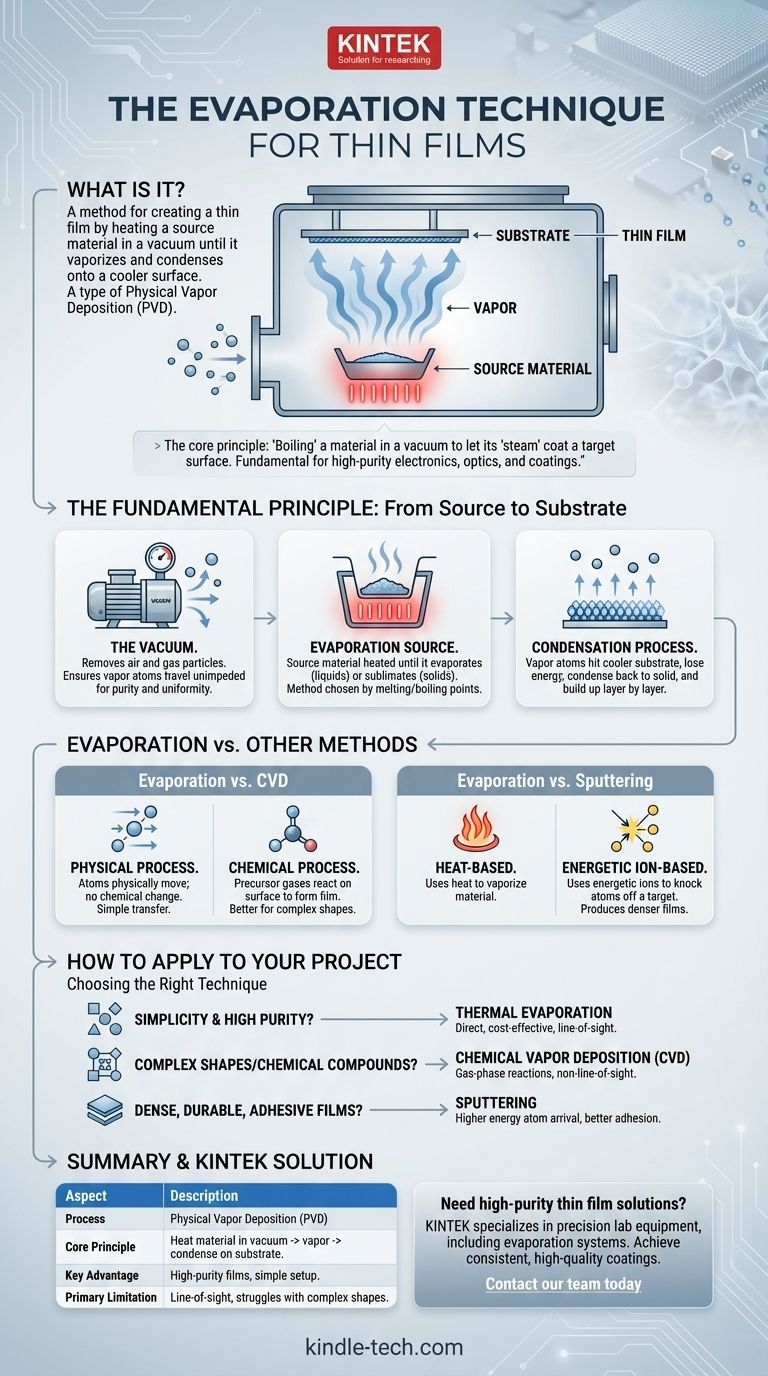
In short, the evaporation technique is a method for creating a thin film by heating a source material inside a vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, ultra-thin layer. It is a sub-category of a broader process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The core principle of evaporation is simple: you are essentially "boiling" a material in a vacuum and letting its "steam" (vapor) coat a target surface. This physical transfer process is one of the most fundamental ways to create high-purity thin films for electronics, optics, and coatings.

The Fundamental Principle: From Source to Substrate
Thermal evaporation is a direct, line-of-sight process that relies on a few critical components working together to physically transport material from a source to a target.
The Role of the Vacuum
Creating a high vacuum is the first and most critical step. A vacuum removes air and other gas particles that would otherwise collide with the evaporated material atoms.
This ensures the vaporized atoms travel unimpeded from the source directly to the substrate, resulting in a purer and more uniform film.
The Evaporation Source
The source material—the substance you want to form the film from—is heated until it evaporates (for liquids) or sublimates (for solids).
This was historically done by placing the material in tungsten wire baskets, as reported by Cartwright and Strong in 1931. The method of heating is chosen based on the material's melting and boiling points.
The Condensation Process
Once the atoms leave the source as a vapor, they travel through the vacuum until they hit the cooler substrate.
Upon contact, the atoms lose their energy, condense back into a solid state, and gradually build up on the surface layer by layer, forming the thin film.
How Evaporation Differs from Other Methods
While evaporation is a cornerstone of thin film creation, it's important to distinguish it from other major deposition techniques. The primary difference lies in how the material is transferred to the substrate.
Evaporation vs. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Evaporation is a physical process. Atoms are physically moved from the source to the substrate without changing their chemical nature.
CVD, in contrast, is a chemical process. It uses precursor gases that undergo chemical reactions on the substrate's surface, and the thin film is a solid product of that reaction.
Evaporation vs. Sputtering
Sputtering is another PVD technique, but it doesn't rely on heat. Instead, it uses energetic ions to physically knock atoms off of a target material, like a microscopic game of billiards.
These "sputtered" atoms are then ejected and deposit onto the substrate. Sputtering often produces denser films than evaporation.
Common Pitfalls and Historical Context
The simplicity of evaporation is one of its greatest strengths, but it also comes with inherent limitations that have been recognized for decades.
A Foundational Discovery
The use of evaporation dates back to 1887, when Nahrwold successfully created platinum thin films by subliming the material in a vacuum. This established the basic principle of using a vacuum for material transport.
The Challenge of Source-Material Interaction
A significant limitation is the potential for the hot source material to react with its container.
In 1931, early researchers failed to evaporate aluminum because it formed an alloy with the tungsten filament used to heat it, causing the filament to burn out. This highlights the critical need for material compatibility in the evaporation process.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a deposition technique depends entirely on the film properties you need and the complexity of your application.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and high-purity films of simple materials: Thermal evaporation is often the most direct and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is coating complex shapes or creating highly specific chemical compounds: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is superior due to its reliance on gas-phase reactions rather than line-of-sight deposition.
- If your primary focus is creating very dense, durable, or adhesive films: Sputtering is generally the better choice, as the atoms arrive at the substrate with much higher energy.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation remains a foundational and widely used technique for its straightforward ability to physically transfer material in a controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on a substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Creates high-purity films with simple material setups. |
| Primary Limitation | Line-of-sight process; can struggle with complex shapes. |
Need to deposit a high-purity thin film for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including evaporation systems, to help you achieve consistent, high-quality coatings. Our experts can help you select the right PVD solution for your specific materials and application. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a covered ceramic boat as a carrier during the high-temperature sulfidation of tungsten oxide?
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is an evaporation machine? Precision Thin Film Deposition for High-Tech Applications
- What are three applications of evaporation in different industries? From OLEDs to Automotive Parts
- Can metals be deposited by evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between thermal evaporator and e-beam evaporator? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Films
- How thick is the film in e-beam evaporation? Achieve Precise Control from Nanometers to Micrometers
- What is vacuum deposition or vacuum thermal evaporation VTE? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating



















