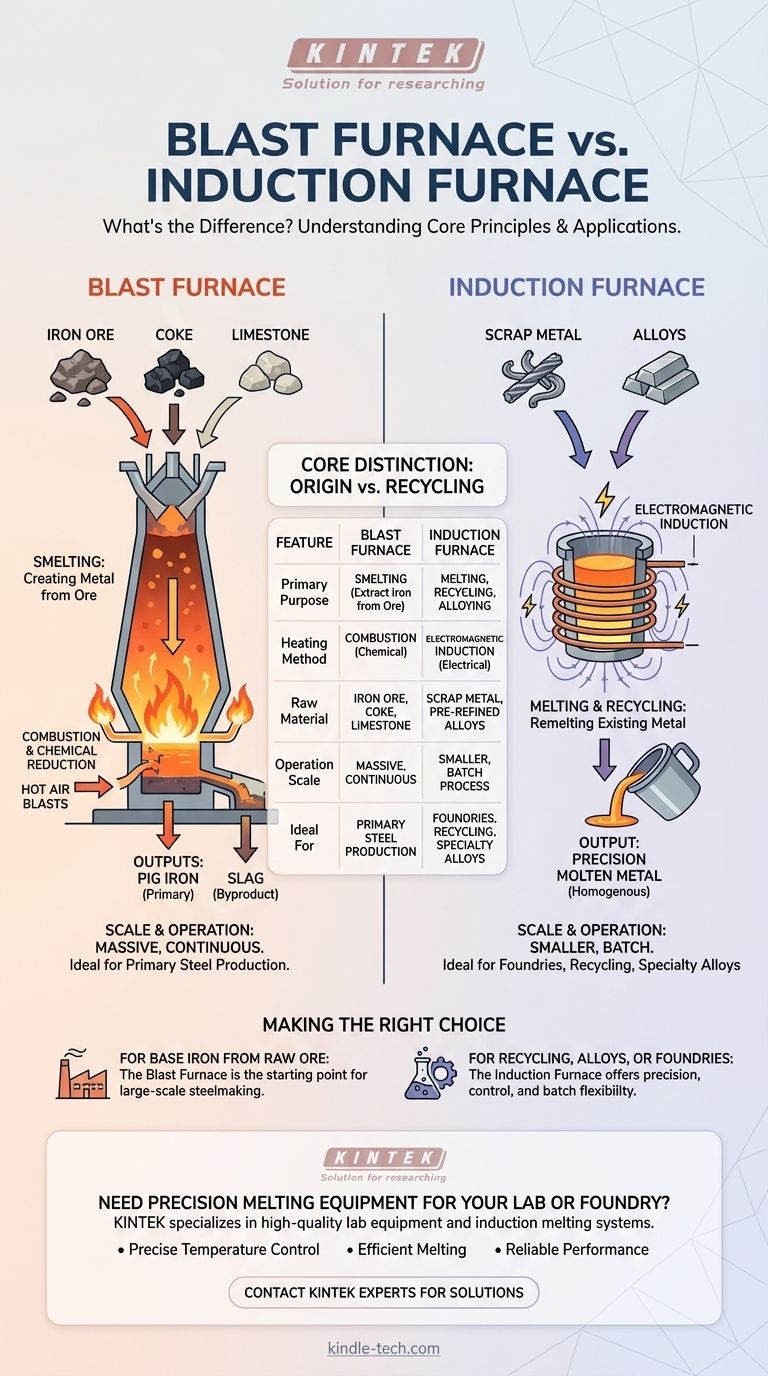
The fundamental difference between a blast furnace and an induction furnace lies in their heating mechanism and primary purpose. A blast furnace uses the combustion of coke to chemically reduce iron ore into molten iron, a process known as smelting. In contrast, an induction furnace uses electricity to generate a powerful electromagnetic field that heats and melts metals that are already refined, making it ideal for recycling and alloying.
The core distinction is one of origin and scale. A blast furnace creates new metal from raw ore in a massive, continuous process, while an induction furnace remelts existing metal or scrap in a controlled, smaller-scale batch process.

The Blast Furnace: Primary Metal Production
A blast furnace is the starting point for most of the world's steel production. Its function is not merely to melt metal, but to chemically transform raw materials into a usable base metal.
How It Works: Chemical Reduction
A blast furnace is a massive, vertical steel shaft lined with heat-resistant brick. Iron ore, coke (a high-carbon fuel derived from coal), and limestone are loaded into the top.
Hot air is blasted into the bottom of the furnace, causing the coke to burn at extremely high temperatures. This combustion produces carbon monoxide, which acts as the primary reducing agent, stripping oxygen atoms from the iron ore.
Key Inputs and Outputs
The primary inputs are iron ore, coke, and limestone. The limestone acts as a flux, combining with impurities to form a liquid byproduct.
The furnace continuously produces two outputs: molten pig iron, which is the primary product, and a layer of molten slag (the impurities) that floats on top and is drained away.
Scale and Operation
Blast furnaces are enormous structures designed for continuous operation, often running for years without stopping. They are part of large, integrated steel mills and represent the pinnacle of industrial-scale primary metal production.
The Induction Furnace: Precision Melting
An induction furnace operates on a completely different principle, offering precision and control that a blast furnace cannot. It excels at melting, holding, and alloying metal, not creating it from ore.
How It Works: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a coil of copper wire through which a powerful alternating electric current is passed. This creates a reversing magnetic field around the metal placed inside the furnace crucible.
This magnetic field induces circulating electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the metal itself. The resistance of the metal to the flow of these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt quickly and efficiently from the inside out.
Key Inputs and Outputs
The key input for an induction furnace is solid metal, typically scrap metal or pre-refined alloys. It is essentially a recycling and refining tool.
The output is molten metal of a precise, homogenous chemical composition, ready for casting. The magnetic field also creates a natural stirring action, ensuring alloys are mixed thoroughly.
Scale and Operation
Induction furnaces range in size but are significantly smaller than blast furnaces. They operate on a batch basis, where a crucible is filled, melted, and emptied for each cycle. This makes them highly flexible and ideal for foundries and specialty metal producers.
Key Distinctions at a Glance
Understanding the core differences helps clarify which technology is appropriate for a given industrial task.
Operating Principle
A blast furnace relies on combustion and chemical reactions to produce metal. An induction furnace relies on electricity and electromagnetic principles.
Raw Materials
A blast furnace is a smelter, processing raw materials like iron ore. An induction furnace is a melter, processing existing materials like scrap metal or ingots.
Primary Purpose
The goal of a blast furnace is smelting—extracting a base metal from its natural ore. The goal of an induction furnace is melting, recycling, and alloying existing metals.
Environmental and Control Factors
Blast furnaces have a large environmental footprint due to direct coke combustion. Induction furnaces are cleaner at the point of use (as they are electric) and offer far greater control over the final temperature and chemical makeup of the metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines which furnace is the only logical choice.
- If your primary focus is producing base iron from raw ore for large-scale steelmaking: The blast furnace is the necessary starting point for this industrial process.
- If your primary focus is recycling scrap metal, creating specialty alloys, or operating a foundry: The precision, control, and batch flexibility of an induction furnace are ideal.
Ultimately, these two furnaces serve fundamentally different stages of the metal lifecycle, from creation to reincarnation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Blast Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Smelting (extracting iron from ore) | Melting, Recycling, Alloying |
| Heating Method | Combustion of Coke (Chemical) | Electromagnetic Induction (Electrical) |
| Raw Material | Iron Ore, Coke, Limestone | Scrap Metal, Pre-refined Alloys |
| Operation Scale | Massive, Continuous | Smaller, Batch Process |
| Ideal For | Primary Steel Production | Foundries, Recycling, Specialty Alloys |
Need Precision Melting Equipment for Your Lab or Foundry?
Understanding the right furnace technology is the first step to optimizing your metal processing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including induction melting systems ideal for research, recycling, and alloy development.
We provide solutions that deliver:
- Precise Temperature Control for consistent, high-quality results.
- Efficient Melting of precious metals, scrap, and alloys.
- Reliable Performance tailored to your laboratory or small-scale production needs.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect melting solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















