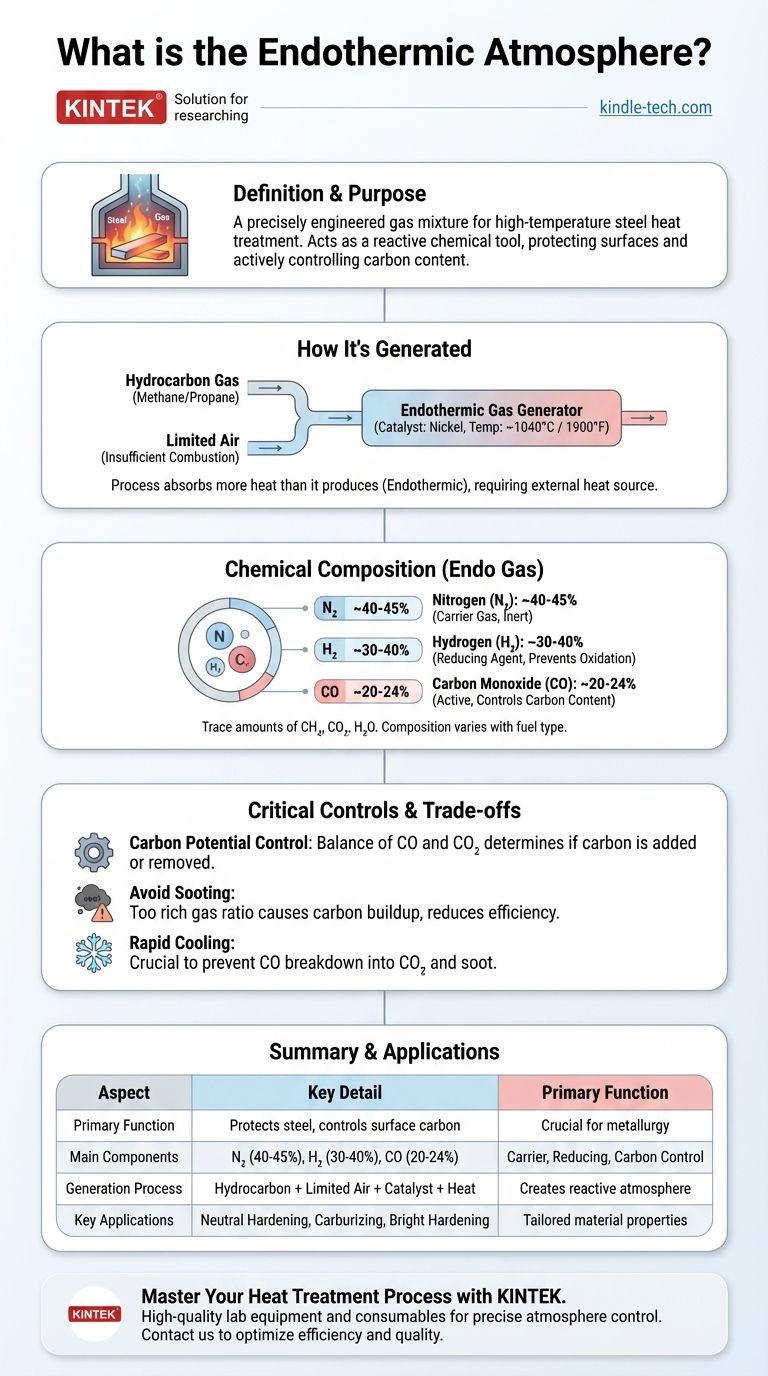
In the world of metallurgy, an endothermic atmosphere is a precisely engineered gas mixture used to protect and control steel surfaces during high-temperature heat treatment. It is produced by reacting a hydrocarbon gas (like methane or propane) with a limited amount of air over a catalyst at high temperatures. The resulting gas is rich in carbon monoxide and hydrogen, making it chemically reactive and ideal for controlling the carbon content of steel.
An endothermic atmosphere is not just a protective blanket; it is a reactive chemical tool. Its primary purpose is to actively manage the carbon on a steel's surface, preventing oxidation and ensuring the final component has the exact properties required.

How an Endothermic Atmosphere is Generated
The creation of an endothermic atmosphere, often called "endo gas," is a controlled industrial process that takes place inside a specialized piece of equipment.
The Core Ingredients: Hydrocarbon Gas and Air
The process begins by mixing a hydrocarbon gas with air. The key is that the amount of air used is intentionally insufficient for complete combustion—typically less than half of what would be needed to burn the fuel completely.
This precise ratio is critical. For example, using methane (CH4) requires an air-to-gas ratio of about 2.77 to 1, while propane (C3H8) needs a ratio closer to 7.16 to 1.
The Reaction Chamber: Generator and Catalyst
This gas-air mixture is compressed and fed into an endothermic gas generator. Inside, it passes through a heated chamber containing a nickel-based catalyst at a temperature of approximately 1900°F (1040°C).
The high heat and the catalyst facilitate a chemical reaction that breaks down the initial hydrocarbon and air mixture.
The Chemical Transformation: Why It's "Endothermic"
The term endothermic means the reaction absorbs more heat than it produces. The incomplete combustion does not generate enough energy on its own to sustain the process.
Therefore, the generator must continuously supply external heat to keep the reaction going, which is the defining characteristic for which the atmosphere is named.
The Chemical Composition of "Endo" Gas
After the reaction, the gas is rapidly cooled. This cooling step is crucial to "freeze" the chemical composition and prevent the desirable components from breaking down into soot and carbon dioxide.
The Primary Components: CO, H₂, and N₂
A typical endothermic atmosphere consists of three main gases:
- Nitrogen (N₂): ~40-45%. Mostly inert, it acts as a carrier gas.
- Hydrogen (H₂): ~30-40%. A strong reducing agent that prevents oxidation (scale) on the steel surface.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): ~20-24%. This is the most active component, responsible for controlling the carbon content of the steel.
The gas also contains trace amounts of unreacted methane (CH₄), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and water vapor (H₂O).
Adjusting the Recipe for Different Fuels
The exact composition varies based on the hydrocarbon fuel used. An atmosphere generated from propane will have a slightly higher concentration of carbon monoxide and nitrogen compared to one generated from methane. This flexibility allows operators to tailor the gas for specific applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Controls
While powerful, an endothermic atmosphere requires careful management to be effective and safe. Its reactive nature is both its greatest strength and a potential source of problems.
The Danger of Sooting
If the hydrocarbon-to-air ratio is too rich (not enough air), the generator can become clogged with carbon soot. This reduces efficiency, requires costly clean-outs, and can introduce soot particles onto the parts being treated.
Controlling the "Carbon Potential"
The most important parameter to control is the carbon potential. This is the ability of the atmosphere to either add, remove, or maintain the carbon concentration in the steel. It is determined by the balance of CO and CO₂ in the gas.
By carefully monitoring and adjusting the gas composition, a heat treater can precisely match the atmosphere's carbon potential to the steel being processed.
The Importance of Rapid Cooling
As mentioned, the gas must be cooled quickly after generation. If it cools too slowly, the primary reaction can reverse itself: the carbon monoxide will break down into carbon dioxide and solid carbon (soot). This depletes the atmosphere of its most useful component and creates a maintenance nightmare.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the function of an endothermic atmosphere allows you to apply it correctly for different metallurgical outcomes.
- If your primary focus is neutral hardening: The atmosphere's carbon potential must be controlled to perfectly match the carbon content of the steel to prevent both carburization and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is carburizing: The atmosphere must be run with a higher carbon potential than the steel, allowing carbon monoxide to transfer carbon atoms into the part's surface.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Your top priority is maintaining the correct gas/air ratio and generator temperature to ensure consistent gas quality and prevent sooting.
Ultimately, mastering the endothermic atmosphere is to master the precise chemical environment that defines modern, high-quality heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Protects steel and actively controls surface carbon content. |
| Main Components | 40-45% Nitrogen (N₂), 30-40% Hydrogen (H₂), 20-24% Carbon Monoxide (CO). |
| Generation Process | Reaction of hydrocarbon gas (e.g., methane, propane) with limited air over a catalyst at ~1040°C (1900°F). |
| Key Applications | Neutral Hardening, Carburizing, Bright Hardening. |
| Critical Control | Carbon potential (balance of CO/CO₂) to prevent decarburization or sooting. |
Master Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Achieving precise metallurgical outcomes requires reliable control over your furnace atmosphere. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for industrial heat treatment. Our solutions help you maintain the exact carbon potential and gas composition needed for perfect results in carburizing, neutral hardening, and more.
Let our experts help you optimize your process efficiency and product quality. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is an atmosphere furnace used to evaluate CO2 tolerance? Testing Bi-doped Oxygen Transport Membranes
- What role does an atmosphere-controlled furnace play in PIP? Achieve High-Strength Ceramic Pyrolysis
- Why is an atmosphere sintering furnace used for post-annealing ZnO ceramics? Optimize Conductivity & Density
- How do controlled atmosphere rooms work? Preserve Freshness with Advanced Gas Control
- What is a reducing atmosphere in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Clean Metal Surfaces
- What roles does an atmosphere tube furnace play in FeAl/Al2O3/TiO2 coating? Expert Guide to Advanced Layer Synthesis
- How does high-purity flowing Argon provide protection during Cr-Al-C annealing? Ensure Superior MAX Phase Integrity
- What is the inert atmosphere for welding? Protect Your Weld Pool from Contamination



















