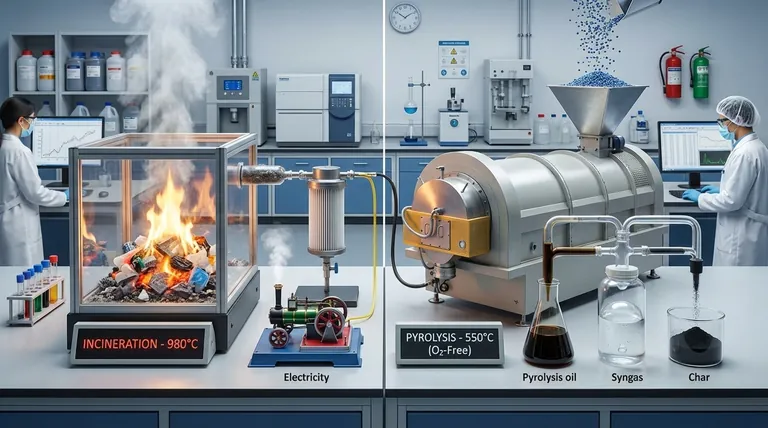
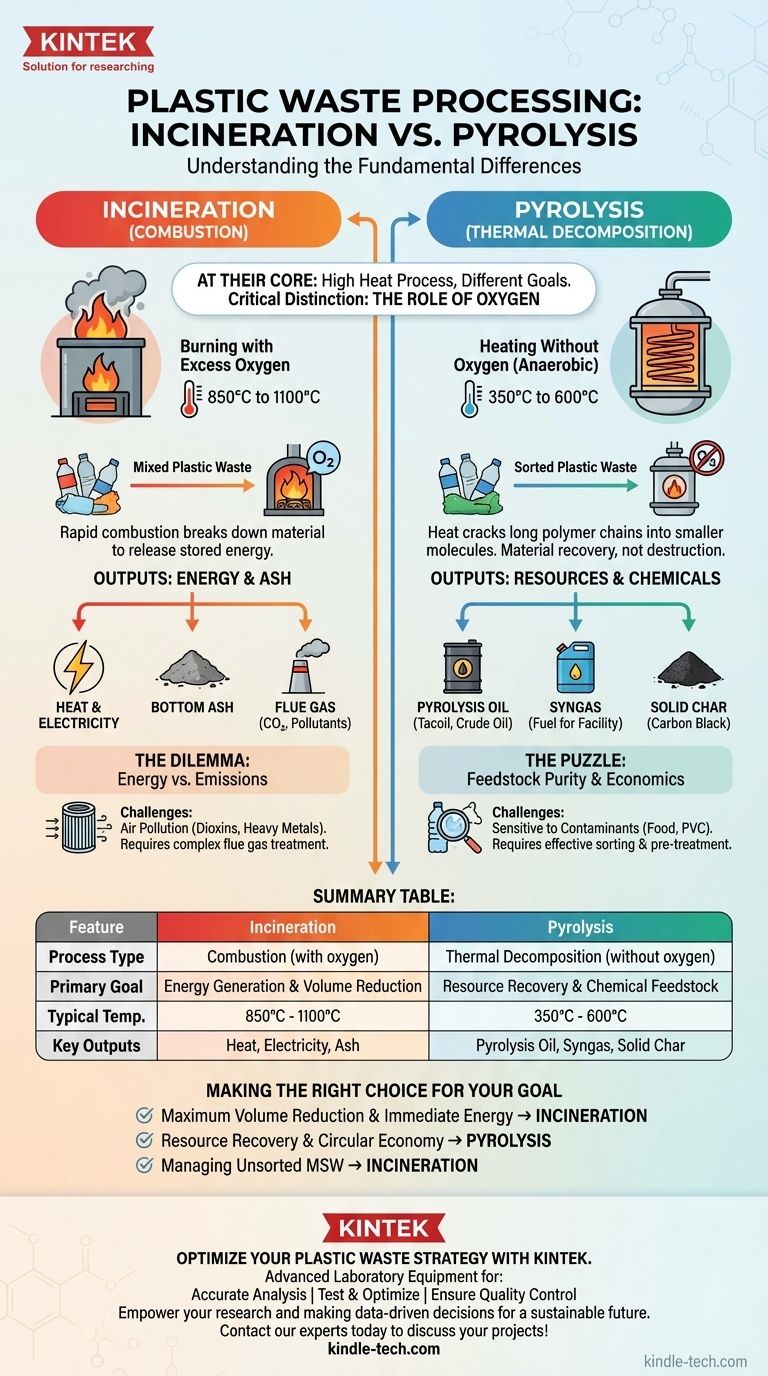
At their core, both pyrolysis and incineration use high heat to process plastic waste, but they operate on fundamentally different chemical principles and for entirely different goals. Incineration is a process of combustion—rapidly burning plastic with oxygen to generate heat—while pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition, using heat in an oxygen-free environment to break plastic down into new chemical products.
The critical distinction is not just temperature, but the presence of oxygen. Incineration destroys plastic to release its stored energy, while pyrolysis deconstructs plastic to recover its chemical value.

The Fundamental Difference: The Role of Oxygen
The presence or absence of oxygen dictates the entire chemical pathway and, consequently, the outcome of each process.
Incineration: Combustion with Excess Oxygen
Incineration is, simply, burning. It involves heating plastic waste to very high temperatures, typically 850°C to 1100°C, in the presence of a large amount of oxygen.
This process causes rapid combustion, an exothermic reaction that breaks down the organic material completely. The primary goal is to release the maximum amount of energy stored in the plastic's chemical bonds.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a form of thermal decomposition. It involves heating plastic waste in a controlled environment, typically between 350°C and 600°C, in the complete or near-complete absence of oxygen.
Because there is no oxygen, the plastic does not burn. Instead, the long polymer chains that make up the plastic are "cracked" by the heat, breaking them down into smaller, simpler molecules. It is a material recovery process, not a destruction process.
A Tale of Two Outputs: Energy vs. Resources
The goal of each process is directly reflected in its primary outputs. One creates immediate energy and ash; the other creates a portfolio of new chemical products.
Incineration's Output: Ash and Energy
The main products of incineration are heat and ash. The intense heat is used to boil water, creating steam that drives turbines to generate electricity in a modern waste-to-energy plant.
The other outputs are flue gas (primarily carbon dioxide and water vapor, but also pollutants) and bottom ash, an inert solid residue that must be landfilled or repurposed.
Pyrolysis's Output: Oil, Gas, and Char
Pyrolysis breaks plastic down into three valuable streams:
- Pyrolysis Oil (or "Tacoil"): A liquid synthetic crude oil that can be refined into new fuels or chemical feedstocks to make new plastics.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (like hydrogen and methane) that can be used to power the pyrolysis facility itself.
- Solid Char (or "Carbon Black"): A solid, carbon-rich residue that can be used as a colorant, an industrial filler, or a soil amendment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a perfect solution. Each comes with significant operational and environmental challenges that must be managed.
The Incineration Dilemma: Energy vs. Emissions
While waste-to-energy plants are an effective way to reduce landfill volume and generate power, the combustion of mixed waste is a major concern.
Burning plastics, especially those containing chlorine like PVC, can create highly toxic dioxins and furans. It also releases heavy metals and acid gases. Modern incinerators require expensive and complex flue gas treatment systems to capture these pollutants before they enter the atmosphere.
The Pyrolysis Puzzle: Feedstock Purity and Economics
Pyrolysis is highly sensitive to the purity of the plastic feedstock. Contaminants like food waste, paper, and certain types of plastic (especially PVC) can degrade the quality of the pyrolysis oil, making it difficult and expensive to refine.
This means that effective sorting and pre-treatment of plastic waste are critical for successful pyrolysis, adding logistical complexity and cost. Achieving economic viability at scale remains a significant challenge for the industry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between incineration and pyrolysis is a strategic decision based on a clear waste management objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum waste volume reduction and immediate energy generation: Incineration is the more mature and direct technology for converting the raw energy value of mixed waste into electricity.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery and advancing a circular economy: Pyrolysis provides a pathway to transform plastic waste back into valuable chemical feedstocks, enabling the creation of new products.
- If your primary focus is managing unsorted municipal solid waste: Modern waste-to-energy incineration plants are specifically designed to handle this complex stream, whereas pyrolysis requires a much cleaner, more homogenous feedstock.
Ultimately, selecting the right technology depends entirely on whether your goal is to destroy waste for its energy or to deconstruct it for its materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Incineration | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Combustion (with oxygen) | Thermal Decomposition (without oxygen) |
| Primary Goal | Energy Generation & Volume Reduction | Resource Recovery & Chemical Feedstock Production |
| Typical Temperature | 850°C - 1100°C | 350°C - 600°C |
| Key Outputs | Heat, Electricity, Ash | Pyrolysis Oil, Syngas, Solid Char |
| Main Challenge | Air Pollution Control | Feedstock Purity & Economic Viability |
Optimize Your Plastic Waste Strategy with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of plastic waste management requires the right tools and expertise. Whether your goal is efficient energy recovery or advancing a circular economy through chemical recycling, KINTEK is your trusted partner.
We provide advanced laboratory equipment and consumables to help you:
- Accurately analyze plastic waste composition.
- Test and optimize pyrolysis or thermal treatment processes on a lab scale.
- Ensure quality control for your feedstocks and outputs.
Let KINTEK's solutions empower your research and development, helping you make data-driven decisions for a sustainable future.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can support your specific plastic waste management projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















