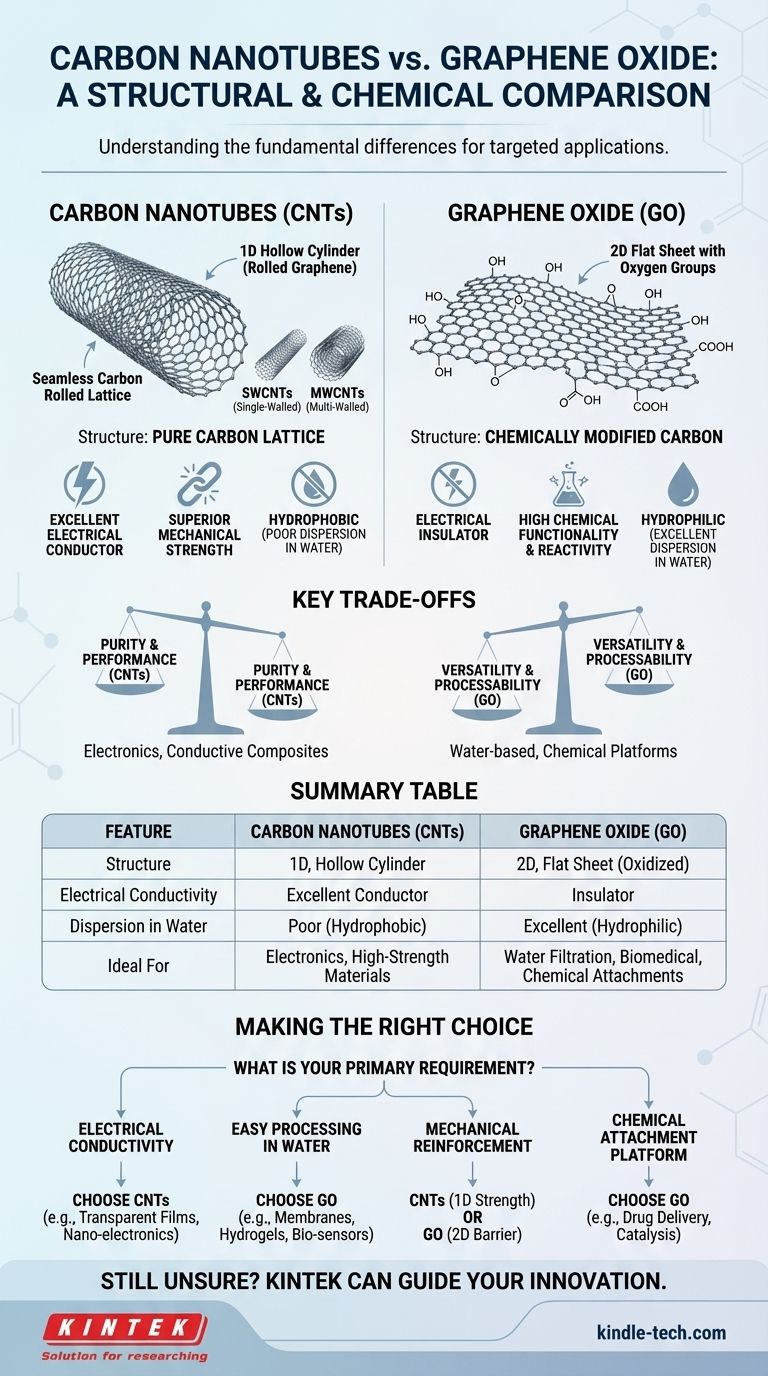
At their core, the primary difference between carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene oxide (GO) lies in their fundamental structure and chemical composition. Carbon nanotubes are one-dimensional, hollow cylinders of pure carbon, essentially a rolled-up sheet of flawless graphene. Graphene oxide, in contrast, is a two-dimensional, flat sheet of carbon that has been chemically modified with oxygen-containing functional groups, which fundamentally alters its properties.
The choice between CNTs and GO is a choice between pristine structure and chemical functionality. CNTs offer superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength in their pure form, while GO's oxygen groups make it easily dispersible in water and chemically reactive, sacrificing conductivity for processability.

Foundational Differences: Structure and Dimensionality
Understanding the shape and arrangement of atoms is the first step in differentiating these two nanomaterials. Their geometry dictates their behavior.
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs): The Rolled-Up Cylinder
CNTs are best visualized as a seamless tube made of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, like a sheet of chicken wire rolled into a cylinder. This gives them a one-dimensional (1D) structure.
They exist in two main forms: single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), which are a single atomic layer thick, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), which consist of multiple concentric tubes. Their structure is almost entirely pure, sp²-hybridized carbon.
Graphene Oxide (GO): The Decorated Sheet
Graphene oxide is a two-dimensional (2D) material. It begins as graphene—a single, flat sheet of carbon atoms—but undergoes a harsh oxidation process.
This process attaches various oxygen-containing functional groups (like hydroxyl, epoxy, and carboxyl groups) to the surface and edges of the sheet. These groups disrupt the perfect hexagonal lattice, creating a new material with vastly different properties.
A Tale of Two Chemistries
The presence or absence of these oxygen groups is the most significant chemical distinction and the source of their most important practical differences.
The Purity of Carbon Nanotubes
CNTs are composed almost entirely of carbon atoms. This pure, ordered graphitic structure is directly responsible for their exceptional intrinsic properties, especially electrical and thermal conductivity.
While CNTs can be chemically functionalized, the process is often difficult and can introduce defects that compromise their inherent strengths.
The Functionality of Graphene Oxide
GO's defining feature is its abundance of oxygen functional groups. These groups make the material hydrophilic, meaning it disperses remarkably well in water and other polar solvents.
This is a massive advantage over pristine CNTs, which are hydrophobic and notoriously difficult to disperse. The functional groups also act as reactive sites for further chemical modification, making GO a versatile platform for building complex materials.
Comparing Key Properties
The differences in structure and chemistry lead directly to a stark contrast in performance metrics.
Electrical Conductivity
CNTs are exceptional electrical conductors. Depending on their specific atomic arrangement (chirality), they can behave as either metals or semiconductors, making them ideal for electronics.
Graphene oxide, conversely, is an electrical insulator. The oxygen groups disrupt the network of delocalized electrons that allows current to flow in pure graphene, effectively shutting down conductivity.
Mechanical Strength
Both materials are renowned for their incredible strength, derived from the strong carbon-carbon bonds.
Due to their flawless cylindrical structure, individual CNTs often exhibit higher tensile strength and stiffness than a sheet of GO. The functional groups and defects in GO can act as weak points, slightly reducing its intrinsic strength compared to pure graphene.
Dispersion and Processability
This is GO's standout advantage. Its hydrophilic nature allows for easy, stable dispersion in water to form solutions that can be cast into films, mixed into composites, or 3D printed.
Pristine CNTs tend to bundle together due to strong van der Waals forces, making them very difficult to separate and disperse uniformly in most solvents without the use of harsh surfactants.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Choosing between these materials is not about which is "better," but which possesses the right set of compromises for a specific task.
Purity vs. Functionality
The core trade-off is performance versus versatility. CNTs offer the peak performance of a pure carbon structure. GO sacrifices some of that peak performance for immense chemical versatility and ease of handling.
Cost and Scalability
The production of GO via chemical exfoliation of graphite is a well-established, scalable, and relatively low-cost process.
High-quality CNT synthesis can be more energy-intensive and expensive, particularly for producing SWCNTs with specific, uniform properties. This makes GO a more accessible material for many large-scale applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most important requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Choose CNTs for applications like transparent conductive films, electrostatic discharge composites, or nano-electronics.
- If your primary focus is easy processing in water: Graphene oxide is the superior choice for water filtration membranes, hydrogels, biomedical sensors, and printable electronics.
- If your primary focus is mechanical reinforcement: Both are excellent. CNTs offer superior 1D reinforcement for strength along an axis, while GO's 2D sheets can provide better barrier properties in films and coatings.
- If your primary focus is a platform for chemical attachment: Graphene oxide is the clear winner, providing a ready-made canvas of reactive sites for drug delivery, catalysis, and sensing applications.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether your application demands the pristine performance of a pure carbon structure or the versatile functionality of a chemically decorated one.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | Graphene Oxide (GO) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | 1D, hollow cylinder (rolled graphene) | 2D, flat sheet with oxygen groups |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor | Insulator |
| Dispersion in Water | Poor (hydrophobic) | Excellent (hydrophilic) |
| Chemical Functionality | Low (pristine carbon) | High (reactive oxygen groups) |
| Ideal For | Electronics, conductive composites | Water-based processing, chemical platforms |
Still Unsure Which Nanomaterial is Right for Your Research?
Choosing between the high-performance purity of carbon nanotubes and the versatile processability of graphene oxide is critical for your project's success. KINTEK, a trusted supplier of advanced laboratory materials, can help you navigate this decision.
We provide high-quality CNTs and GO, along with the expert technical support to ensure you select the ideal material for your specific application in electronics, composites, biomedicine, or filtration.
Let our expertise guide your innovation. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's materials can accelerate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential Components for Extreme Heat & Electrical Insulation
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- How do porcelain boats and quartz tubes function in CVD of BN? Optimize Your Boron Nitride Coating Efficiency
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential for Extreme Heat, Insulation & Purity



















