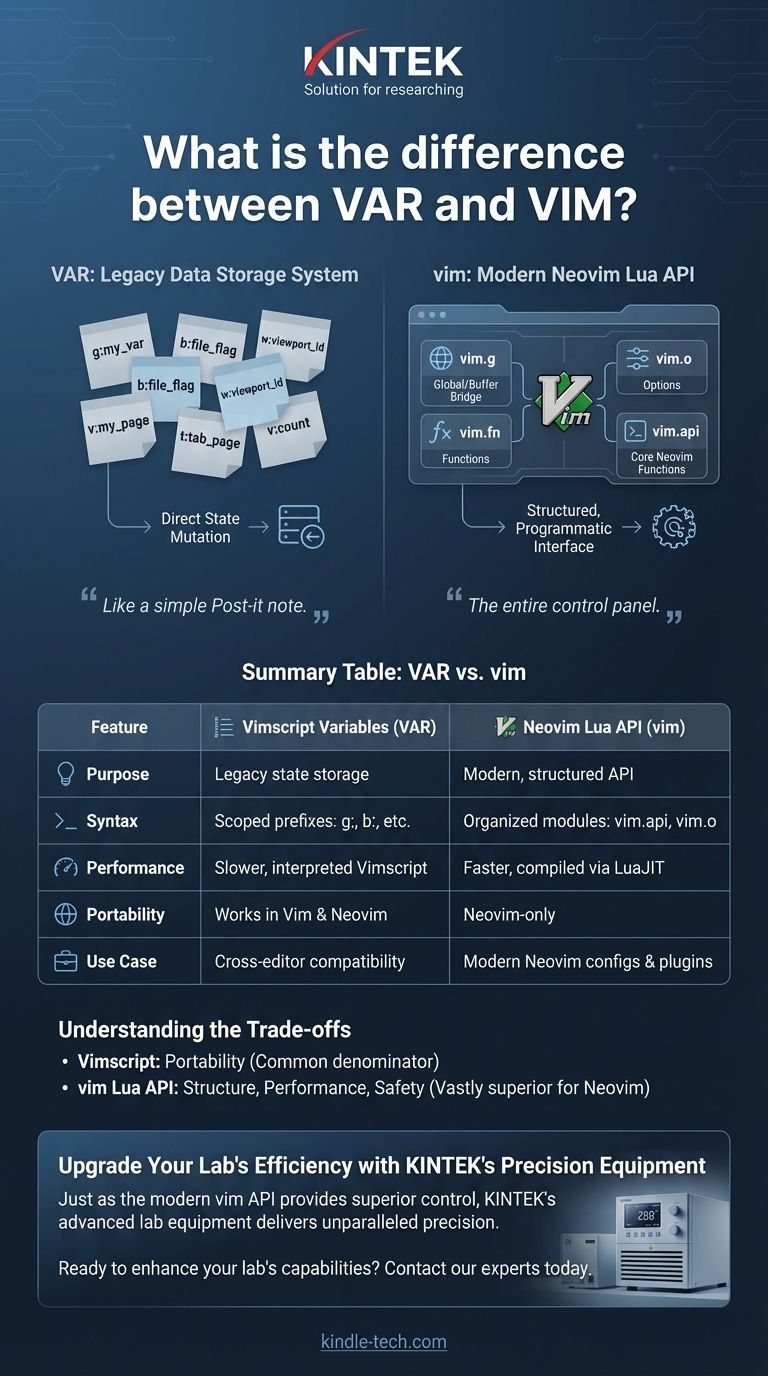
At its core, the distinction between "VAR" and "vim" is a distinction between a legacy data storage system and a modern, comprehensive programming interface. A "VAR" refers to a traditional Vimscript variable (like g:my_var), which is a simple key-value store. In contrast, vim is the global Lua object in Neovim that provides a structured, powerful, and complete API for interacting with every aspect of the editor.
In short, think of a Vimscript variable as a simple Post-it note you stick somewhere in the editor. The
vimobject, however, is the entire control panel, giving you access to the editor's engine, settings, and functions through a clean and modern interface.

Understanding "VAR": The Vimscript Variable System
The term "VAR" isn't a formal keyword but represents the traditional method of storing state in Vim using Vimscript variables. This system is defined by its use of special prefixes to denote scope.
The Role of Scoped Prefixes
Vimscript variables are always preceded by a prefix that defines their lifetime and visibility. Understanding these is key to understanding the old system.
g:(Global): Accessible everywhere, across all tabs, windows, and buffers. This is the most common for user configuration and plugin settings.b:(Buffer): Tied to a specific buffer (a file loaded into memory). Useful for storing buffer-local information, like compiler flags for a specific file.w:(Window): Tied to a specific window (a viewport onto a buffer).t:(Tab): Tied to a specific tab page.v:(Vim-internal): Reserved for variables defined by Vim itself, likev:count.
The Core Concept: Direct State Mutation
Working with these variables involves directly setting or getting a value in a specific scope. In Vimscript, you use let g:my_var = 'value'. In Neovim's Lua, you would use vim.g.my_var = 'value'. In both cases, you are directly manipulating a global key-value dictionary.
Understanding "vim": The Neovim Lua API
When developers refer to vim, they mean the primary entry point for all interactions with Neovim from a Lua environment (init.lua or Lua plugins). It is a global Lua table that acts as a structured and well-documented namespace.
A Programmatic and Structured Interface
Unlike the scattered nature of Vimscript variables, the vim object organizes access to the editor's internals into logical sub-modules. This makes code easier to write, read, and debug.
Key API Submodules
The vim object contains many modules, but a few are fundamental for replacing traditional Vimscript patterns:
vim.gandvim.b: These are Lua tables that act as a bridge to access global (g:) and buffer-local (b:) Vimscript variables. Settingvim.g.my_varis the same as settingg:my_var.vim.o: A direct, structured way to get and set editor options (e.g.,vim.o.tabstop = 4), which is far superior to the oldset tabstop=4command.vim.fn: A bridge to call any built-in Vimscript function (e.g.,vim.fn.expand('%')to get the current file path).vim.api: The core of Neovim. This provides a stable, fast, and feature-rich set of functions for manipulating buffers, windows, and the editor state in a programmatic way.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Legacy vs. Modern
Choosing between these two approaches depends entirely on your goal, specifically whether you prioritize compatibility with older Vim versions or the power and clarity of the modern Neovim ecosystem.
The Case for Vimscript Variables
The primary reason to use the g:var style is portability. If you are writing a plugin or a configuration snippet that must run on both standard Vim and Neovim, you must use Vimscript. It is the common denominator.
The Case for the vim Lua API
For any work targeting only Neovim, the vim API is vastly superior. It offers structure and discoverability (your language server can provide autocompletion for vim.api.*), significantly better performance via LuaJIT, and improved safety through a well-defined API rather than direct state mutation.
The vim.g Bridge: The Best of Both Worlds
The vim.g table is the critical link. When writing a Neovim plugin in Lua, you use vim.g to define configuration variables. This allows your users to configure your plugin using either traditional Vimscript (let g:my_plugin_setting = 1) in their init.vim or Lua (vim.g.my_plugin_setting = 1) in their init.lua.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your specific context—whether you're writing a personal configuration, a public plugin, or a cross-compatible script.
- If your primary focus is a personal Neovim configuration (
init.lua): Default to thevimLua API for everything (vim.o,vim.keymap.set,vim.api). It is faster, cleaner, and more maintainable. - If your primary focus is writing a modern Neovim plugin: Build your internal logic using the
vim.apiand other Lua modules. Expose user-facing settings viavim.gto provide a stable configuration interface. - If your primary focus is compatibility with classic Vim: You have no choice but to use the traditional Vimscript variable system (
g:,b:, etc.) and Vimscript functions.
By understanding this distinction, you can write more effective, maintainable, and performant editor configurations and plugins.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vimscript Variables (VAR) | Neovim Lua API (vim) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Legacy state storage | Modern, structured API for editor control |
| Syntax | Scoped prefixes (g:, b:, etc.) | Organized modules (vim.api, vim.o, etc.) |
| Performance | Slower, interpreted Vimscript | Faster, compiled via LuaJIT |
| Portability | Works in Vim & Neovim | Neovim-only |
| Use Case | Cross-editor compatibility | Modern Neovim configs & plugins |
Upgrade Your Lab's Efficiency with KINTEK's Precision Equipment
Just as the modern vim API provides superior control and performance for Neovim users, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment delivers unparalleled precision and reliability for your research needs. Our products are designed with the same philosophy of structured, high-performance interfaces that empower users to achieve better results.
Whether you're setting up a new laboratory or upgrading existing systems, KINTEK specializes in providing the tools that researchers trust. Our equipment ensures accurate temperature control, consistent results, and long-term durability—helping your team focus on discovery rather than equipment limitations.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your specific research requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity










