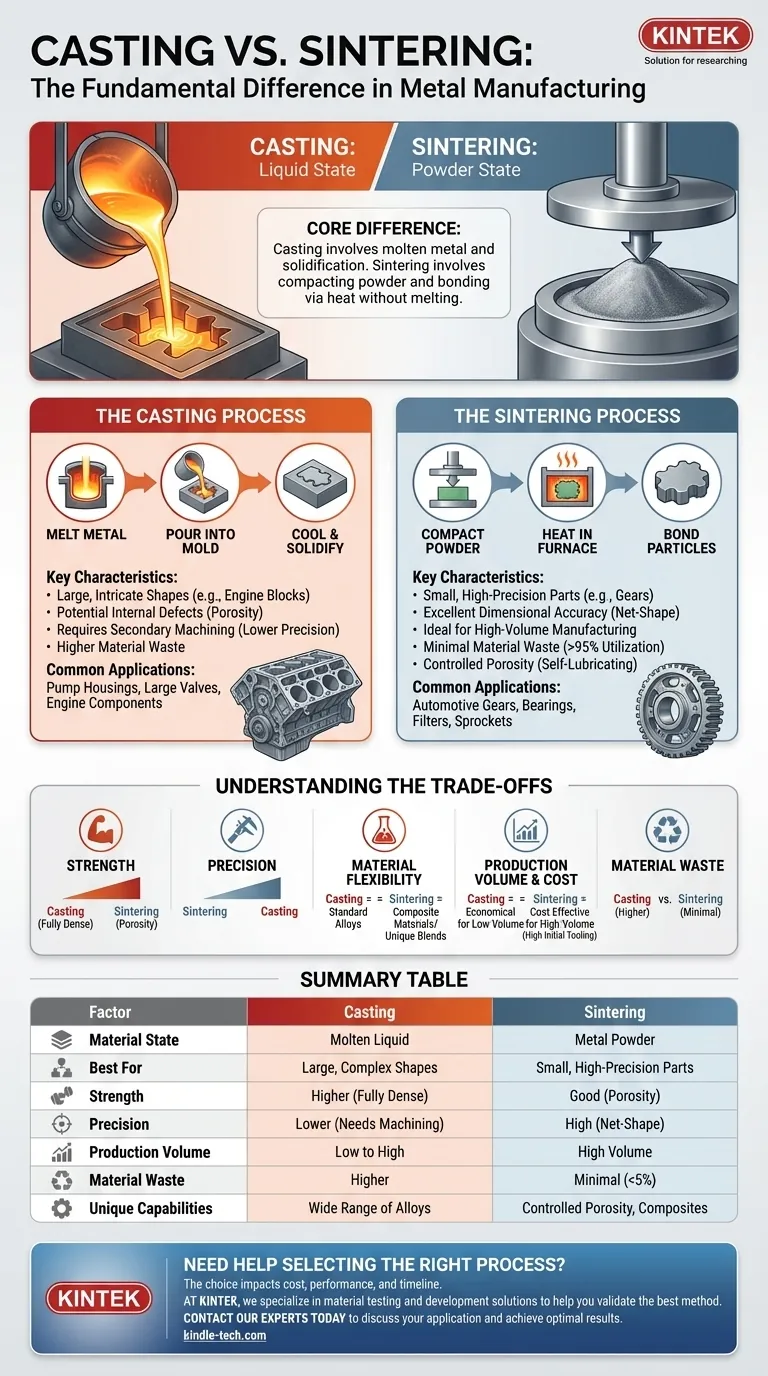
At its core, the difference between casting and sintering comes down to the state of the metal during manufacturing. Casting involves shaping parts from molten, liquid metal poured into a mold. In contrast, sintering forms parts by compressing metal powder and then heating it until the particles bond together, all without ever reaching the melting point.
The fundamental choice between casting and sintering is a trade-off between size and precision. Casting excels at creating large, structurally complex components, while sintering is the superior method for producing vast quantities of small, highly precise parts with minimal waste.

The Casting Process: From Liquid to Solid
Casting is one of the oldest manufacturing processes, relying on the simple principle of turning a solid into a liquid and back into a solid in a desired shape.
The Core Principle
The process begins by melting a metal or alloy into a fully liquid state. This molten metal is then poured into a cavity, or mold, that reflects the final part's geometry. As the metal cools and solidifies, it takes the shape of the mold.
Key Characteristics
Casting is exceptionally versatile for producing very large or intricate shapes, like engine blocks, that would be impossible to machine from a solid block. However, the cooling process can introduce internal defects like porosity and shrinkage, and the resulting surface finish and dimensional accuracy often require secondary machining.
Common Applications
This method is the go-to for large-scale items where absolute precision out of the mold is secondary to overall form and strength. Think of applications like pump housings, large valves, engine components, and decorative hardware.
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
Sintering, a key discipline within powder metallurgy, builds parts from the ground up by fusing fine metal particles together using heat and pressure.
The Core Principle
First, a precise blend of metal powders is compacted in a die under extreme pressure to form a "green" part. This part is solid but fragile. It is then placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature below the metal's melting point, causing the particles to bond and diffuse into a solid, coherent mass.
Key Characteristics
Sintering is an ideal process for high-volume manufacturing of small, geometrically complex parts. It produces components with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish, often eliminating the need for any secondary machining. This is known as a net-shape process. It also allows for the creation of unique alloy blends and parts with controlled porosity.
Common Applications
You will find sintered parts in countless applications that demand high precision and volume, such as automotive gears, self-lubricating bearings (which retain oil in their pores), engine sprockets, and porous metal filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two methods requires a clear understanding of your project's priorities, from mechanical properties to production cost.
Strength vs. Precision
A fully dense cast part, especially after heat treatment, will generally exhibit higher tensile and impact strength than a standard sintered part due to the absence of inherent porosity. However, a sintered part typically offers far superior dimensional precision and consistency from part to part without costly machining.
Material Selection & Flexibility
Casting can accommodate a very wide range of standard alloys. Sintering shines by allowing the creation of composite materials and pseudo-alloys that cannot be made by melting, such as combining metals with ceramics or graphite. It is also essential for working with metals that have extremely high melting points, like tungsten.
Production Volume & Cost
Casting can be economical for low-volume runs, especially methods like sand casting where tooling is inexpensive. Sintering, conversely, has high initial tooling costs for the dies but becomes extremely cost-effective at high production volumes due to its high speed, automation, and minimal material waste.
Material Waste
Sintering is a highly sustainable process, with material utilization often exceeding 95%. Casting generates more waste through the runners, gates, and sprues that feed the mold, as well as the material removed during subsequent machining operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision hinges on four key factors: part size, production volume, required precision, and material properties.
- If your primary focus is large, complex components: Casting is the only practical choice for producing items like large machinery housings or engine blocks.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, precise parts: Sintering offers unmatched speed, consistency, and cost-effectiveness per part.
- If your primary focus is parts with controlled porosity or unique material blends: Sintering is the definitive method for applications like filters or self-lubricating bearings.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or very low-volume runs: Casting methods are generally more economical due to significantly lower initial tooling investments.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental state of the material—liquid versus powder—is the key to selecting the process that best aligns with your engineering and business goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Casting | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Material State | Molten (Liquid) Metal | Metal Powder |
| Best For | Large, Complex Shapes | Small, High-Precision Parts |
| Strength | Higher (Fully Dense) | Good (Can Have Porosity) |
| Precision | Lower (Often Needs Machining) | High (Net-Shape Process) |
| Production Volume | Low to High | High Volume (Cost-Effective) |
| Material Waste | Higher | Minimal (<5%) |
| Unique Capabilities | Wide Range of Standard Alloys | Controlled Porosity, Composite Materials |
Need help selecting the right process for your metal parts?
The choice between casting and sintering directly impacts your project's cost, performance, and timeline. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and development, helping you validate the best manufacturing method for your specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how our solutions can help you achieve optimal results. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Expert Guide for Ti-22Al-25Nb Fabrication
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al



















