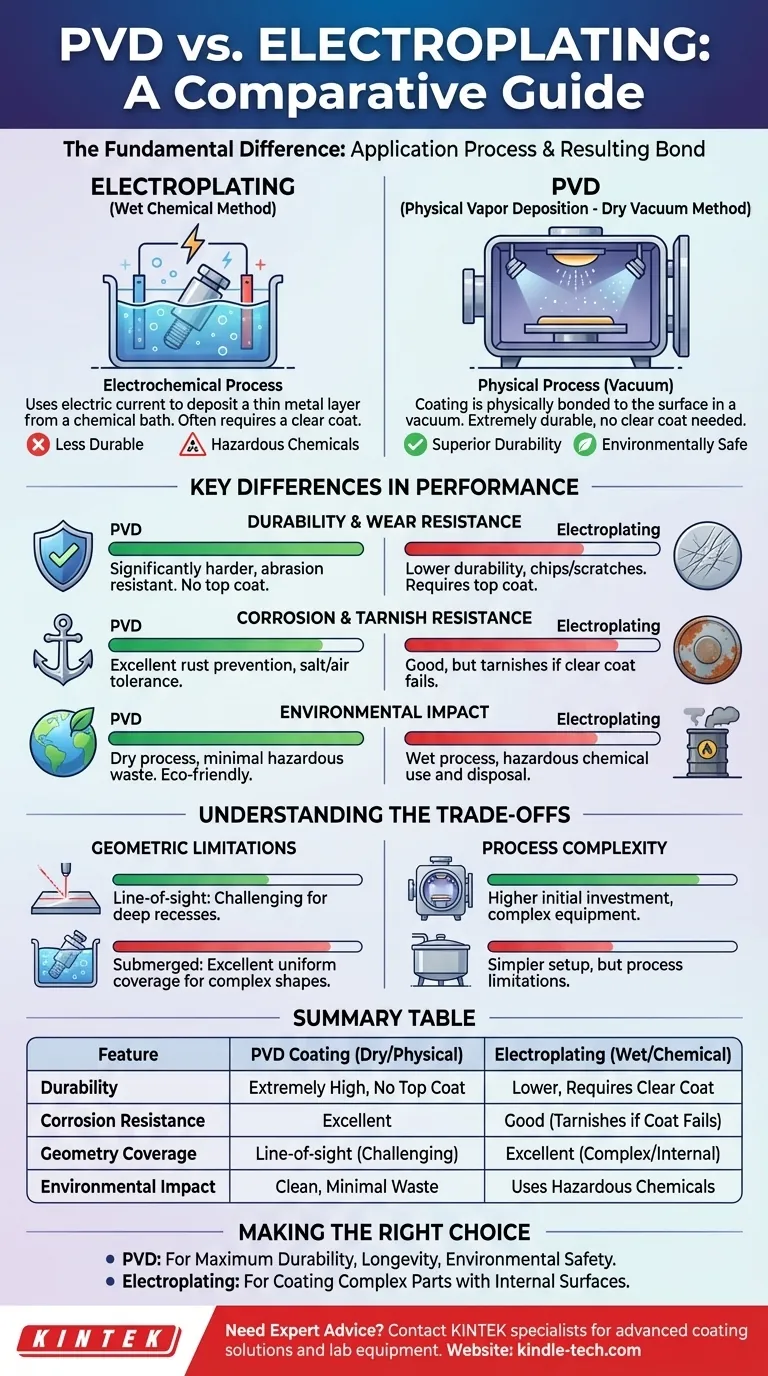
The fundamental difference between PVD and electroplating lies in the application process and the resulting bond. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a dry vacuum process where a coating is physically bonded to a surface, creating an extremely durable finish. In contrast, electroplating is a wet chemical process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal, which is often less durable and requires a protective clear coat.
While both methods apply a metal finish, the choice between them is a trade-off between modern durability and traditional application. PVD offers a vastly superior, more rugged, and environmentally safe coating, whereas electroplating is an older method with different geometric capabilities.

How Each Process Works
To understand the differences in performance, it's essential to understand how each coating is applied. The two methods are fundamentally different at a molecular level.
Electroplating: The Wet Chemical Method
Electroplating involves submerging a conductive part (the substrate) into a chemical bath containing dissolved metal ions.
An electric current is passed through the bath, causing the metal ions to plate onto the surface of the substrate. This is an electrochemical process.
PVD: The Dry Vacuum Method
PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, occurs inside a high-vacuum chamber. The coating material is vaporized from a solid source using methods like sputtering.
This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the substrate, forming a thin, highly adherent film. This is a physical, not chemical, process.
Key Differences in Performance
The differences in the application process directly lead to significant disparities in the final product's durability, appearance, and environmental impact.
Durability and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are significantly harder and more resistant to wear and abrasion than electroplated finishes.
Traditional electroplating often requires a clear top coat for protection, which can degrade, chip, or scratch over time. PVD does not require a clear coat, as the finish itself is exceptionally rugged.
Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
PVD demonstrates a much higher tolerance to corrosion from salt, air, and other elements. This makes it more effective at preventing rust.
Electroplated finishes, particularly brass and gold, can easily tarnish or corrode once the protective clear coat is compromised.
Environmental Impact
PVD is widely considered an environmentally safe process. It is a dry process that does not release harmful chemicals or hazardous waste.
Electroplating, being a wet chemical process, involves the use of and disposal of hazardous chemicals, posing a greater environmental challenge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating is not just about which is "better" but which is right for the specific part and goal. PVD's advantages come with certain process limitations.
Geometric Limitations
PVD is primarily a "line-of-sight" process. This means it can only coat surfaces that are directly exposed to the vapor source within the vacuum chamber.
This makes it challenging to uniformly coat complex shapes with deep recesses or internal channels. Electroplating, which involves submerging the entire part in a liquid solution, is often better at providing even coverage on intricate geometries.
Process Complexity
The equipment for PVD (a high-vacuum chamber) is more complex and typically represents a higher initial investment than an electroplating setup.
However, the resulting durability can lead to a longer product life, justifying the initial process complexity for high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: PVD is the clear choice due to its superior resistance to wear, corrosion, and tarnishing.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex part with internal surfaces: Electroplating's wet process may provide more uniform coverage than the line-of-sight nature of PVD.
- If your primary focus is environmental safety and a clean process: PVD is the superior option, as it avoids the use and disposal of harsh chemicals.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences empowers you to select the finishing process that delivers the precise performance your product requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Dry, vacuum-based (physical) | Wet, chemical bath (electrochemical) |
| Durability | Extremely high, no top coat needed | Lower, often requires a protective clear coat |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good, but can tarnish if top coat fails |
| Geometry Coverage | Line-of-sight (challenging for deep recesses) | Excellent for complex shapes & internal surfaces |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, minimal hazardous waste | Uses and produces hazardous chemicals |
Need expert advice on the best coating for your components?
Choosing between PVD and electroplating is critical for your product's performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. The right choice depends on your specific requirements for durability, part geometry, and environmental considerations.
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions and lab equipment. Our experts can help you navigate these trade-offs to select the perfect finishing process for your application, ensuring optimal results.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can enhance your product's quality and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is the main function of hot press forming? Achieve Superior Strength & Precision in Manufacturing



















