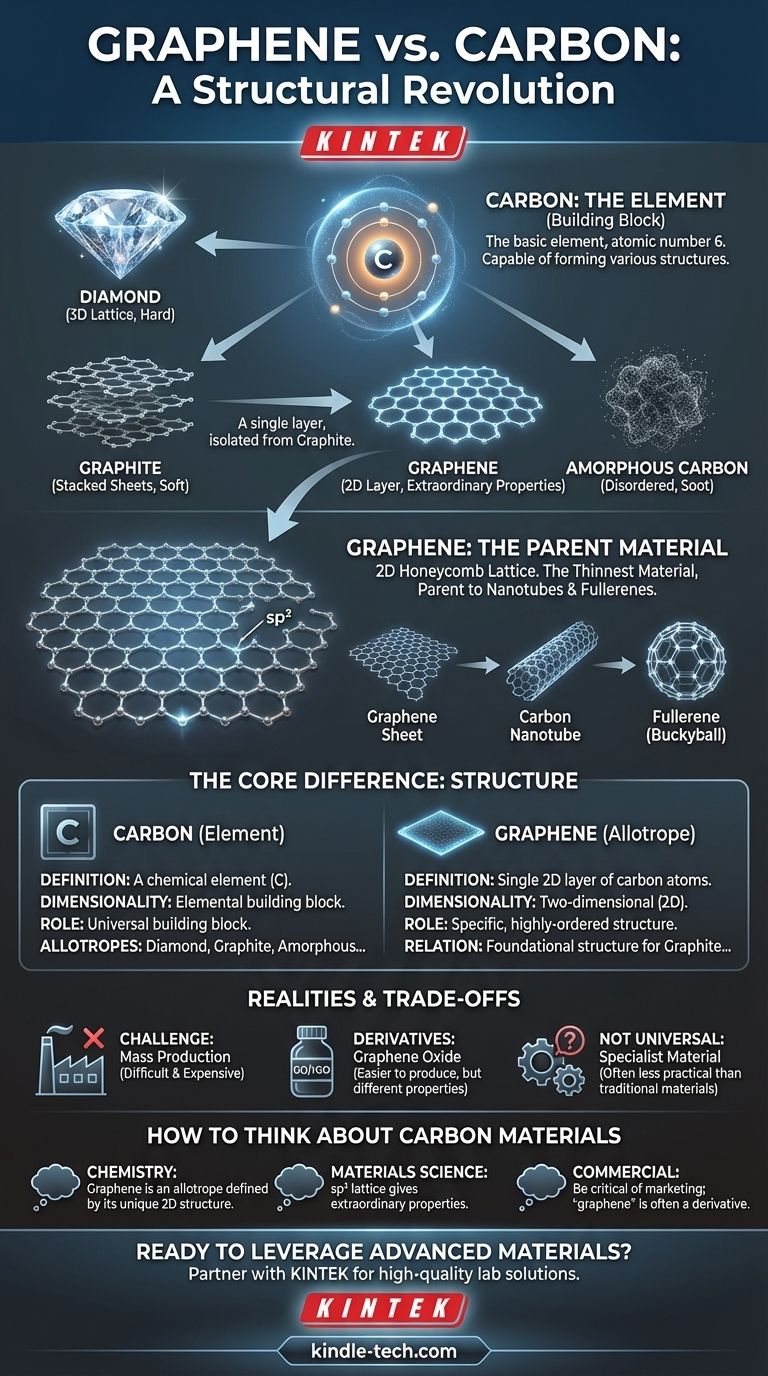
The fundamental difference is not one of substance, but of structure. Graphene is not a different material from carbon; it is a specific, two-dimensional form of the element carbon. While carbon is the basic element, graphene is a single, one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a precise honeycomb lattice, and this unique arrangement is the source of all its extraordinary properties.
The core distinction to remember is that "carbon" is the element—the building block—while "graphene" is a specific, highly-ordered structure built exclusively from those blocks. Think of it like diamond and graphite: both are pure carbon, but their different atomic arrangements give them vastly different properties.

From Element to Allotrope: The Foundation of Carbon
To grasp the role of graphene, we must first understand the versatility of its parent element, carbon. This context is essential for appreciating why a simple structural change can create a revolutionary material.
Carbon: The Universal Building Block
Carbon is an element (atomic number 6) found in the periodic table. Its defining feature is its ability to form strong covalent bonds with itself and many other elements, creating a vast number of compounds.
In its elemental form, carbon can exist in several different structural configurations.
The Concept of Allotropes
These different structural forms of a single element are called allotropes. The atoms are identical, but their arrangement in space is different, leading to dramatically different physical and chemical properties.
The classic example is the relationship between soft, gray graphite used in pencils and hard, transparent diamond used in jewelry. Both are pure carbon, but their properties diverge entirely because of their atomic structure.
Common Carbon Allotropes
Graphene is just one of several important carbon allotropes. The main ones include:
- Diamond: Carbon atoms are arranged in a rigid, three-dimensional tetrahedral lattice. This makes it incredibly hard.
- Graphite: Carbon atoms are arranged in sheets of a hexagonal lattice, which are stacked on top of each other. These layers can slide easily, making graphite soft.
- Graphene: A single, isolated layer of the hexagonal lattice that makes up graphite.
- Amorphous Carbon: A form, like soot or charcoal, where carbon atoms have no long-range crystalline order.
What Makes Graphene a Unique Form of Carbon?
Graphene’s fame comes from being the purest expression of carbon's two-dimensional potential. It is the foundational structure for other allotropes.
A True Two-Dimensional Material
Graphene's defining characteristic is that it is a single atomic layer. At just one atom thick, it is the thinnest material ever created, a true 2D plane of atoms.
The Honeycomb Lattice
The carbon atoms in graphene are linked by sp² bonds, forming a perfectly repeating hexagonal pattern, much like a honeycomb or chicken wire. This flat, tightly bonded structure is the source of its remarkable stability and strength.
The Parent of Other Materials
Understanding graphene clarifies its relationship to other carbon forms. You can think of graphite as simply a stack of countless graphene sheets. Furthermore, you can conceptually roll a graphene sheet into a tube to form a carbon nanotube or wrap it into a sphere to form a fullerene (buckyball).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Realities
While graphene's properties are extraordinary, its real-world application is constrained by significant practical challenges. Acknowledging these limitations is key to an objective understanding.
The Challenge of Mass Production
Producing large, defect-free sheets of pristine graphene is extremely difficult and expensive. The famous "Scotch tape method" used for its discovery (peeling layers off graphite) is not scalable for industrial use.
"Graphene" vs. Graphene Derivatives
Many products marketed as containing "graphene" actually use related materials like graphene oxide (GO) or reduced graphene oxide (rGO). These are easier and cheaper to produce in bulk but have different, and often inferior, electrical and mechanical properties compared to pure graphene.
Not a Universal Solution
Graphene is a specialist material. While it is stronger than steel and more conductive than copper, its cost and integration difficulties mean that traditional materials remain more practical and cost-effective for the vast majority of applications.
How to Think About Carbon Materials
Your perspective on the carbon-graphene relationship depends on your goal. Use these points to frame your thinking.
- If your primary focus is on fundamental chemistry: Remember that graphene is an allotrope of the element carbon, defined by its unique 2D honeycomb structure.
- If your primary focus is on material science: Concentrate on how graphene's
sp²-bonded lattice gives rise to extraordinary properties—strength, conductivity, and lightness—that are fundamentally different from 3D allotropes like diamond. - If your primary focus is on commercial products: Be critical of marketing claims and understand that the "graphene" used is often a derivative, where the challenge lies in achieving cost-effective production at scale.
Ultimately, recognizing the difference between carbon the element and graphene the structure is the key to understanding a new class of materials engineered at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Carbon (Element) | Graphene (Allotrope) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A chemical element (C) | A single layer of carbon atoms in a 2D honeycomb lattice |
| Dimensionality | N/A (Elemental building block) | Two-dimensional (2D) |
| Key Allotropes | Diamond, Graphite, Amorphous Carbon | The foundational structure for Graphite, Carbon Nanotubes |
| Primary Distinction | The universal building block | A specific, highly-ordered structure made from carbon atoms |
Ready to leverage advanced materials in your research?
Understanding the nuances of materials like graphene is key to innovation. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to push the boundaries of material science. Whether you're working with carbon allotropes or other advanced materials, our products support precision, reliability, and discovery.
Let KINTEK be your partner in research. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory orbital shaker during BMP testing? Maximize Methane Yield Accuracy
- What is the role of laboratory stirring equipment in nZVI preparation? Achieve Stable and Uniform Nano Slurries
- What is the function of a laboratory shaker during batch adsorption experiments? Optimize Fly Ash Kinetic Research
- What role does a laboratory shaker play in the extraction of plant compounds for green synthesis? Maximize Your Yield
- How does a laboratory stirrer influence MOF product quality? Master Precision in Non-Solvothermal Synthesis



















