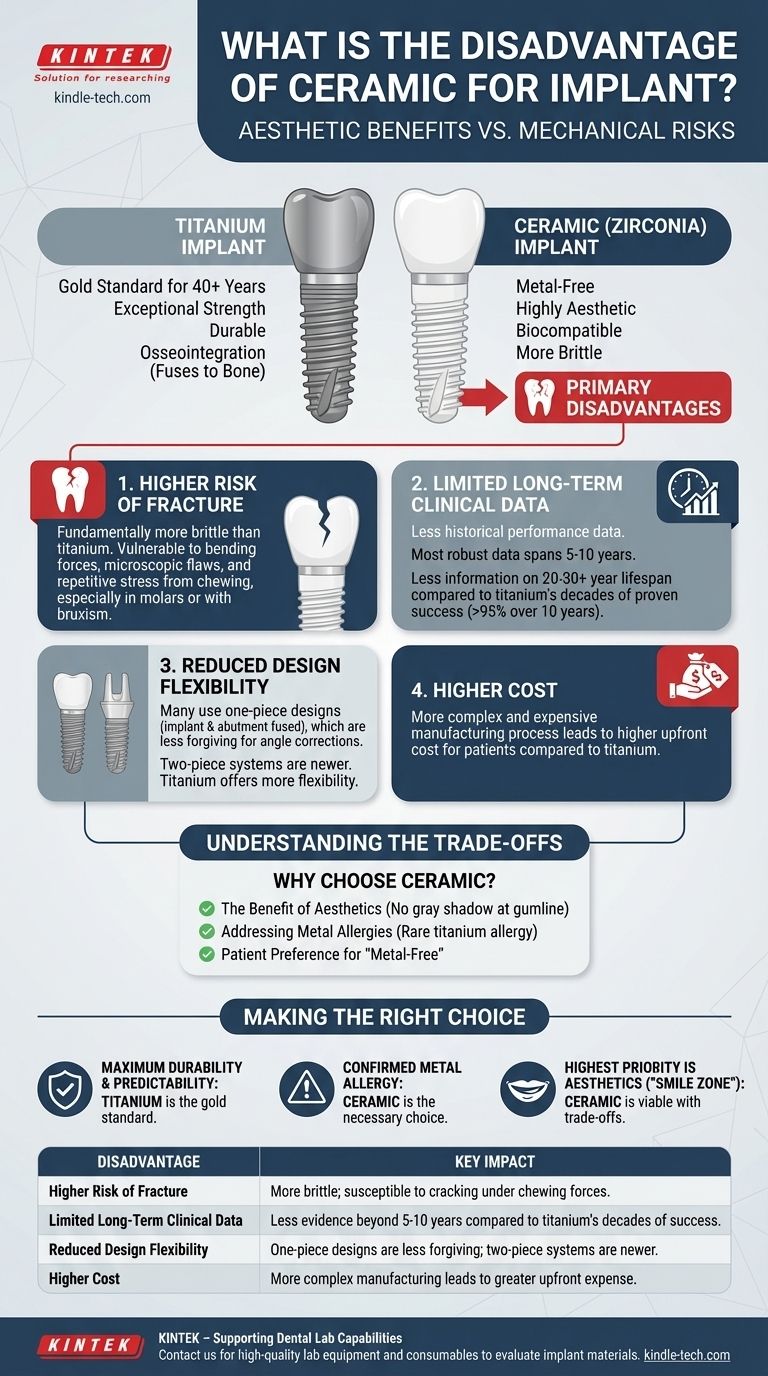
While highly aesthetic and biocompatible, the primary disadvantage of ceramic dental implants is their higher risk of mechanical failure, specifically fracture. Unlike metal-based titanium, ceramic is a more brittle material, making it more susceptible to cracking under the heavy, repetitive forces of chewing, particularly for implants placed in the back of the mouth. This lower fracture resistance, combined with less long-term clinical data, represents the core trade-off when considering this option.
The choice between implant materials is not about which is "better," but which is most appropriate for a specific clinical situation. Ceramic (zirconia) implants offer a metal-free, aesthetically superior solution but at the cost of higher fracture risk and less long-term data compared to the proven strength and decades-long track record of titanium.

The Core Problem: Material Properties
To understand the disadvantages, you must first understand the fundamental difference between the two materials used for dental implants.
What is a Titanium Implant?
Titanium is a metal that has been the gold standard in dental and medical implants for over 40 years. Its primary advantage is its exceptional strength, durability, and a well-documented ability to fuse directly to bone in a process called osseointegration.
What is a Ceramic Implant?
Ceramic implants are typically made from zirconium dioxide, often called zirconia. This is a white, crystalline, metal-free material. It was introduced as an alternative for patients with specific needs, such as metal allergies or high aesthetic demands.
Primary Disadvantages of Ceramic Implants
While zirconia technology is constantly improving, it carries inherent risks and limitations you must weigh against its benefits.
Higher Risk of Fracture
Ceramic is fundamentally more brittle than titanium. While very strong under compression (biting down), it is more vulnerable to fracture from bending forces or microscopic surface flaws.
A small crack can propagate over time, potentially leading to a complete fracture of the implant. This risk is higher in patients who grind their teeth (bruxism) or for implants replacing molars, where bite forces are greatest.
Limited Long-Term Clinical Data
Titanium implants have an enormous body of scientific literature and clinical follow-up spanning decades, with success rates often exceeding 95% over 10 years.
Zirconia implants have a much shorter history, with most robust data covering 5- to 10-year windows. While results are promising, we simply have less information on their performance over a 20- or 30-year lifespan.
Reduced Design Flexibility
Most titanium implants use a two-piece design: the implant screw that goes into the bone and a separate connector piece called an abutment. This allows the surgeon and restorative dentist to correct for minor angle discrepancies when placing the final crown.
Many ceramic implants, especially earlier generations, use a one-piece design where the implant and abutment are fused. This is less forgiving; if the implant is not placed at the perfect angle, it can be very difficult to create an ideal final crown. While two-piece zirconia systems now exist, they are a newer technology.
Higher Cost
The manufacturing process for zirconia implants is more complex and expensive than for titanium implants. This higher manufacturing cost is typically passed on to the patient, making ceramic implants a more expensive option upfront.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Choose Ceramic?
Given these disadvantages, ceramic implants are generally reserved for patients whose needs justify the trade-offs. They solve specific problems that titanium cannot.
The Benefit of Aesthetics
For patients with thin gum tissue, especially in the front of the mouth, a dark titanium implant can sometimes show through, creating a faint gray shadow at the gumline. Because zirconia is white, it eliminates this aesthetic concern entirely, providing a more natural-looking result.
Addressing Metal Allergies
While extremely rare, some individuals have a true, diagnosed allergy to titanium or other metals in the alloy. For these patients, a metal-free zirconia implant is not just an option—it is the necessary and correct clinical choice.
Patient Preference for "Metal-Free"
Some patients simply prefer to avoid having any metal placed in their body for personal or holistic health reasons. Zirconia provides a high-quality, scientifically-backed alternative that meets this preference.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision should be made in close consultation with your surgeon, based on your specific anatomy, health, and priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and long-term predictability: Titanium remains the gold standard with decades of proven success and superior strength.
- If you have a confirmed titanium allergy or severe metal sensitivity: A ceramic implant is the most appropriate and necessary choice for your health and safety.
- If your highest priority is aesthetics in the front of your mouth (the "smile zone"): Ceramic is a viable option, provided you understand and accept the potential trade-offs in longevity and cost.
Your choice of implant material is a critical medical decision that will impact you for decades; it requires a detailed evaluation by an experienced implant specialist who can assess your individual risk factors.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Higher Risk of Fracture | More brittle material, susceptible to cracking under chewing forces, especially in molars or patients with bruxism. |
| Limited Long-Term Clinical Data | Less evidence beyond 5-10 years compared to titanium's decades of proven success rates (>95%). |
| Reduced Design Flexibility | One-piece designs are less forgiving for placement angles; two-piece systems are newer and less established. |
| Higher Cost | More complex manufacturing leads to greater upfront expense for patients. |
Choosing the right dental implant material is critical for long-term success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support dental professionals in evaluating materials like ceramic and titanium for implants. Our products help ensure precise testing and reliable outcomes for your patients. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and support your clinical decisions. Reach out via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What function do alumina ceramic plates serve as supports in the preparation of molecular sieve membranes?
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining











