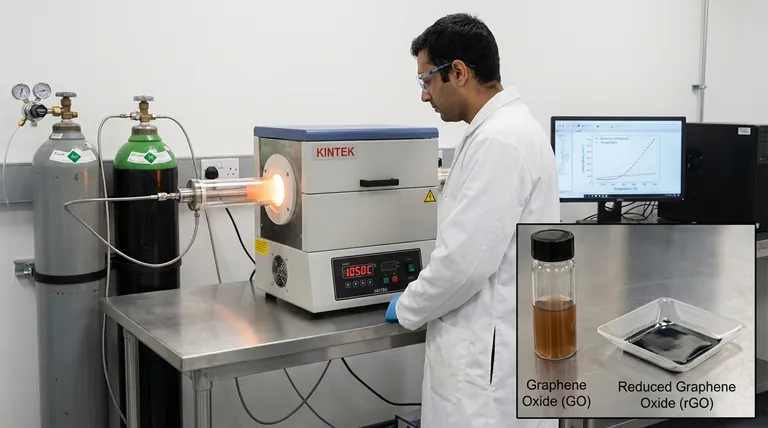
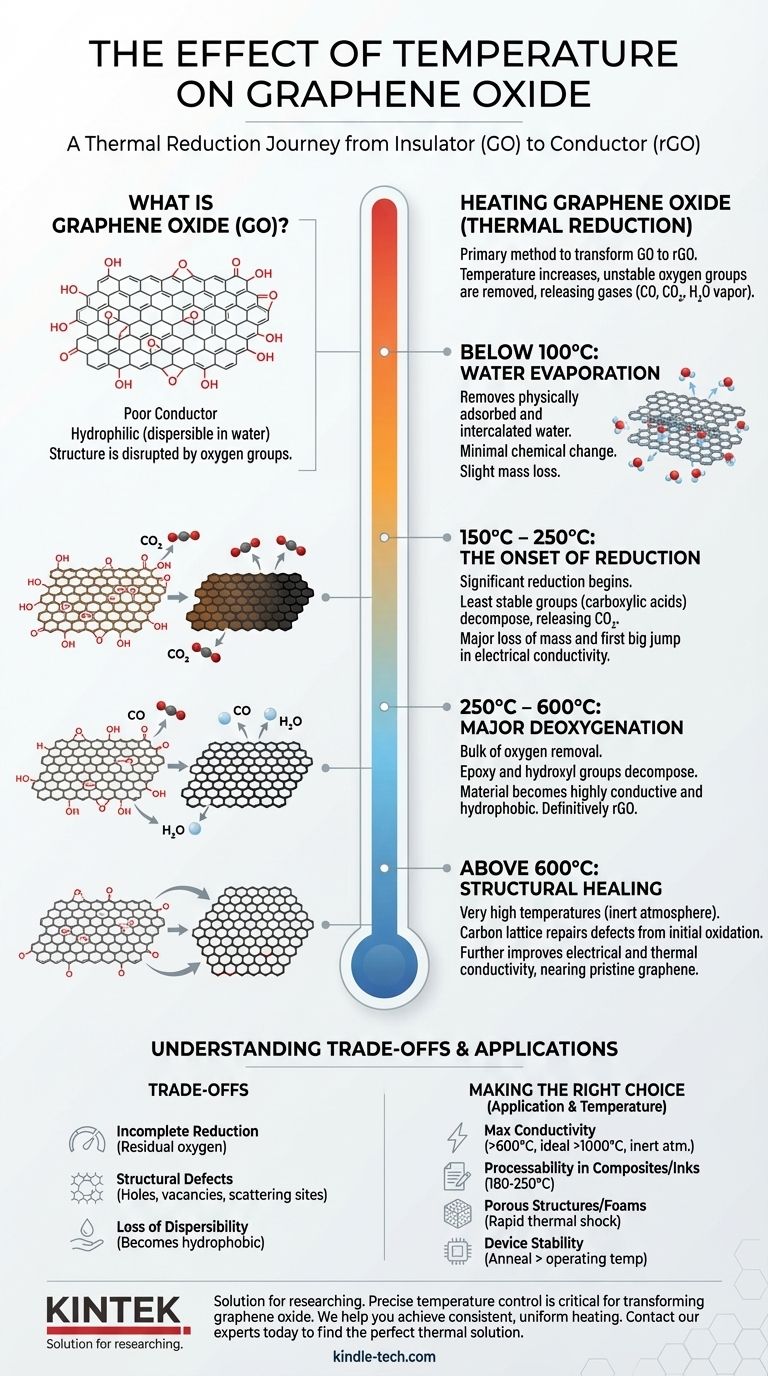
Heating graphene oxide is the primary method used to transform its chemical structure and properties, a process known as thermal reduction. As temperature increases, the oxygen-containing functional groups attached to the graphene sheets become unstable and are systematically removed, releasing gases like CO, CO₂, and water vapor. This converts the material from graphene oxide (GO)—an electrical insulator—into reduced graphene oxide (rGO), a material that more closely resembles pristine graphene and is electrically conductive.
Temperature is not merely a condition for graphene oxide; it is the principal tool for its controlled reduction. By precisely managing heat, you can tune the material's properties, systematically converting it from an insulating, water-dispersible sheet into a conductive, graphene-like structure.

The Mechanism of Thermal Reduction
What is Graphene Oxide (GO)?
Graphene oxide is produced by the harsh oxidation of graphite. This process attaches various oxygen-containing functional groups (like hydroxyl, epoxy, and carboxyl groups) to the carbon lattice.
These groups disrupt the flat, interconnected network of carbon atoms, which is why GO is a poor electrical conductor. However, they also make GO hydrophilic, allowing it to be easily dispersed in water to form stable, single-sheet suspensions.
The Role of Oxygen Functional Groups
The oxygen groups on the GO sheet are the key to its thermal transformation. They are significantly less stable than the carbon-carbon bonds that form the graphene lattice.
When heated, these groups decompose and detach from the carbon sheet, taking the oxygen atoms with them. This process is irreversible and fundamentally changes the material.
From GO to Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
The goal of heating GO is to remove the oxygen and restore the conductive network of sp²-hybridized carbon atoms. The resulting material is called reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
As oxygen is removed, the C/O (carbon-to-oxygen) ratio of the material increases, and its electrical conductivity can improve by several orders of magnitude. The structure becomes more ordered and graphene-like.
Key Temperature Stages and Their Impact
The transformation of GO to rGO does not happen all at once. It occurs in distinct stages as the temperature rises, with different functional groups breaking down at different points.
Below 100°C: Water Evaporation
At low temperatures, the primary effect is the removal of physically adsorbed and intercalated water molecules from between the GO sheets. This causes a slight mass loss but does not chemically alter the GO structure itself.
150°C – 250°C: The Onset of Reduction
This is the most critical temperature range where significant reduction begins. The least stable functional groups, primarily carboxylic acids, start to decompose, releasing CO₂.
This stage is marked by a significant loss of mass and the first major jump in electrical conductivity. The material also begins to change color, turning from brown to black.
250°C – 600°C: Major Deoxygenation
In this range, the more stable epoxy and hydroxyl groups decompose, releasing CO and H₂O. This is where the bulk of the oxygen is removed from the material.
The structure becomes far more conductive and hydrophobic as the oxygen content plummets. The material is now definitively rGO.
Above 600°C: Structural Healing
At very high temperatures (typically performed in an inert atmosphere like argon or nitrogen to prevent burning), the carbon lattice itself can begin to repair.
This "healing" process removes structural defects created during the initial oxidation, further improving electrical and thermal conductivity. The higher the temperature, the closer the rGO gets to the properties of pristine graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal Reduction
While thermal reduction is effective, it is not a perfect process and comes with important trade-offs.
Incomplete Reduction
Even at very high temperatures, it is nearly impossible to remove all oxygen functional groups. The final rGO will always contain some residual oxygen and defects, meaning its conductivity will not match that of flawless, pristine graphene.
Creation of Structural Defects
The rapid, sometimes explosive, departure of oxygen groups can create new holes, vacancies, and other defects in the carbon lattice. These defects act as scattering sites for electrons, limiting the material's ultimate electrical performance. There is a trade-off between removing insulating oxygen and introducing new structural flaws.
Loss of Dispersibility
One of GO's most useful properties is its ability to be processed in water. As it is reduced, it loses its hydrophilic functional groups and becomes hydrophobic. This makes the resulting rGO very difficult to disperse in water, complicating its use in inks, composites, and coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
How you use temperature depends entirely on your end goal. You must balance the desired properties with the practical trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is maximum electrical conductivity: You must use high reduction temperatures (over 600°C, and ideally >1000°C) in an inert atmosphere to remove the maximum amount of oxygen and heal structural defects.
- If your primary focus is processability in composites or inks: A milder thermal treatment (e.g., 180-250°C) is often best. This provides a significant boost in conductivity while retaining enough functionality to aid dispersion in certain solvents.
- If your primary focus is creating porous structures or foams: A rapid, high-temperature "thermal shock" can cause a fast expansion and exfoliation as gases evolve, creating a highly porous, low-density rGO aerogel.
- If your primary focus is device stability: You must anneal the GO or rGO component at a temperature higher than its intended operating temperature. This ensures its properties will not change due to unintended thermal reduction during use.
By understanding these temperature-dependent transformations, you can precisely engineer graphene oxide to achieve your specific material and device goals.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Process | Main Effects |
|---|---|---|
| < 100°C | Water Evaporation | Removes adsorbed water; minimal chemical change. |
| 150°C – 250°C | Onset of Reduction | CO₂ release; first major conductivity increase. |
| 250°C – 600°C | Major Deoxygenation | CO/H₂O release; bulk oxygen removal; high conductivity. |
| > 600°C | Structural Healing | Defect repair; conductivity approaches pristine graphene. |
Ready to Optimize Your Graphene Oxide Thermal Reduction Process?
Precise temperature control is critical for transforming graphene oxide into the high-performance material you need. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including precision furnaces and thermal processing systems, designed to meet the exacting demands of graphene research and production.
We help you:
- Achieve consistent, uniform heating for reliable GO-to-rGO conversion.
- Select the right equipment for your specific application, whether for maximum conductivity or processability.
- Ensure stability and reproducibility in your thermal reduction experiments.
Don't let temperature variability compromise your results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential



















