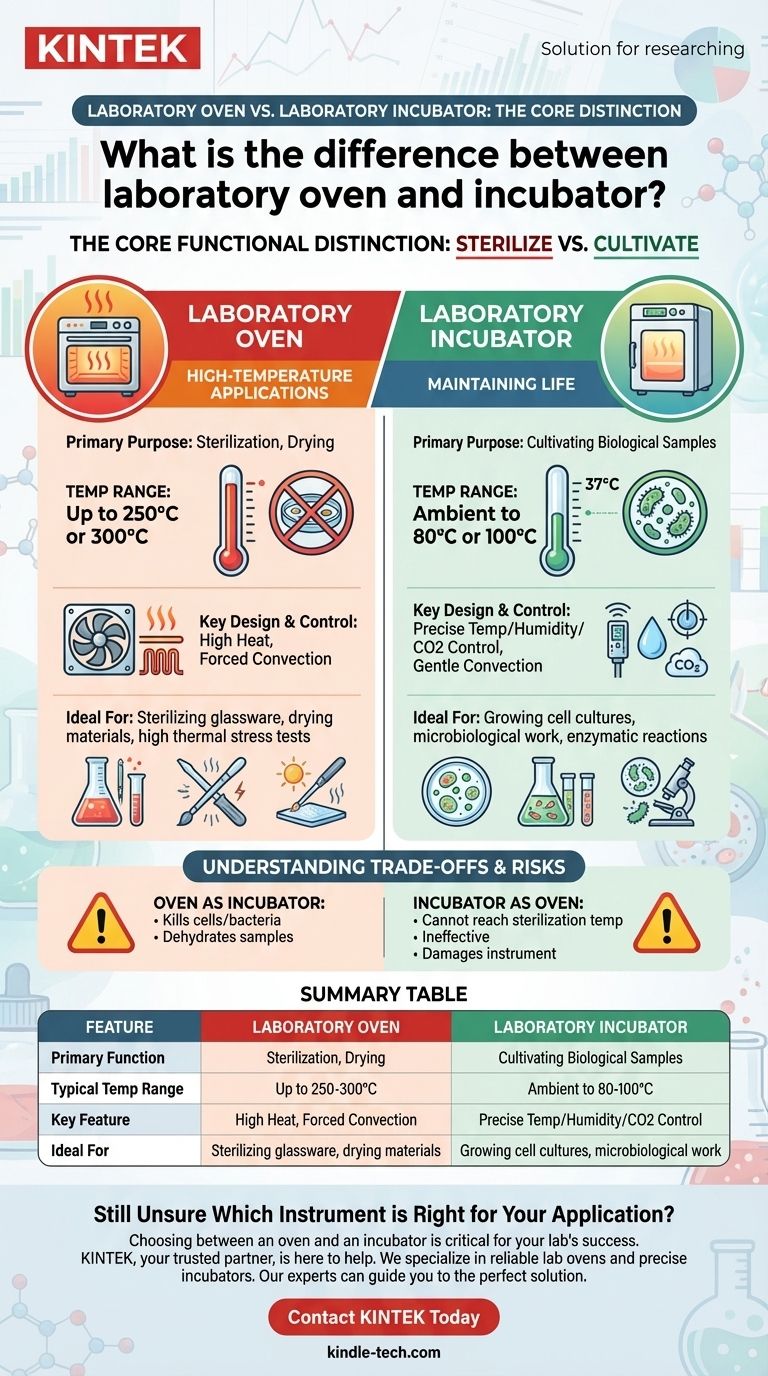
At its core, the difference between a laboratory oven and an incubator is their intended purpose, which dictates their temperature range and control capabilities. A laboratory oven is designed for high-temperature applications like sterilization and drying, operating well above the boiling point of water. An incubator, in contrast, is designed to provide a stable, controlled environment at temperatures near physiological conditions to cultivate and grow biological samples like cells or microbes.
While both instruments are heated, insulated boxes, their functions are fundamentally opposed: an oven uses high heat to eliminate life and moisture, whereas an incubator uses gentle, stable warmth to sustain and promote life.
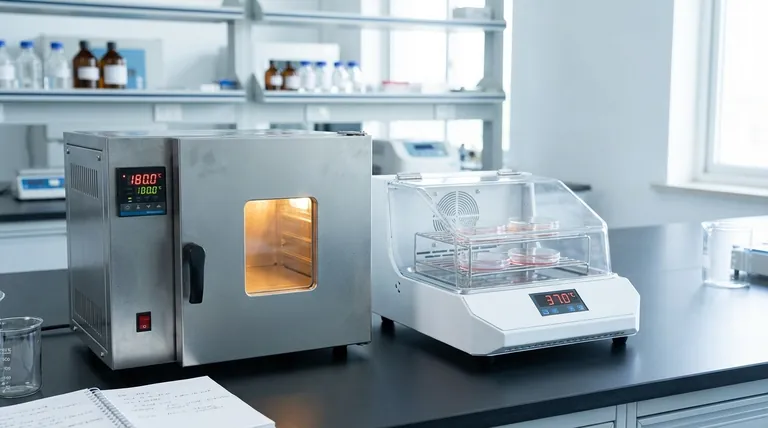

The Core Functional Distinction: Sterilize vs. Cultivate
The most critical distinction lies in the scientific goal each instrument is built to achieve. This primary function influences every aspect of their design, from heating elements to control systems.
A Laboratory Oven's Purpose: High-Temperature Applications
An oven is a high-heat workhorse. Its primary role is to create an environment hot enough for processes like dry-heat sterilization, which typically requires temperatures of 160-180°C to kill all microorganisms.
They are also used for drying glassware, removing residual moisture, or performing material tests that require high thermal stress. Their temperature range usually extends from slightly above ambient to 250°C or even 300°C.
An Incubator's Purpose: Maintaining Life
An incubator functions as an artificial environment optimized for biological growth. Its goal is to maintain a constant, uniform temperature that mimics physiological conditions, such as the human body's 37°C.
This stability is crucial for growing cell cultures, microbiological colonies, and conducting enzymatic reactions. The temperature range is therefore much lower, typically from just above ambient temperature up to 80°C or 100°C.
Key Differences in Design and Control
The opposing functions of sterilizing versus cultivating demand very different engineering solutions.
Temperature Range and Precision
Ovens are built to generate intense heat. Their control systems are robust but are not optimized for fine-tuning near room temperature.
Incubators, however, are engineered for exceptional thermal stability within their narrow operating range. A deviation of even a single degree can ruin a sensitive cell culture, so their controllers and sensors are far more precise.
Advanced Environmental Control
Beyond temperature, many biological applications require control over other atmospheric conditions. This is a capability exclusive to incubators.
Specialized incubators can regulate humidity to prevent samples from drying out and control CO2 levels to maintain the proper pH in cell culture media. Ovens have no such features.
Construction and Air Circulation
While both are insulated and have safety features to prevent overheating, their internal construction differs. Ovens often use powerful fans (forced convection) to ensure temperature uniformity at high setpoints.
Incubators may use gentle gravity convection to prevent disturbing or drying out delicate samples. Those with fans use them to provide gentle air circulation for stability, not the aggressive heat distribution seen in ovens.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing the wrong instrument is not a minor mistake; it can invalidate your results or destroy your samples.
The Danger of Using an Oven as an Incubator
This is the most common and critical error. An oven's temperature control is too imprecise at the low temperatures required for incubation. It will overshoot the setpoint, killing your cells or bacteria.
Furthermore, the dry, high-heat environment of an oven will rapidly dehydrate your samples and culture media, rendering them useless.
The Limitation of Using an Incubator as an Oven
This is functionally impossible. An incubator cannot reach the high temperatures required for proper dry-heat sterilization or for most drying protocols.
Attempting to use an incubator for these tasks will be ineffective and could potentially damage the instrument's sensitive sensors and control systems, which are not designed for prolonged high-heat operation.
Decontamination vs. Sterilization
Some high-end incubators offer a high-heat "decontamination cycle" that might reach 90°C or higher. It is critical to understand that this reduces microbial load but is not true sterilization. Sterilization requires the much higher temperatures that only a laboratory oven can provide.
Choosing the Right Instrument for Your Application
Your choice must be driven entirely by the requirements of your scientific protocol.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing glassware or metal instruments: You must use a laboratory oven for its ability to reliably reach and hold temperatures above 160°C.
- If your primary focus is growing cell or bacterial cultures: You need an incubator for its precise, stable control of temperature and, if necessary, humidity and CO2.
- If your primary focus is drying powdered samples or baking materials: A laboratory oven is the correct choice to aggressively remove moisture at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is performing enzymatic reactions at a stable 37°C: An incubator is the only suitable option to guarantee the required thermal stability.
Aligning your instrument to your objective is the foundation for achieving reliable and repeatable scientific outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Oven | Laboratory Incubator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sterilization, Drying | Cultivating Biological Samples |
| Typical Temp Range | Up to 250-300°C | Ambient to 80-100°C |
| Key Feature | High Heat, Forced Convection | Precise Temp/Humidity/CO2 Control |
| Ideal For | Sterilizing glassware, drying materials | Growing cell cultures, microbiological work |
Still Unsure Which Instrument is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between an oven and an incubator is critical for your lab's success. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment, is here to help.
We specialize in providing reliable lab ovens for high-temperature processes and precise incubators for sensitive biological work. Our experts can guide you to the perfect solution for your specific needs, ensuring accurate and repeatable results.
Contact us today via the form below to discuss your requirements and let KINTEK equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a thermostatic shaker required for SSF of rice husk solids? Maximize Your Ethanol Yield with Precision Agitation
- What critical reaction conditions does a shaking incubator provide? Optimize Cassava Cellulose Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- What role does a constant temperature orbital shaker play in biomass processing? Maximize Your Fermentation Yields
- What is the importance of a constant temperature shaking incubator? Ensure Precise Bacterial Growth and Membrane Tests
- What role does a laboratory constant temperature shaker play in the fungal strain cultivation stage? Boost Mycelium Growth



















