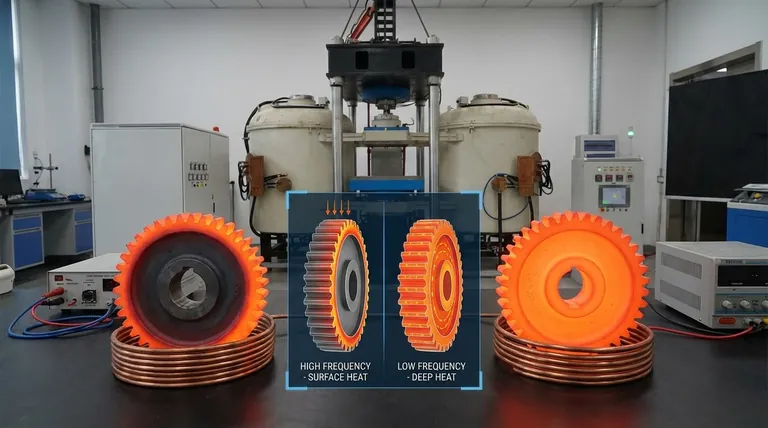
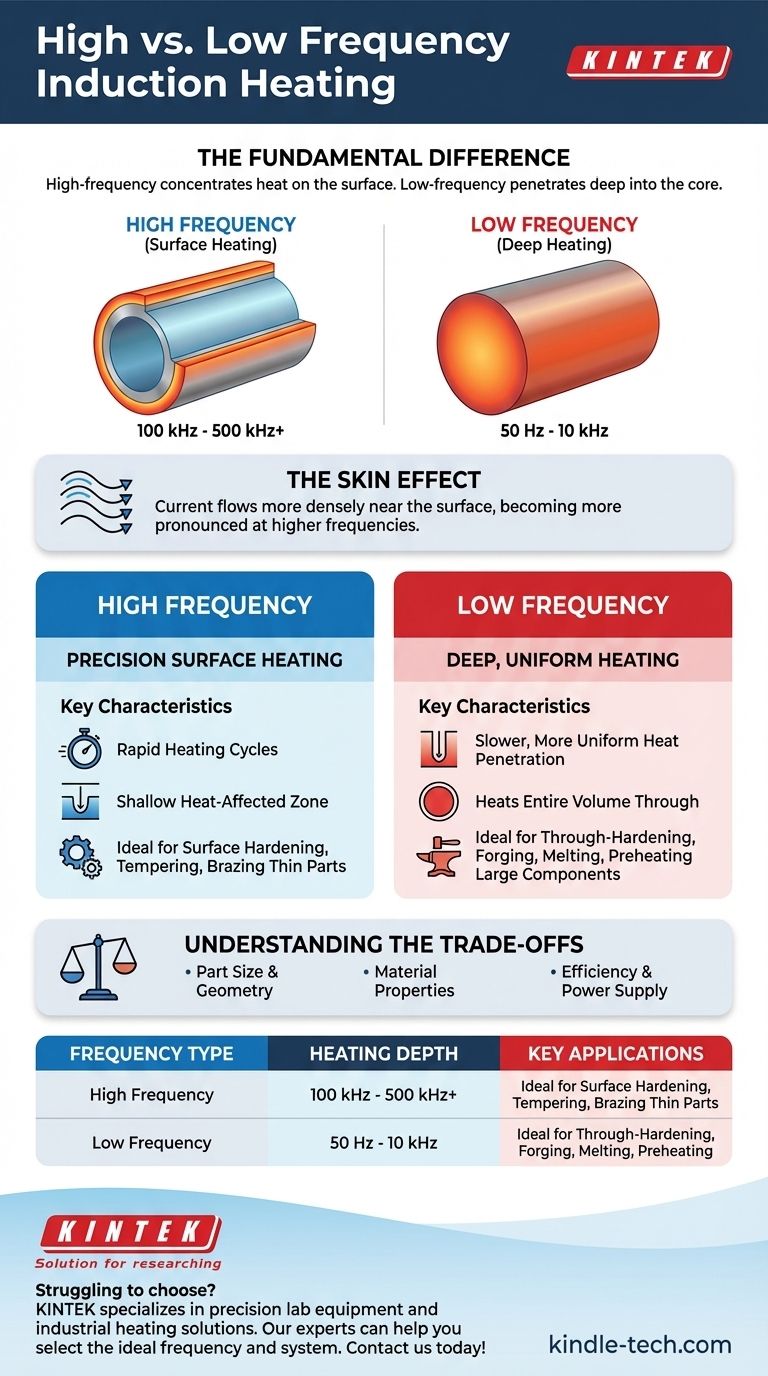
The fundamental difference is that high-frequency induction heating concentrates heat on the surface of a material, while low-frequency induction heating penetrates deep into the material's core. This behavior is governed by a physical principle known as the "skin effect," making the choice of frequency a critical factor for achieving specific metallurgical outcomes.
The core takeaway is that frequency is the primary control for determining where the heat is generated within a conductive part. High frequency is for surface-level work, while low frequency is for heating the entire volume through.
The Core Principle: The "Skin Effect"
To understand the difference, you must first understand the physics of how induction works. Induction heating uses an alternating magnetic field to induce an electric current (an eddy current) inside a conductive part, and the resistance to this current flow generates heat.
What is the Skin Effect?
The skin effect is a natural tendency of alternating current (AC) to flow more densely near the surface, or "skin," of a conductor. The current is not distributed evenly throughout the material's cross-section.
This phenomenon becomes more pronounced as the frequency of the alternating current increases.
How Frequency Controls Heating Depth
The relationship is straightforward: higher frequency leads to a more extreme skin effect, forcing the induced current into a very thin layer at the surface. This results in rapid, shallow heating.
Conversely, a lower frequency reduces the skin effect, allowing the induced current and the resulting heat to penetrate much deeper into the part.
High-Frequency Induction: Precision Surface Heating
High-frequency (HF) induction typically operates in the range of 100 kHz to 500 kHz and higher. It is the tool of choice when the heating objective is localized to the surface.
Key Characteristics
HF systems are defined by rapid heating cycles and a shallow heat-affected zone. The energy is transferred very quickly to a small surface volume, leaving the core of the part relatively cool.
Common Applications
This precise surface heating is ideal for applications like case hardening gears and shafts, where a hard, wear-resistant surface is needed over a softer, more ductile core. It's also used for tempering, brazing, and soldering small or thin parts.
Low-Frequency Induction: Deep, Uniform Heating
Low-frequency induction operates at much lower frequencies, often from 50/60 Hz (line frequency) up to around 10 kHz. It is used when the goal is to heat the entire mass of a component.
Key Characteristics
Low-frequency systems provide slower, more uniform, and deeper heat penetration. Because the skin effect is less pronounced, the induced currents can travel deep into the material's cross-section.
Common Applications
The most common uses for low-frequency induction are through-hardening of large components, preheating for welding, forging, and melting large volumes of metal in foundries. Heating a large steel billet before it is forged into shape requires this deep, uniform heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a frequency is not just about depth; it involves balancing several interdependent factors to create an efficient and effective process.
Part Size and Geometry
The size of the workpiece is a critical factor. For a large, thick part, a high frequency would only heat the surface and would be incredibly inefficient for heating the entire mass. A low frequency is required for deep penetration.
Material Properties
The material's resistivity and magnetic permeability directly impact the heating process. Magnetic materials like steel are much easier to heat below their Curie temperature (where they lose their magnetic properties) than non-magnetic materials like aluminum or copper.
Efficiency and Power Supply
Matching the frequency to the application is key to an efficient system. Using the wrong frequency can lead to excessive heating times, wasted energy, and poor metallurgical results. The power supply and induction coil must be designed specifically for the intended frequency range and application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection process always begins with the desired outcome. You must define what you are trying to accomplish with the heat before you can select the right tool.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or brazing thin components: High frequency provides the rapid, shallow heating you need for a hard outer case without affecting the core.
- If your primary focus is heating a large billet for forging or melting: Low frequency is the only way to achieve the deep, uniform heat penetration required to heat the entire volume.
- If your primary focus is through-hardening a medium-sized part: A medium frequency (e.g., 3 kHz to 10 kHz) often provides the best balance between heating time and penetration depth.
Ultimately, frequency is the lever you pull to control the precise location and depth of heat in your induction process.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Type | Heating Depth | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High Frequency (100 kHz - 500 kHz+) | Shallow (Surface) | Case Hardening, Tempering, Brazing Thin Parts |
| Low Frequency (50 Hz - 10 kHz) | Deep (Core) | Through-Hardening, Forging, Melting, Preheating |
Struggling to choose the right induction heating process for your application?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and industrial heating solutions. Our experts can help you select the ideal frequency and system to achieve your specific metallurgical goals—whether you need rapid surface hardening or deep, uniform heating for large components.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and results. Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate nanocrystalline structures? Enhance Fe–Cu–Ni–Sn–VN Composite Hardness
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity



















