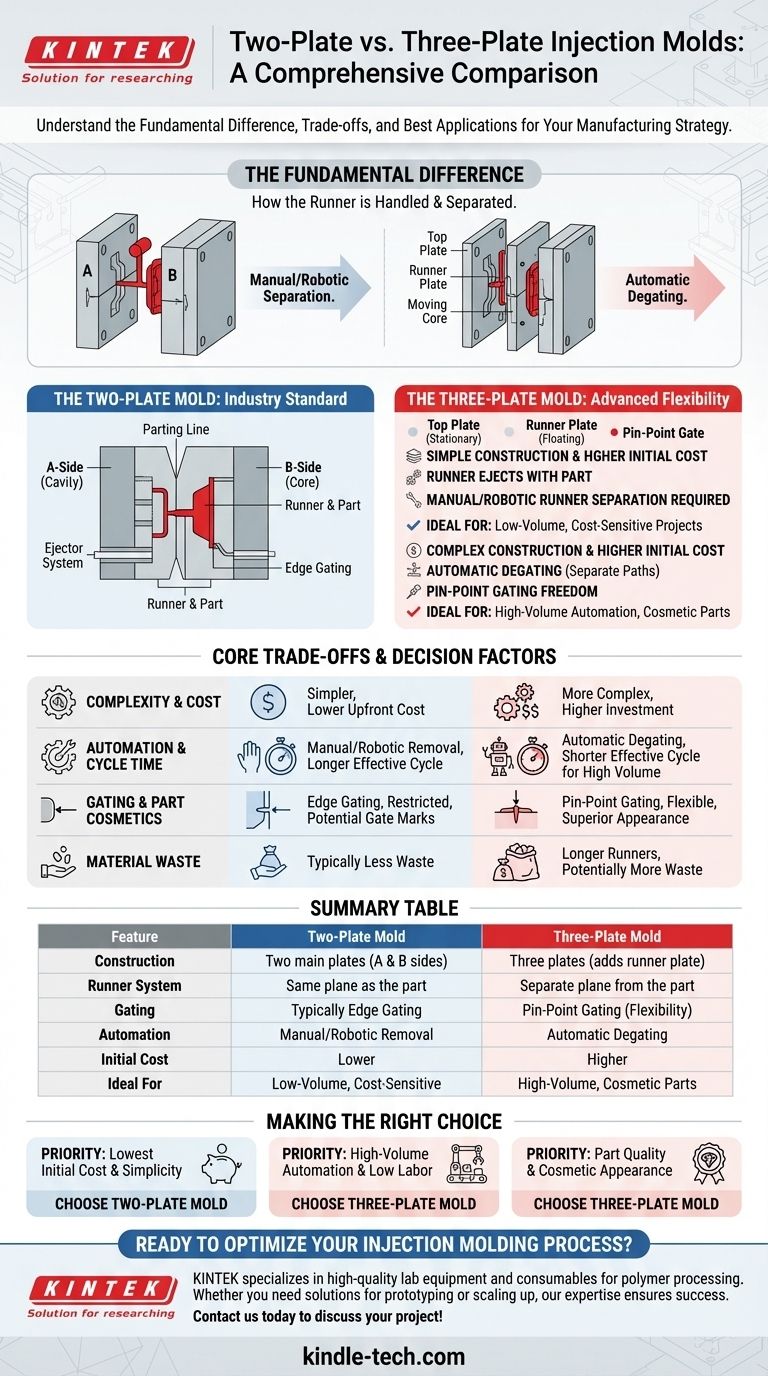
The fundamental difference between a two-plate and a three-plate mold lies in their construction and how they handle the plastic delivery system, known as the runner. In a two-plate mold, the runner system is on the same plane as the part and is ejected along with it. A three-plate mold adds an extra plate to create a separate path for the runner, allowing it to be automatically separated from the part during the molding cycle.
The choice is not merely mechanical; it's a strategic decision. A two-plate mold prioritizes simplicity and lower initial cost, while a three-plate mold prioritizes automation, design flexibility, and superior part cosmetics.

The Two-Plate Mold: The Industry Standard
A two-plate mold is the most common type of injection mold due to its straightforward design and cost-effectiveness.
Basic Construction
This design consists of two main plates, often called the 'A' side (cavity) and 'B' side (core), which meet at a single parting line.
The Runner System
The runner, which carries molten plastic from the sprue to the part cavity, is machined into the surface of the parting line.
Ejection Process
When the mold opens, the runner and the finished part are stuck to one side and are pushed out together by the ejector system.
Key Implication
This design almost always requires a secondary operation to manually or robotically separate the part from the runner, adding labor or automation costs to each cycle.
The Three-Plate Mold: Advanced Flexibility
The three-plate mold introduces complexity to solve the inherent limitations of the two-plate design, particularly around automation and gating.
Advanced Construction
As the name implies, this design uses three plates: a stationary top plate, a floating runner plate in the middle, and the moving core half. This creates two parting lines.
The Runner System
The runner system is contained entirely on its own plane between the top plate and the runner plate. This is the critical distinction.
Automatic Degating
As the mold opens, the first parting line separates the runner from the part. The second parting line then opens to eject the part, while the runner is ejected separately. This process is called automatic degating.
Gating Freedom
Because the runner is on a separate level, plastic can be injected directly into the top surface of a part using a pin-point gate. This offers far greater flexibility for part design and can hide gate marks in non-cosmetic areas.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Choosing between these two systems requires a clear understanding of the compromises you are making in cost, speed, and quality.
Mold Complexity and Cost
A two-plate mold is simpler, faster to manufacture, and has a lower upfront cost. A three-plate mold is significantly more complex, requiring more precision machining and components, leading to higher initial investment and maintenance costs.
Cycle Time and Automation
While a three-plate mold's mechanical cycle might be slightly longer, its effective cycle time is often shorter for high-volume production. This is because it eliminates the time and cost associated with post-process runner removal.
Part Design and Gate Location
Two-plate molds are generally restricted to edge gating, where the plastic enters the part from the side along the parting line. Three-plate molds allow for pin-point gating anywhere on the part surface, which is ideal for achieving a uniform plastic flow and better cosmetic appearance.
Material Waste
Three-plate mold runner systems are typically longer and more complex than those in two-plate molds. This can result in more plastic waste per cycle, which can be a significant cost factor, especially with expensive engineering-grade resins.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal choice is dictated entirely by your project's priorities.
- If your primary focus is lowest initial tool cost and simplicity: A two-plate mold is almost always the correct choice, especially for lower-volume production runs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume automation and minimizing labor: A three-plate mold's automatic degating capability will provide a superior return on investment.
- If your primary focus is part quality and cosmetic appearance: A three-plate mold offers the gating flexibility needed to produce cosmetically flawless parts without visible gate marks on the edges.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction elevates your decision-making from simple mechanics to a core manufacturing strategy for your product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Two-Plate Mold | Three-Plate Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Two main plates (A & B sides) | Three plates (adds a runner plate) |
| Runner System | On the same plane as the part | On a separate plane from the part |
| Gating | Typically edge gating | Pin-point gating (more flexibility) |
| Automation | Manual/robotic runner removal | Automatic degating (no secondary operation) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal For | Low-volume, cost-sensitive projects | High-volume automation, cosmetic parts |
Ready to optimize your injection molding process? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for polymer processing and material testing. Whether you're prototyping with a simple two-plate mold or scaling up with an automated three-plate system, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- High Performance Lab Homogenizer for Pharma Cosmetics and Food R&D
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
- What is mould in manufacturing? Unlock Mass Production with Precision Tooling
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- What is a pressing die? The Precision Tool for Shaping Powder into Solid Pellets
- How do steel molds and hydraulic equipment collaborate for high-density molding? Optimize WC/Cu FGM Green Body Prep











