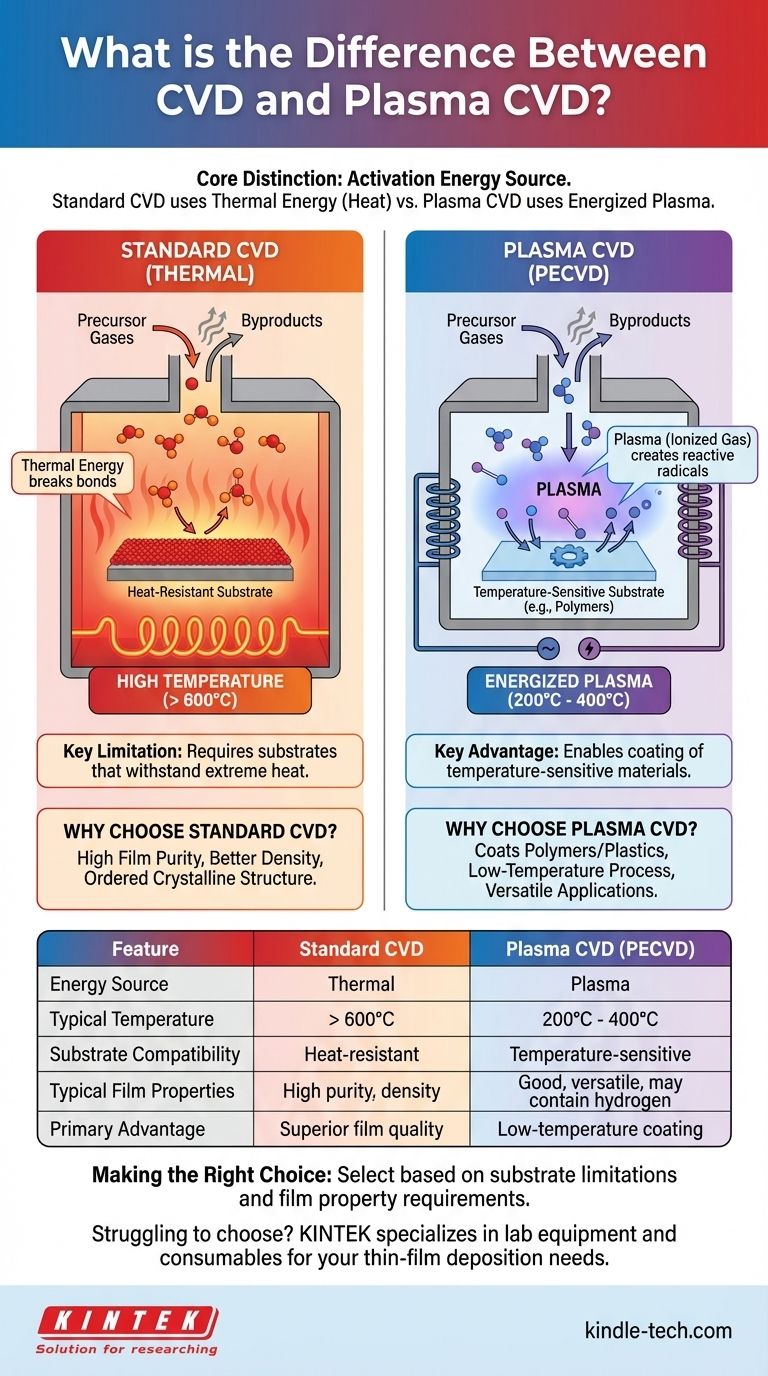
In essence, the difference between standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the source of energy used to drive the process. Standard CVD relies exclusively on high temperatures to initiate the chemical reactions that form a film, whereas PECVD uses an energized plasma to do so, allowing the process to occur at much lower temperatures.
The core distinction is not in the chemistry but in the activation energy. Traditional CVD uses thermal energy (heat), limiting it to heat-resistant substrates. Plasma CVD substitutes that heat with energy from a plasma, unlocking the ability to coat temperature-sensitive materials.

The Foundation: How Standard CVD Works
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process used to create high-quality, high-performance solid thin films. The technique involves exposing a substrate to one or more volatile precursor gases, which react or decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit.
The Critical Role of Thermal Energy
In a standard thermal CVD process, the entire reaction chamber, including the substrate, is heated to very high temperatures, often exceeding 600°C.
This intense heat provides the necessary activation energy to break the chemical bonds within the precursor gas molecules.
The Reaction on the Surface
Once broken down into more reactive components, these molecules react on and with the hot substrate surface. This chemical reaction results in the formation of a dense, solid thin film, with byproducts being exhausted from the chamber.
The High-Temperature Limitation
The reliance on high heat is the defining characteristic and primary limitation of standard CVD. The substrate must be able to withstand these extreme temperatures without melting, warping, or otherwise degrading.
The Innovation: Introducing Plasma CVD (PECVD)
Plasma-Enhanced CVD, sometimes called Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD), is an advanced form of CVD that overcomes the temperature limitation of the traditional process.
Replacing Heat with Plasma
Instead of heating the entire chamber, PECVD uses an electromagnetic field (such as radio frequency or microwave) to excite the precursor gases into a plasma state.
A plasma is an ionized gas—a highly energetic state of matter containing free ions and radicals.
Creating Reactive Species without Heat
These radicals and ions within the plasma are extremely reactive. They provide the chemical species needed for the deposition reaction to occur, effectively replacing the function of high thermal energy.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Because the energy for the reaction comes from the plasma itself and not from heating the substrate, the deposition can occur at significantly lower temperatures, typically in the 200-400°C range. This makes it possible to coat materials that would be destroyed by a standard CVD process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between thermal CVD and PECVD involves a direct trade-off between film properties and substrate compatibility. Neither method is universally superior; they are tools for different jobs.
Why Choose Standard CVD?
The high temperatures used in standard CVD often result in films with higher purity, better density, and a more ordered crystalline structure. When the absolute highest film quality is required and the substrate can tolerate the heat (e.g., silicon wafers, ceramics, metals), thermal CVD is often the preferred method.
Why Choose Plasma CVD?
The primary driver for choosing PECVD is its ability to coat temperature-sensitive substrates. This includes polymers, plastics, and fully fabricated electronic devices that already contain low-melting-point materials. It opens up coating possibilities that are physically impossible with standard CVD.
Potential Considerations for PECVD
While powerful, PECVD can introduce complexities. The films may have a higher concentration of incorporated elements like hydrogen (from the precursor gases), which can affect optical or electrical properties. The equipment is also generally more complex and expensive than a basic thermal CVD system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the limitations of your substrate and the specific film properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and crystallinity on a heat-tolerant substrate: Traditional thermal CVD is often the superior and simpler choice.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer or a pre-fabricated device: Plasma CVD is the necessary and enabling technology.
- If you need a balance of good film properties at a moderate temperature: PECVD offers a versatile middle ground that is suitable for a vast range of modern applications.
Understanding this fundamental difference between thermal and plasma energy is the key to selecting the right deposition process for your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard CVD | Plasma CVD (PECVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal (High Heat) | Plasma (Ionized Gas) |
| Typical Temperature | > 600°C | 200°C - 400°C |
| Substrate Compatibility | Heat-resistant materials (e.g., silicon, ceramics) | Temperature-sensitive materials (e.g., polymers, plastics) |
| Typical Film Properties | Higher purity, density, and crystallinity | Good properties, but may contain hydrogen; versatile |
| Primary Advantage | Superior film quality on tolerant substrates | Enables coating of low-temperature materials |
Struggling to choose the right deposition process for your substrate and film requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your thin-film deposition needs. Whether you require the high-purity films of standard CVD or the low-temperature capabilities of PECVD, our team can help you select the perfect system to enhance your research and development.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















