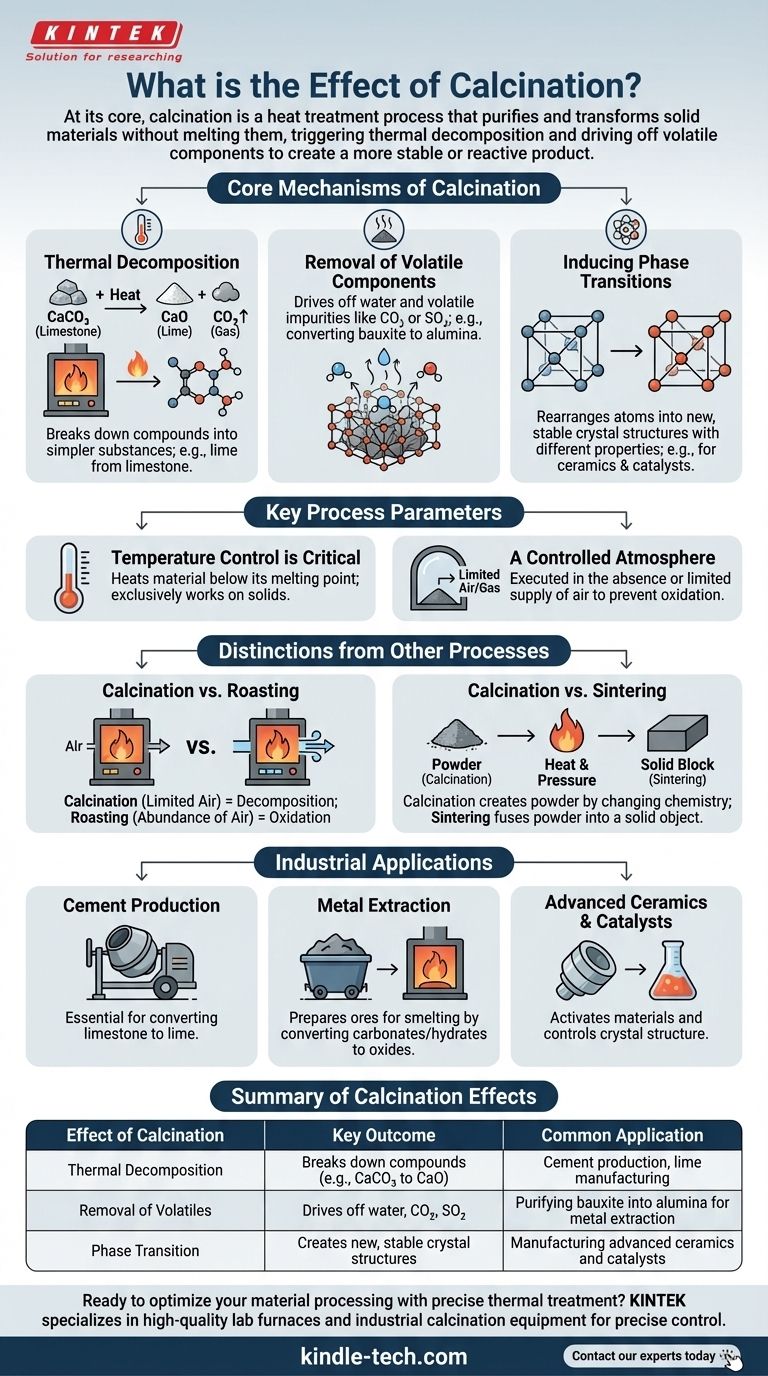
At its core, calcination is a heat treatment process that purifies and transforms solid materials without melting them. By heating a substance to a high temperature in a controlled atmosphere with little to no air, the process triggers thermal decomposition, driving off volatile components like water and carbon dioxide to create a more stable or reactive product.
Calcination is not merely about heating a substance. It is a precise thermal engineering step designed to fundamentally change a material's chemical composition and crystalline structure, preparing it for its next stage of industrial use.
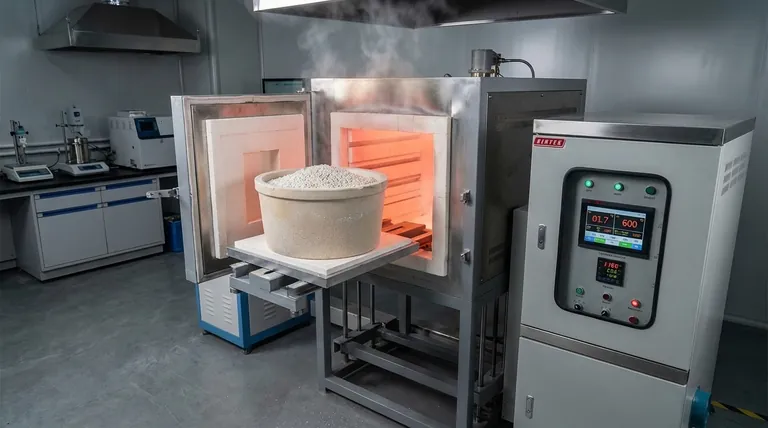

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand the effect of calcination, you must first grasp the key transformations it induces. The process is defined by specific chemical and physical changes that occur under controlled heat.
Thermal Decomposition
The primary effect of calcination is often thermal decomposition. This is a chemical reaction where heat breaks down a compound into simpler substances.
A classic example is the production of lime from limestone. When limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is calcined, it decomposes into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, which is driven off.
Removal of Volatile Components
Calcination is exceptionally effective at removing volatile impurities or components that are chemically or physically bound within a solid.
This includes removing molecular water from hydrated minerals, such as converting bauxite ore (hydrated aluminum oxide) into alumina (Al₂O₃) for aluminum production. It also removes other volatile substances like sulfur dioxide.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can also force a material's atoms to rearrange into a different, often more stable or useful, crystal structure. This is known as a phase transition.
Even if the chemical formula doesn't change, this new crystalline phase can have vastly different physical properties, such as hardness, density, or reactivity, which is critical in the manufacturing of ceramics and catalysts.
Key Process Parameters
The outcome of calcination is not accidental; it is dictated by precise control over two main factors.
Temperature Control is Critical
The process requires heating the material to a temperature high enough to trigger decomposition but below its melting point.
This distinction is crucial. Melting would create a liquid phase, fundamentally changing the process to smelting or fusion. Calcination exclusively works on solids.
A Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is defined by its execution in the absence or a limited supply of air.
This prevents unwanted combustion or oxidation. This separates it from a similar heat process called "roasting," which is intentionally performed in the presence of air to oxidize a material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
It is common to confuse calcination with other thermal processes. Clarifying these differences reveals its unique purpose.
Calcination vs. Roasting
The key difference is the atmosphere. Calcination is a decomposition process that happens in little to no air. Roasting is an oxidation process that happens in an abundance of air, typically used to convert sulfide ores to oxides.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These are two distinct, often sequential, steps. Calcination changes the chemistry of a material to create a powder (like an oxide). Sintering then takes that powder and heats it (again, below melting) to fuse the particles together and create a solid, dense object.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Calcination is a foundational step in many industrial value chains. Its application depends entirely on your starting material and desired end product.
- If your primary focus is producing cement: Calcination is the non-negotiable step for converting limestone into lime, the primary ingredient in cement.
- If your primary focus is extracting metals: Use calcination to convert carbonate or hydrate ores into their more easily processed oxides before smelting.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced ceramics or catalysts: Calcination is used to activate materials, control their final crystal structure, and achieve a high surface area.
Ultimately, calcination is the essential tool for chemically and physically preparing a raw material for its final purpose.
Summary Table:
| Effect of Calcination | Key Outcome | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaks down compounds (e.g., CaCO₃ to CaO) | Cement production, lime manufacturing |
| Removal of Volatiles | Drives off water, CO₂, SO₂ | Purifying bauxite into alumina for metal extraction |
| Phase Transition | Creates new, stable crystal structures | Manufacturing advanced ceramics and catalysts |
Ready to optimize your material processing with precise thermal treatment?
Calcination is a critical first step in countless industrial and laboratory processes. Whether you are developing new ceramics, purifying ores for metal extraction, or producing cement, the right equipment is essential for achieving the desired chemical and physical transformations.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and industrial calcination equipment designed for precise temperature control and atmospheric management. Our solutions help you drive off volatile components, induce phase transitions, and create superior materials reliably and efficiently.
Let KINTEK be your partner in thermal processing. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect calcination solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Application
- What is the temperature accuracy of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab



















