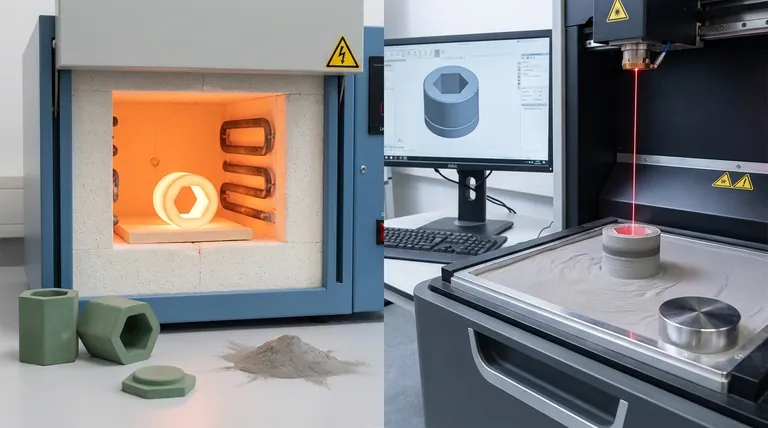
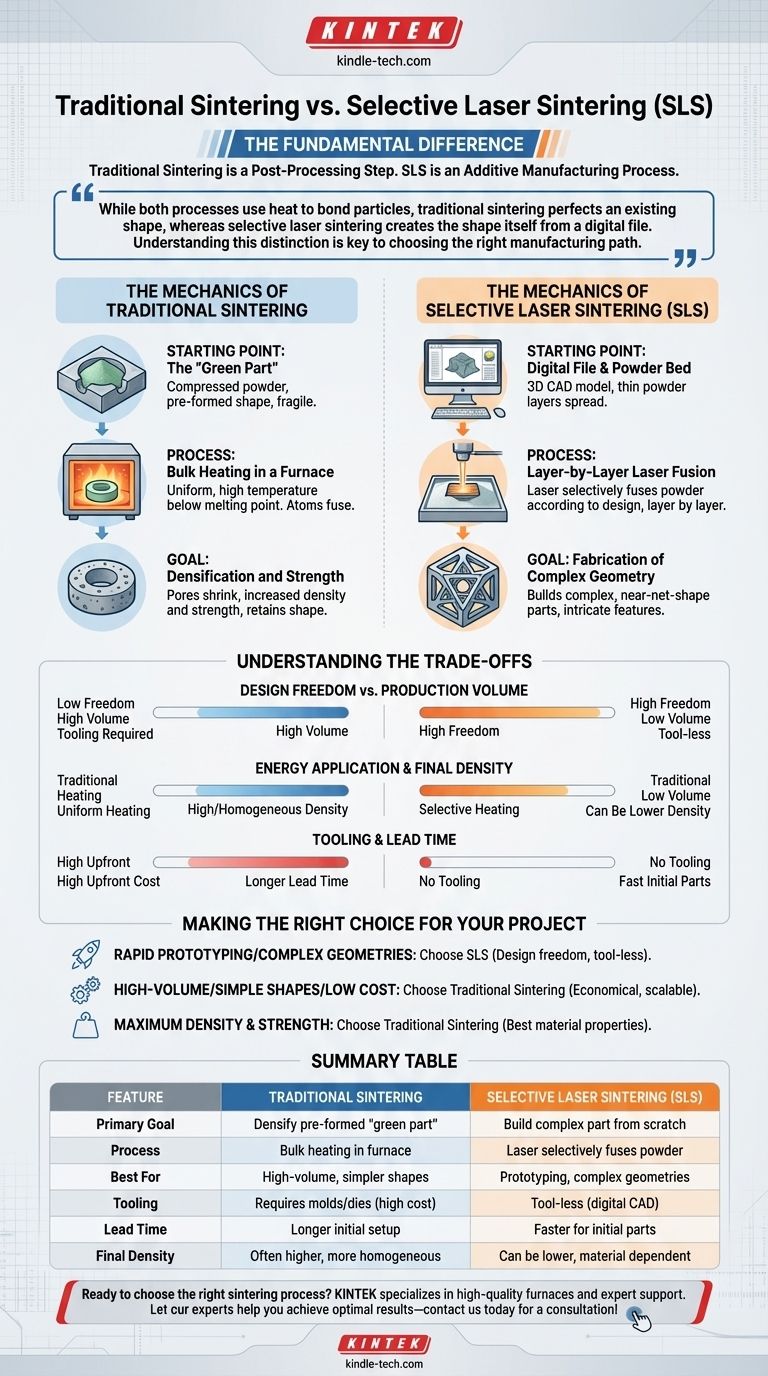
The fundamental difference lies in their manufacturing approach. Traditional sintering is a post-processing step that heats an entire pre-formed object to increase its density and strength. In contrast, selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing process that builds an object from scratch, using a laser to fuse powdered material together layer by layer.
While both processes use heat to bond particles, traditional sintering perfects an existing shape, whereas selective laser sintering creates the shape itself from a digital file. Understanding this distinction is key to choosing the right manufacturing path.

The Mechanics of Traditional Sintering
Traditional sintering is a foundational process in powder metallurgy, ceramics, and other material sciences. Its primary goal is not to create a shape, but to transform a fragile, porous object into a solid, durable one.
The Starting Point: The "Green Part"
The process begins with a "green part"—a component formed by compressing powder into a desired shape using a die or mold. This part is solid enough to be handled but lacks the final strength and density required for its application.
The Process: Bulk Heating in a Furnace
The green part is placed inside a furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point. This uniform, ambient heat causes the atoms in the individual powder particles to diffuse across the boundaries, fusing them together.
The Goal: Densification and Strength
As the particles fuse, the pores and voids between them shrink or close up entirely. The result is a component that is significantly denser, stronger, and less porous than the initial green part, while largely retaining its original shape.
The Mechanics of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective laser sintering is a type of 3D printing that falls under the umbrella of additive manufacturing. It builds parts directly from a digital design without the need for molds or tooling.
The Starting Point: A Digital File and a Powder Bed
The process begins with a 3D CAD model and a machine containing a bed of fine polymer, metal, or ceramic powder. A roller or blade spreads a thin, uniform layer of this powder across a build platform.
The Process: Layer-by-Layer Laser Fusion
Guided by the CAD file, a high-power laser selectively scans the cross-section of the part onto the surface of the powder bed. The laser's energy heats the powder just enough to melt or fuse the particles together in that specific area. The platform then lowers, a new layer of powder is applied, and the process repeats.
The Goal: Fabrication of Complex Geometry
The objective of SLS is to build a complete, near-net-shape part from the ground up. Because it builds layer by layer, it can produce incredibly complex geometries, internal channels, and intricate features that are impossible to create with traditional molding and sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two methods requires a clear understanding of their inherent strengths and weaknesses, which are directly tied to their different mechanisms.
Design Freedom vs. Production Volume
SLS offers nearly unlimited geometric freedom, making it ideal for prototypes, custom parts, and complex, low-volume production. Traditional sintering, which relies on molds to create the green part, is better suited for high-volume manufacturing of simpler, repeatable shapes where tooling costs can be amortized.
Energy Application and Final Density
The selective heating of SLS is efficient for creating a shape, but it can sometimes result in lower final density and different material microstructures compared to traditional methods. The uniform, sustained heating in a furnace during traditional sintering often produces parts with higher density and more homogenous mechanical properties.
Tooling and Lead Time
SLS is a "tool-less" process, meaning you can go from a digital file to a physical part very quickly. Traditional sintering requires significant upfront investment in time and money to create the molds or dies for the green part, leading to longer initial lead times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your decision should be driven entirely by your project's goals for geometry, volume, and material performance.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or complex, custom geometries: SLS is the superior choice due to its design freedom and tool-less nature.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a simple shape at the lowest possible cost: Traditional sintering is the more economical and scalable solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving the maximum possible material density and mechanical strength: Traditional sintering processes, especially when combined with pressure, often yield the best material properties.
Ultimately, choosing the right method means aligning the process capabilities with your specific manufacturing needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Sintering | Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Densify and strengthen a pre-formed 'green part' | Build a complex part from scratch (Additive Manufacturing) |
| Process | Bulk heating of an entire part in a furnace | Laser selectively fuses powder layer by layer |
| Best For | High-volume production of simpler shapes | Prototyping, custom parts, and complex geometries |
| Tooling | Requires molds/dies (high upfront cost) | Tool-less (uses a digital CAD file) |
| Lead Time | Longer initial setup | Faster for initial parts and prototypes |
| Final Part Density | Often higher and more homogeneous | Can be lower, depending on material and settings |
Ready to choose the right sintering process for your project? The right lab equipment is crucial for success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality furnaces for traditional sintering and provides expert support for all your laboratory needs. Let our experts help you achieve optimal results—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?



















