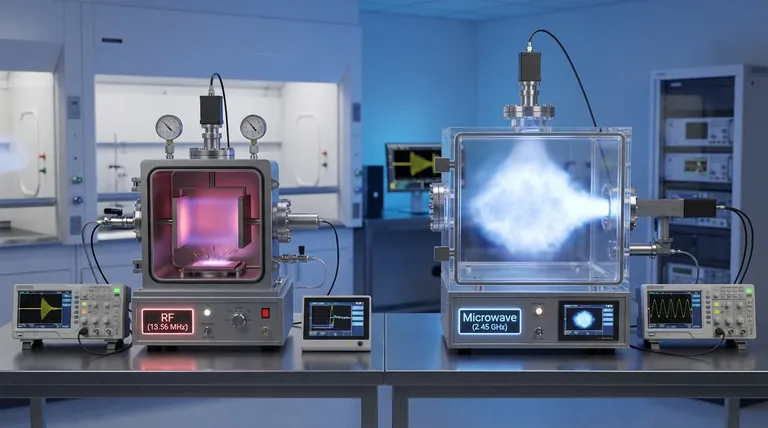
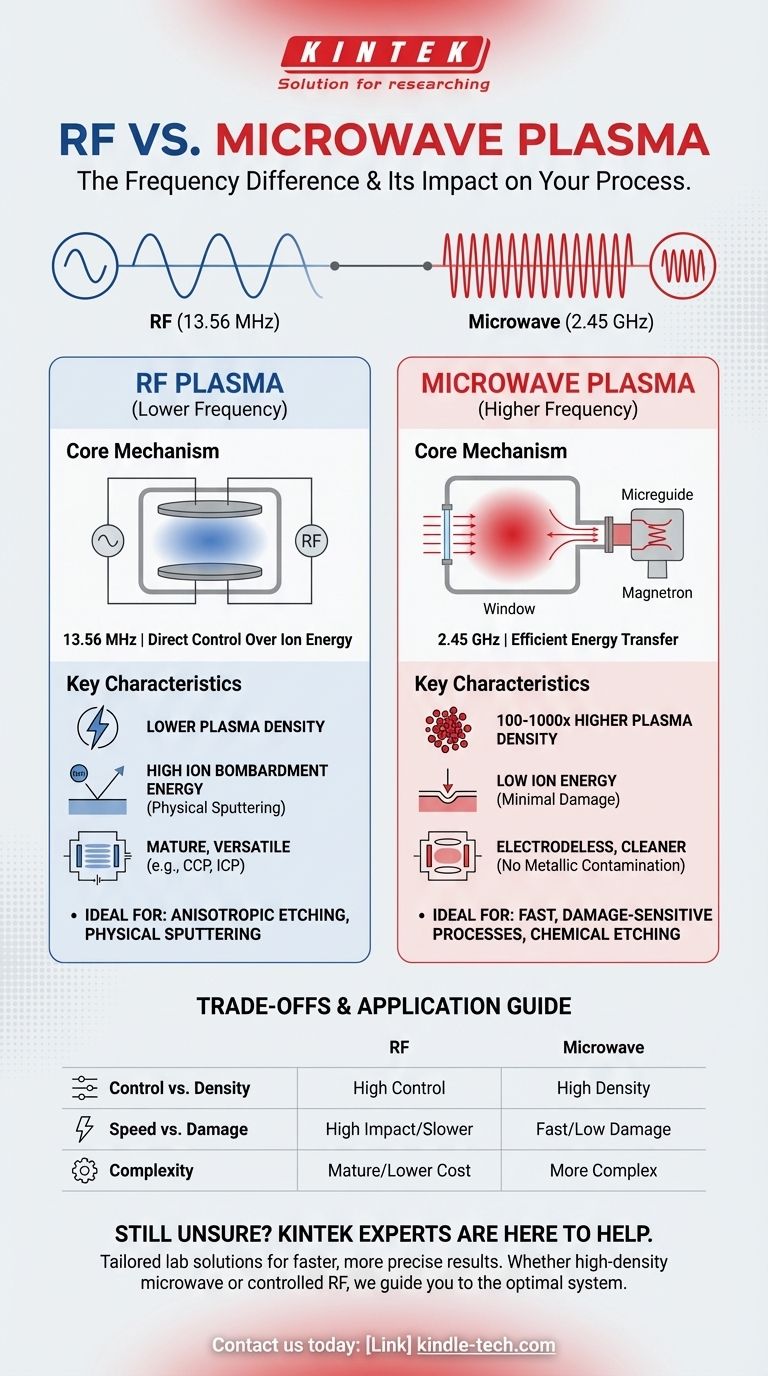
At the most fundamental level, the difference between RF and microwave plasma is the frequency of the electromagnetic field used to generate and sustain it. RF (Radio Frequency) systems operate at lower frequencies, typically 13.56 MHz, while microwave systems use much higher frequencies, usually 2.45 GHz. This seemingly simple difference in frequency profoundly alters how energy is transferred into the gas, leading to distinct plasma characteristics and dictating which technology is better suited for a given application.
The choice between RF and microwave plasma is a strategic decision based on your process requirements. Microwave plasma excels at creating a very high density of reactive species with low ion energy, making it ideal for fast, damage-sensitive processes. RF plasma offers more direct control over ion bombardment energy, establishing it as a versatile tool where physical sputtering is a critical part of the process.

The Core Mechanism: How Frequency Shapes the Plasma
The operating frequency is not just a number; it is the primary variable that controls the physics of the plasma generation. This has direct consequences for plasma density and the energy of the ions bombarding your substrate.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
In any plasma, free electrons oscillate in response to the applied electromagnetic field. Between collisions with gas atoms, these electrons absorb energy, which they then transfer through those collisions to ionize the gas and create more free electrons, sustaining the plasma.
At microwave's very high frequency (2.45 GHz), electrons have time to oscillate hundreds of times between each collision. This allows them to absorb energy far more efficiently than in a lower-frequency RF field, where an electron may only oscillate a few times before a collision.
Resulting Plasma Density
This superior energy transfer efficiency means microwave systems are exceptionally effective at ionization. As a result, microwave plasma is typically much denser than conventional RF plasma.
We often see plasma densities 100 to 1,000 times higher in microwave systems compared to standard capacitively coupled RF systems. This high density of ions and radicals can dramatically accelerate chemical processes like etching and deposition.
Ion Bombardment Energy
In a typical RF system using two parallel plates (Capacitively Coupled Plasma or CCP), a "self-bias" voltage naturally develops on the powered electrode. This bias accelerates positive ions toward the substrate, causing them to arrive with significant kinetic energy. This is often desirable for physically sputtering material or for anisotropic (directional) etching.
Microwave systems, by contrast, are often electrodeless. The energy is coupled into the chamber through a dielectric window (like quartz) via a waveguide. This design means there is no inherent high-voltage electrode, and ions drift to surfaces with much lower energy, minimizing physical damage to sensitive substrates.
Practical Implications for System Design
The difference in frequency and coupling mechanism leads to fundamentally different hardware configurations.
RF System Architecture
RF systems most often use either capacitive or inductive coupling. Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) systems are common, using parallel plate electrodes inside the vacuum chamber. Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) systems use an antenna coil outside the chamber to induce a current, which also generates a very high-density plasma, often with lower ion energy than CCP.
Microwave System Architecture
Microwave systems typically use a magnetron (the same device found in a microwave oven) to generate the high-frequency waves. These waves are guided into the chamber through a waveguide and a dielectric window. This "electrodeless" design is a key advantage, as it minimizes a potential source of metallic contamination that can occur from electrode sputtering in RF systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; they represent a classic engineering trade-off between different performance characteristics.
Control vs. Density
RF CCP systems provide a direct, albeit coupled, way to control ion energy by simply adjusting the input power. Microwave systems provide extreme plasma density but have inherently low ion energy. To control ion energy in a microwave system, a secondary RF bias must often be added to the substrate holder, increasing system complexity.
Process Speed vs. Potential Damage
The high radical density in microwave plasma enables extremely fast chemical etching or deposition rates at lower temperatures. However, its low ion energy makes it less effective for processes that require strong physical sputtering to break chemical bonds or remove stubborn material. The high ion energy in RF CCP is excellent for physical bombardment but can cause crystalline damage or defects on sensitive materials.
System Maturity vs. Complexity
RF plasma technology, particularly CCP, is a very mature and well-understood field, with robust and often lower-cost systems available. Microwave plasma systems can be more complex, involving components like magnetrons, circulators, and tuners that require specialized expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your application's specific needs for speed, directionality, and substrate sensitivity should dictate your choice.
- If your primary focus is high-speed etching or deposition on sensitive substrates: Microwave plasma is often superior due to its unmatched density of reactive species and inherently low ion bombardment energy.
- If your primary focus is controlling etch directionality (anisotropy) and breaking strong bonds: An RF system, particularly one where you can independently control ion energy (like a biased ICP or a standard CCP), is the more conventional and powerful tool.
- If your primary focus is surface cleaning, sterilization, or polymer activation: Both can be effective, but the high flux of radicals from a microwave plasma can offer significant speed advantages at lower process temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding that you are choosing between a high-density, low-impact chemical tool (microwave) and a highly controllable, high-impact physical tool (RF) is the key to matching the plasma to your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | RF Plasma | Microwave Plasma |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 13.56 MHz | 2.45 GHz |
| Plasma Density | Lower | 100-1000x Higher |
| Ion Bombardment Energy | High (Controllable) | Low (Minimal Damage) |
| Ideal For | Anisotropic Etching, Sputtering | Fast, Sensitive Processes, Chemical Etching |
| System Complexity | Mature, Lower Cost | More Complex, Electrodeless Design |
Still unsure which plasma technology is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for your laboratory needs. Whether you require the high-density, low-damage capabilities of microwave plasma or the controlled ion energy of RF plasma, we can guide you to the optimal system for faster, more precise results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific process requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- What is a microwave plasma reactor? Unlock Precision Synthesis of High-Performance Materials
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















