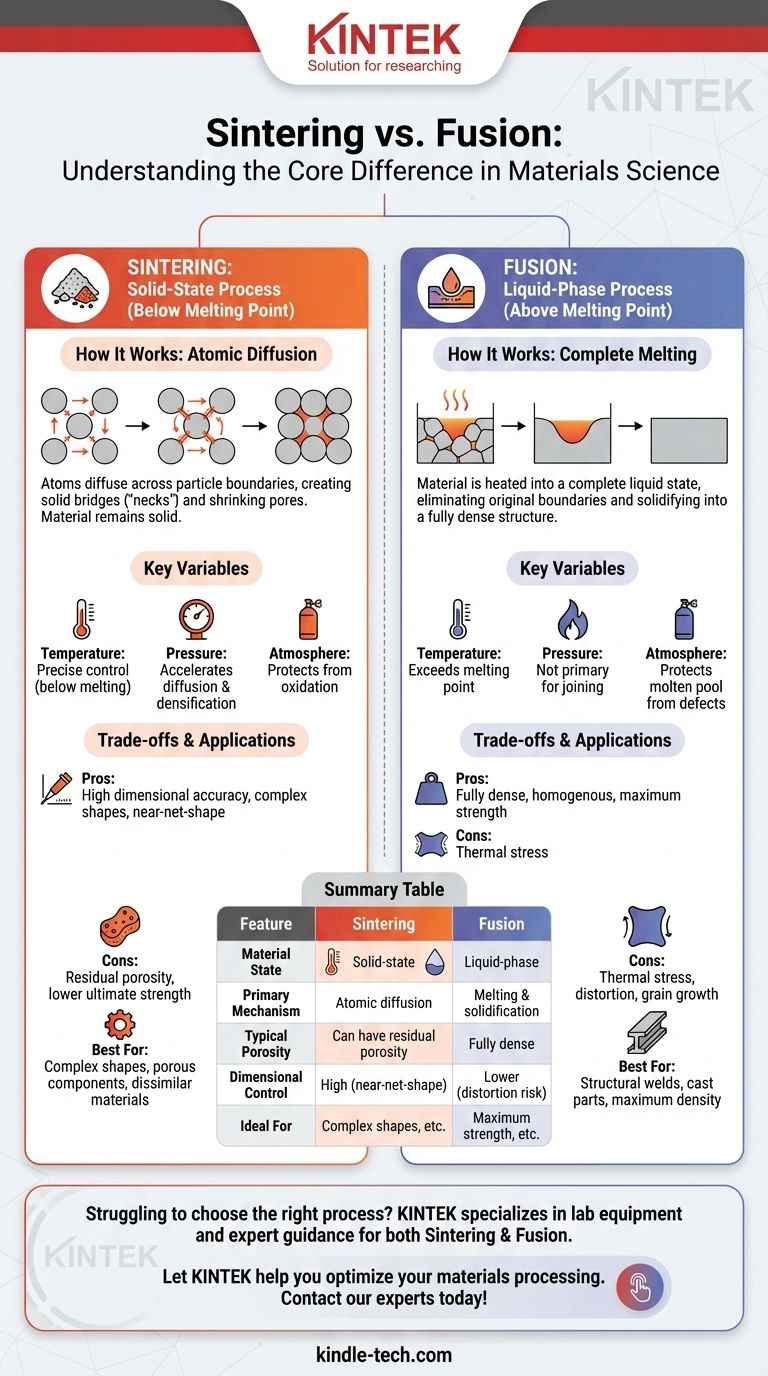
In materials science, the distinction is fundamental: Sintering is a solid-state process that bonds particles together using heat and pressure below their melting point. In contrast, fusion involves heating a material above its melting point until it becomes a complete liquid, which then solidifies into a single, continuous piece upon cooling.
The essential difference lies in the state of the material during processing. Sintering modifies and joins materials while they remain solid, whereas fusion transforms them into a liquid to reshape or join them. This choice between a solid-state or liquid-phase process dictates the final properties, precision, and applications of the part.
The Core Mechanism: Solid State vs. Liquid Phase
To truly grasp the difference, you must understand the physics at work. One process relies on atomic movement in solids, while the other leverages the complete freedom of movement in liquids.
How Sintering Works: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering is primarily a process used in powder metallurgy and ceramics. It begins with a collection of fine particles, often compacted into a desired shape (a "green part").
These particles are then heated to a high temperature, but one that is safely below the material's melting point. This heat gives the atoms within each particle enough energy to move.
At the points where particles touch, atoms diffuse across the boundary, creating a solid bridge or "neck." As this process continues, these necks grow, the particles bond together, and the gaps between them (pores) shrink, increasing the part's density and strength.
How Fusion Works: Complete Melting
Fusion is a more intuitive concept, seen in processes like welding or casting. The goal is to deliver enough thermal energy to completely overcome the bonds holding the material in its solid, crystalline state.
The material is heated past its melting point, forming a molten pool. In this liquid state, the original particle or piece boundaries are completely eliminated.
As the liquid cools and solidifies, it forms a new, continuous solid structure. This process typically results in a fully dense part, as the liquid fills all available space before solidifying.
Key Process Variables and Their Impact
The outcomes of both sintering and fusion are highly dependent on controlling a few critical variables.
The Role of Temperature
For sintering, temperature control is a matter of precision. It must be high enough to activate atomic diffusion but low enough to prevent widespread melting, which would destroy the part's shape.
For fusion, the goal is simply to exceed the melting temperature to ensure a fully liquid, homogenous pool that can flow and solidify correctly.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure is a key lever in sintering. Applying external pressure, as in hot pressing, forces particles into closer contact, which helps break down surface oxide layers and accelerates the diffusion and densification process.
In most fusion processes, pressure is not the primary mechanism for joining. The complete melting and subsequent solidification are what create the bond.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The surrounding atmosphere is critical for both processes, especially with reactive materials like metals.
In sintering, atmospheres like hydrogen or nitrogen are often required to prevent oxidation and help remove impurities from the particle surfaces, enabling a stronger bond and achieving a fully dense part.
Similarly, fusion processes like welding use shielding gases to protect the molten pool from oxygen and nitrogen in the air, which would otherwise create defects and weaken the final joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally superior; they represent a classic engineering trade-off between precision and absolute density.
Sintering: Precision at a Cost
The primary advantage of sintering is its ability to create complex, net-shape or near-net-shape parts with high dimensional accuracy. This minimizes the need for post-processing and machining.
However, completely eliminating porosity can be challenging. Residual pores can remain in the final part, which may compromise its ultimate mechanical strength compared to a fully fused equivalent.
Fusion: Strength at a Cost
The main benefit of fusion is its ability to create fully dense, homogenous structures with high strength and no internal voids.
The downside is that the intense heat and subsequent cooling can introduce thermal stresses, distortion, and undesirable changes to the material's microstructure (like large grain growth). It is generally less suited for creating intricate, standalone parts directly from a powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice between these processes depends entirely on the material you are using and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, near-net-shape parts or porous components: Sintering offers superior dimensional control and the unique ability to engineer porosity.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum strength and a fully dense, non-porous structure: Fusion is the more direct path, ideal for applications like structural welds or cast components.
- If your primary focus is combining materials with vastly different melting points: Sintering is often the only viable option, as it avoids melting the lower-temperature material.
Understanding this core difference between solid-state bonding and liquid-phase joining empowers you to select the most effective manufacturing process for your material and design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sintering | Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| Material State | Solid-state (below melting point) | Liquid-phase (above melting point) |
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion and neck growth | Melting and solidification |
| Typical Porosity | Can have residual porosity | Fully dense, non-porous |
| Dimensional Control | High (near-net-shape) | Lower risk of distortion |
| Ideal For | Complex shapes, porous components, dissimilar materials | Maximum strength, structural welds, cast parts |
Struggling to choose the right process for your materials? The choice between sintering and fusion is critical for achieving your desired part properties. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and expert guidance needed for both sintering furnaces and fusion systems. Whether you're developing complex ceramic components or requiring fully dense metal parts, our solutions ensure optimal temperature control, atmosphere management, and process reliability.
Let KINTEK help you optimize your materials processing. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how our equipment can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum oven in degassing siloxane oligomers? Ensure Perfect UV Curing and Surface Finish
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- What is the vacuum brazing technique? Achieve Superior, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Which type of furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Heat Treating Solution
- How does a vertical furnace achieve energy-saving sintering? Harness Internal Energy for Efficient Pellet Treatment
- What is vacuum deposition of metal? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Control for Superior Performance
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc furnace with a tungsten electrode? Achieve High-Purity Alloy Melting
- What are the uses of heat treated aluminum alloys? Unlock High-Strength, Lightweight Performance



















