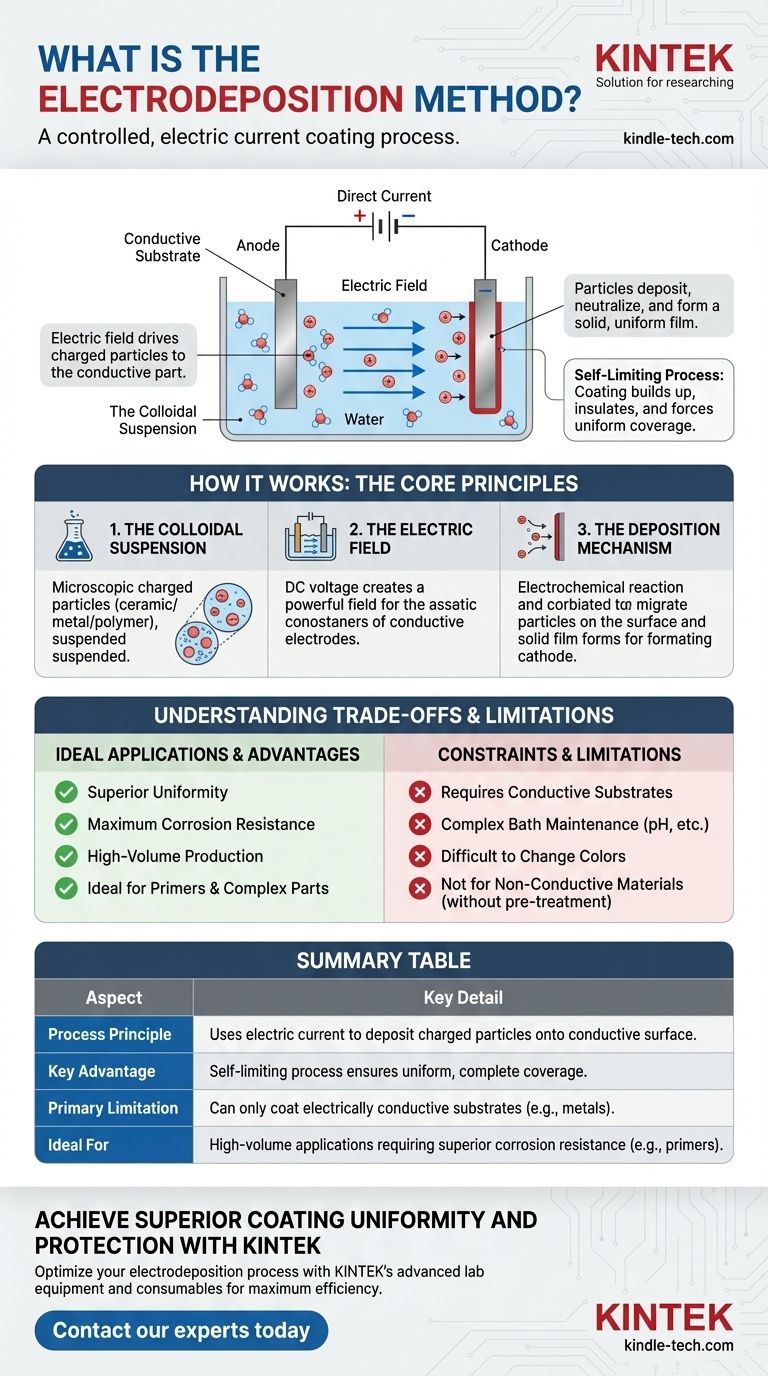
At its core, electrodeposition is a coating process that uses an electric current to deposit a material from a liquid solution onto a conductive surface. Unlike methods that spray or physically transfer a coating, this technique functions like a controlled, reverse-plating process, "pulling" charged paint or material particles out of a liquid bath and onto the target object with an electric field.
The central principle of electrodeposition is using electrical attraction to achieve a superior result. By submerging a conductive part in a specialized liquid bath and applying a direct current, charged coating particles migrate and adhere to the part, creating an exceptionally uniform and complete film.
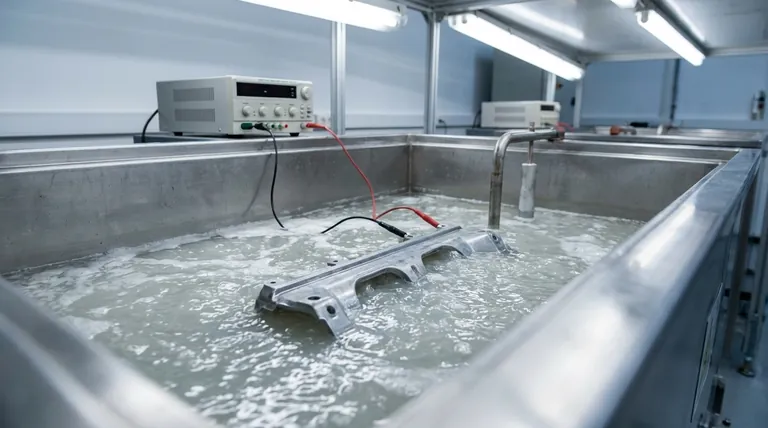

How Electrodeposition Works: The Core Principles
To understand why this method is so effective, particularly in industrial applications, we need to look at the three key components of the process: the suspension, the electric field, and the deposition mechanism itself.
The Colloidal Suspension (The "Paint")
The process begins not with traditional liquid paint but with a colloidal suspension. The coating material—be it a polymer resin for a primer, a ceramic, or a metal—is ground into microscopic particles.
These particles are then suspended in a liquid, typically water, and are given a stable electrical charge using specialized chemistry. This charged, liquid mixture forms the deposition bath.
The Electric Field (The "Brush")
The part to be coated must be electrically conductive. It is submerged into the bath and acts as one electrode in an electrical circuit (e.g., the cathode, or negative electrode). Another electrode (the anode) is also placed in the bath.
When a direct current (DC) voltage is applied, a powerful electric field is established throughout the liquid. This field is the driving force of the entire process.
The Deposition Mechanism
Because the coating particles in the bath are charged, they immediately begin to migrate through the liquid under the influence of the electric field. They are drawn toward the oppositely charged electrode—the part being coated.
Upon reaching the surface of the part, the particles undergo an electrochemical reaction that neutralizes their charge. This causes them to become insoluble in the bath, depositing onto the surface as a solid, uniform film.
A critical feature of this process is that it is self-limiting. As the coating builds up, it acts as an insulator, which reduces the electric field strength at that spot. The current then naturally seeks out the uncoated, bare areas of the part, forcing the coating to build there until the entire surface is covered uniformly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, electrodeposition is a specialized process with distinct constraints that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Requires Conductive Substrates
The most significant limitation is that the part itself must be a component in an electrical circuit. This means electrodeposition can only be used on conductive materials, such as metals. Non-conductive substrates like wood, plastic, or glass cannot be coated without first applying a conductive layer.
Bath Complexity and Maintenance
The chemical composition of the electrodeposition bath is complex and must be strictly monitored and maintained. Factors like pH, conductivity, particle concentration, and solvent levels must remain within tight tolerances to ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Difficulty in Changing Colors
Because the process relies on a large tank or bath of the coating suspension, changing colors is a major operational undertaking. It requires draining, cleaning, and refilling the entire system. Consequently, electrodeposition is most efficient for high-volume production of a single color, which is why it is predominantly used for primers (like black or gray) rather than for topcoats.
Is Electrodeposition the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing a coating method depends entirely on the material, the complexity of the part, and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion resistance and uniform coverage on complex metal parts: Electrodeposition is the industry standard and likely the best choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is coating non-conductive materials like wood or plastic: This method is fundamentally incompatible unless you can apply a conductive pre-treatment.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production requiring frequent color changes: The operational overhead of managing the bath makes electrodeposition highly inefficient for this goal.
Ultimately, electrodeposition is an advanced manufacturing tool designed for achieving superior uniformity and protection where other methods fail.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Principle | Uses electric current to deposit charged particles from a liquid bath onto a conductive surface. |
| Key Advantage | Self-limiting process ensures uniform, complete coverage, even on complex geometries. |
| Primary Limitation | Can only coat electrically conductive substrates (e.g., metals). |
| Ideal For | High-volume applications requiring superior corrosion resistance, like primers. |
Achieve Superior Coating Uniformity and Protection with KINTEK
Does your laboratory or production line require exceptionally uniform and durable coatings for metal components? The electrodeposition process is a benchmark for quality and reliability in industrial coating.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to implement and optimize coating processes like electrodeposition. Our expertise helps ensure your operations achieve maximum efficiency and product performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can meet your specific coating challenges and enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently



















