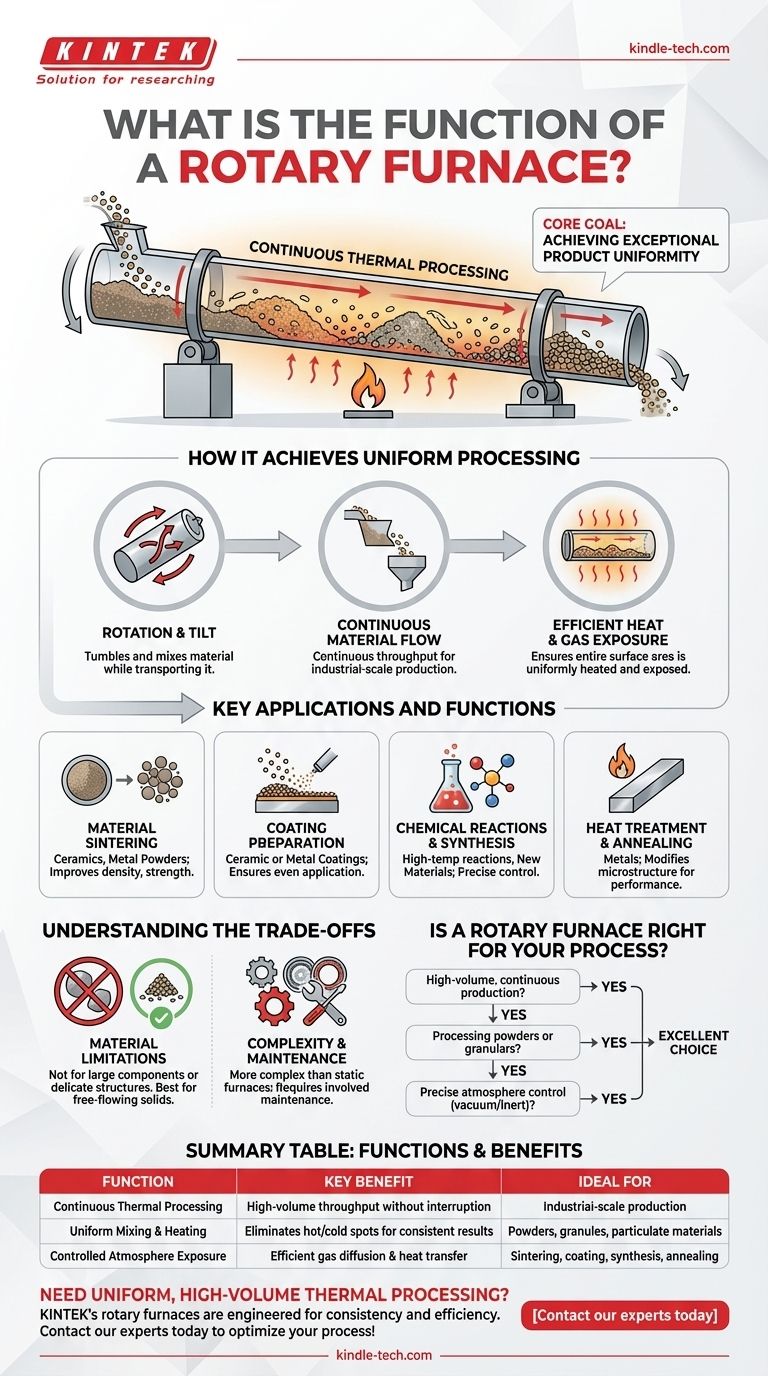
At its core, a rotary furnace is a highly efficient tool for the continuous thermal processing of materials. It uses a combination of slow rotation, a slight incline, and controlled heating to ensure that every particle of a substance is uniformly heated, mixed, and exposed to a specific atmosphere as it moves from one end of a cylindrical tube to the other.
A rotary furnace excels at one primary goal: achieving exceptional product uniformity in high-temperature processes. By constantly tumbling and mixing materials, it eliminates the hot and cold spots common in static furnaces, ensuring a more consistent and efficient outcome.

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Uniform Processing
To understand its function, it's essential to break down its core operational principles. The design is engineered for consistency and continuous operation.
The Core Mechanism: Rotation and Tilt
A rotary furnace consists of a long, cylindrical tube that rotates slowly around its central axis.
This tube is also tilted at a slight angle. This combination of rotation and incline gently tumbles the material, mixing it thoroughly while simultaneously transporting it from the feed-in end to the discharge end.
Continuous Material Flow
Unlike a batch furnace where materials are loaded and unloaded in static cycles, a rotary furnace is designed for continuous throughput.
Raw material is fed into the higher end of the tube and, through the furnace's motion, travels its length to be discharged as a finished product at the lower end. This makes it ideal for industrial-scale production.
Efficient Heat and Gas Exposure
The constant tumbling is the furnace's key advantage. It ensures the entire surface area of the material is consistently exposed to the heat source and the internal atmosphere.
This action dramatically improves heat transfer and gas diffusion, leading to faster processing times, lower gas consumption, and higher overall efficiency compared to static heat treatment methods.
Key Applications and Functions
The unique capabilities of a rotary furnace make it indispensable for a range of specific industrial and laboratory processes.
Material Sintering
It is frequently used for sintering materials like ceramics and metal powders. The uniform heating helps improve the density, strength, and corrosion resistance of the final product.
Coating Preparation
The furnace can be used to apply ceramic or metal coatings onto substrates. The consistent exposure ensures the coating is applied evenly, enhancing wear resistance and other surface properties.
Chemical Reactions and Synthesis
Rotary furnaces provide a controlled environment for high-temperature chemical reactions, making them ideal for synthesizing new materials or preparing catalysts where temperature uniformity is critical.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
For metals, the furnace is used for heat treatment processes like annealing. This modifies the material's microstructure to improve its performance, ductility, and strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Their primary strength lies in processing granular or powdered materials.
Material Limitations
They are generally not suitable for large, single-part components or materials that could be damaged by the tumbling action. The process is designed for free-flowing solids, not large, delicate structures.
Complexity and Maintenance
The mechanical system involving rotation, seals, and drive mechanisms is more complex than a static box furnace. This can lead to higher initial costs and more involved maintenance requirements to ensure reliable, continuous operation.
Is a Rotary Furnace Right for Your Process?
Choosing the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A rotary furnace is an excellent choice for its ability to process material without interruption, ensuring high throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granulars: The constant mixing action provides a level of temperature and atmospheric uniformity that is very difficult to achieve in a static furnace.
- If your primary focus is reactions requiring precise atmosphere control: The sealed tube design is ideal for processes that require a vacuum or a specific reducing or inert gas atmosphere.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace is the definitive tool when uniform, efficient, and continuous thermal processing of particulate materials is the goal.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Thermal Processing | High-volume throughput without interruption | Industrial-scale production |
| Uniform Mixing & Heating | Eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent results | Powders, granules, and particulate materials |
| Controlled Atmosphere Exposure | Efficient gas diffusion and heat transfer | Sintering, coating, synthesis, and annealing |
Need uniform, high-volume thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK's rotary furnaces are engineered for exceptional consistency and efficiency in sintering, coating preparation, and heat treatment. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution perfectly tailored to your production goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary furnace can optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of calcination? Choosing the Right Method for Your Material
- What is the main function of calcination? Purify, Transform, and Prepare Materials with Heat
- What are the byproducts of biomass gasification? Unlocking Syngas, Biochar, and More
- What are the advantages of co-pyrolysis? Unlock Superior Bio-Oil & Synergistic Waste Conversion
- What are the different temperatures of pyrolysis? A Guide to Optimizing Biochar, Bio-Oil, and Syngas Production
- Is pyrolysis process safe? A Guide to Engineering Safety in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the pyrolysis method for plastic waste? Convert Non-Recyclable Plastics into Fuel
- What is carbon pyrolysis? Unlock Energy and Products from Waste Materials



















