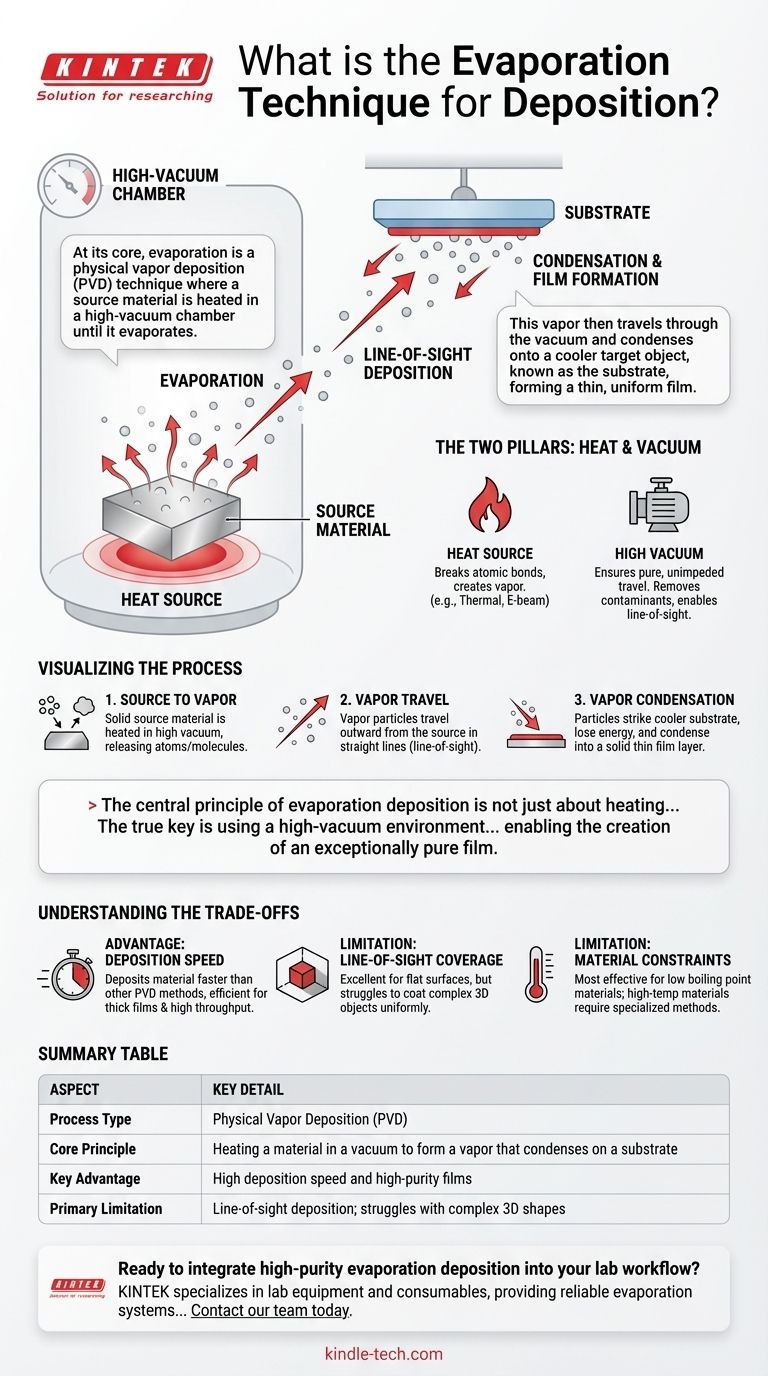
At its core, evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique where a source material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target object, known as the substrate, forming a thin, uniform film. It is one of the most fundamental methods for creating high-purity coatings.
The central principle of evaporation deposition is not just about heating a material until it becomes a gas. The true key is using a high-vacuum environment to ensure those gas particles travel unimpeded and uncontaminated from the source to the substrate, enabling the creation of an exceptionally pure film.

The Two Pillars of Evaporation: Heat and Vacuum
The entire process is governed by two critical environmental factors: the energy source that causes evaporation and the vacuum that enables pure deposition.
The Role of the Heat Source
The primary function of the heat source is to supply enough thermal energy to the source material to break its atomic bonds and transition it into a gaseous state. The method of heating defines the specific type of evaporation technique.
Common methods include vacuum thermal evaporation, which uses electrical resistance to heat the material, and electron beam evaporation, which uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons.
The Critical Function of the Vacuum
The vacuum is not merely an empty space; it is an active component of the process. A high-vacuum environment is essential for two reasons.
First, it removes atmospheric and other unwanted gas molecules. This prevents the source material vapor from reacting with contaminants like oxygen or nitrogen, which would compromise the purity of the final film.
Second, the near-absence of other particles allows the evaporated material to travel in a straight, uninterrupted path to the substrate. This is known as line-of-sight deposition.
Visualizing the Deposition Process
To understand the process intuitively, you can compare it to the condensation that forms on the lid of a boiling pot of water.
The Journey from Source to Substrate
A solid source material, often in the form of pellets or a small ingot, is placed inside the vacuum chamber. Once the chamber is pumped down to a high vacuum, the heat source is activated.
As the material heats up, it begins to evaporate, releasing atoms or molecules into the chamber. These vapor particles travel outward from the source in straight lines.
When these particles strike the cooler substrate, they lose their energy and condense back into a solid state, gradually building up a thin film layer by layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, evaporation has distinct advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Advantage: Deposition Speed
Generally, thermal evaporation can deposit material at a much faster rate than other PVD methods like sputtering. This makes it highly efficient for creating thicker films or for high-throughput manufacturing processes, such as producing metallized plastic films for packaging.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Coverage
The straight-line path of the vapor particles means that evaporation is excellent for coating flat, simple surfaces. However, it struggles to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional objects with sharp edges or deep trenches, as some surfaces will be in the "shadow" of the source.
Limitation: Material Constraints
Evaporation is most effective for materials with a relatively low boiling point. Materials that require extremely high temperatures to evaporate can be difficult or impossible to process with standard thermal evaporation techniques, often requiring more specialized methods like electron beam evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right deposition technique requires aligning the method's characteristics with your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-speed coating of simple surfaces: Thermal evaporation is often the most cost-effective and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity for sensitive electronics: A highly controlled variant like Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating complex, 3D geometries: You may need to consider an alternative PVD process like sputtering, which is less directional.
Understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to select the precise tool required to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to form a vapor that condenses on a substrate |
| Key Advantage | High deposition speed and high-purity films |
| Primary Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition; struggles with complex 3D shapes |
Ready to integrate high-purity evaporation deposition into your lab workflow? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable evaporation systems for applications in electronics, optics, and materials science. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to achieve superior thin film coatings with high efficiency and purity. Contact our team today to discuss your specific deposition needs and enhance your research or production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems



















