformity.
The Tube Furnace: Uniformity in a Confined Space
The sample is placed inside the tube, which has a limited inner diameter. This can make placing large or irregularly shaped samples difficult.
However, this cylindrical geometry is excellent for achieving a highly uniform temperature zone along a specific length of the tube, ensuring consistent heating for smaller samples.
The Muffle Furnace: Volume and Accessibility
The muffle furnace features a much larger, typically rectangular chamber.
This design makes it simple to place multiple samples, large crucibles, or components that would not fit inside a tube. It prioritizes throughput and ease of loading over atmospheric precision.
Precision in Temperature and Process
Beyond the atmosphere, the design of each furnace affects how temperature can be controlled and manipulated.
Immediate Control and Response
Because a tube furnace heats a smaller, more confined volume, it can often heat up and cool down faster, allowing for more immediate response to temperature adjustments.
Managing Temperature Gradients
The design of a tube furnace, with its ends often exposed, is uniquely suited for creating controlled temperature gradients.
By using multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the tube's length, you can establish a specific temperature profile, which is critical for specialized applications like crystal growth or material purification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is a universal solution. The choice involves balancing capability against practicality.
Cost and Complexity
A tube furnace is typically more expensive due to its need for a sealed system, gas flow controllers, and potential vacuum components. A muffle furnace's simpler design makes it a more cost-effective solution for general-purpose heating.
Sample Throughput vs. Process Specificity
A muffle furnace excels at batch processing, allowing you to heat many samples at once. A tube furnace is designed for highly specific processes that often involve a lower volume of material.
A Note on Shared Capabilities
Both furnace types can reach similarly high temperatures and are equipped with critical safety features like over-temperature protection and automatic shutoffs. The key differentiator remains the process environment they create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be driven entirely by the requirements of your material and the process you intend to run.
- If your primary focus is CVD, annealing in an inert gas, or creating a temperature gradient: The atmospheric and thermal control of a tube furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is ashing, calcination, or bulk heat treatment in air: A muffle furnace offers the best combination of capacity, simplicity, and value.
- If you need to process large or awkwardly shaped samples: The larger, more accessible chamber of a muffle furnace is the correct choice.
- If budget and simplicity are your main constraints for air-based heating: The muffle furnace is the most practical and economical option.
By understanding that the core difference lies in atmospheric control versus sample volume, you can confidently select the right furnace to achieve your goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Precise atmosphere control (inert gas, vacuum) | High-temperature heating in ambient air |
| Ideal For | CVD, Annealing, processes requiring specific gas | Ashing, Calcination, general heat treatment |
| Sample Capacity | Limited by tube diameter | Larger, batch-friendly chamber |
| Key Advantage | Atmospheric & thermal gradient control | High sample volume & simplicity |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher | Lower |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace is critical for your research outcomes. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment, is here to help.
We specialize in providing the right heating solutions for your specific application. Our experts can guide you to the perfect furnace to ensure:
- Optimal Process Control: Achieve precise results with the correct atmospheric conditions.
- Maximized Efficiency: Process samples effectively, whether you need high throughput or specialized environments.
- Confident Investment: Get the right tool for your budget and technical requirements.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our technical team today for a personalized recommendation and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification
- What are the applications of tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















