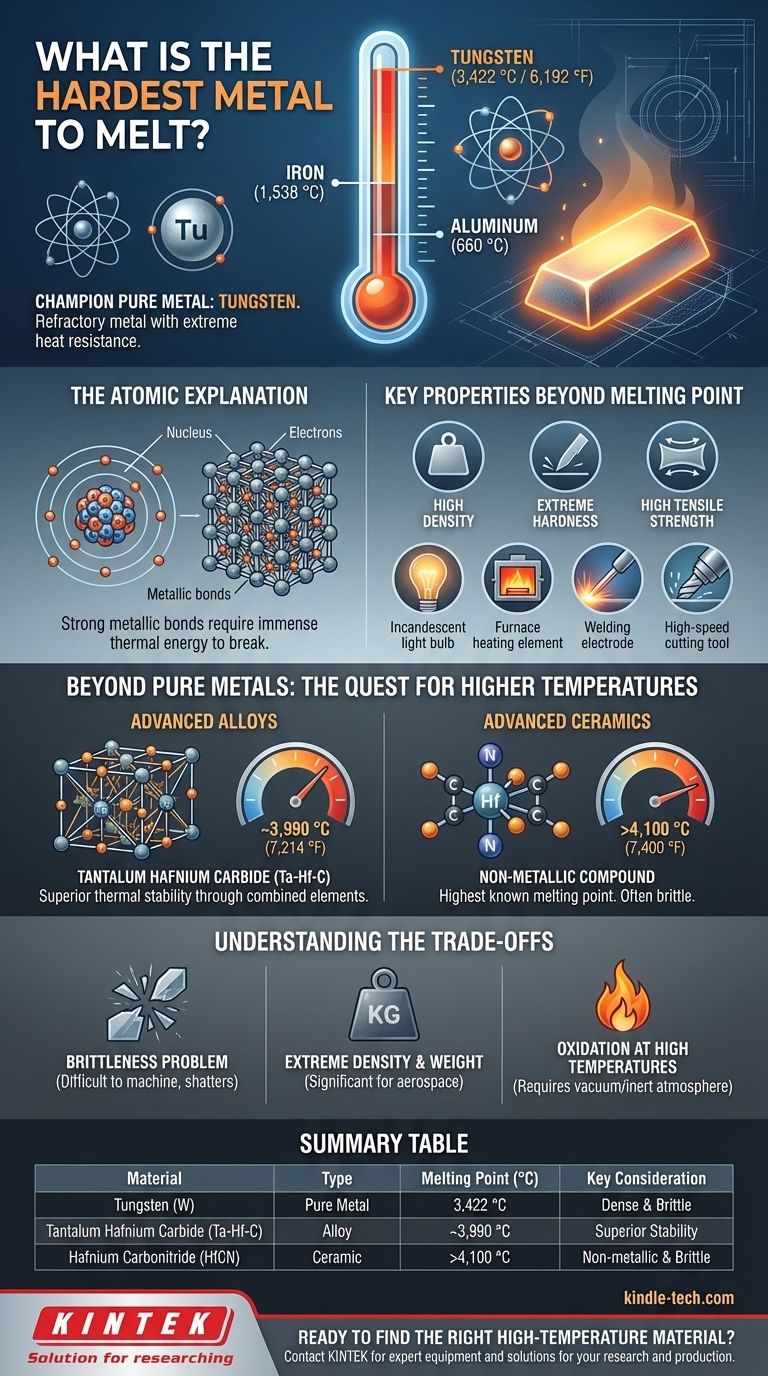
By the numbers, the hardest pure metal to melt is tungsten. With a melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F), it stands far above other elemental metals like iron or aluminum. This incredible resistance to heat is why it belongs to a special class of materials known as refractory metals.
The question of the "hardest metal to melt" moves beyond a simple trivia answer. While tungsten is the champion among pure elements, the true frontier of high-temperature materials lies in engineered alloys and ceramic compounds that can withstand even more extreme conditions.
What Makes Tungsten the Champion?
The properties that make tungsten so difficult to melt are rooted in its atomic structure. Understanding this is key to understanding high-performance materials in general.
The Atomic Explanation
Tungsten has an extremely high number of protons in its nucleus, which creates a powerful positive charge. This charge pulls its electrons into very strong metallic bonds, which act like a tightly woven, three-dimensional lattice. To melt the metal, you must supply enough thermal energy to break these bonds and allow the atoms to move freely, and for tungsten, that energy requirement is immense.
Key Properties Beyond Melting Point
A high melting point rarely exists in isolation. Tungsten is also known for its:
- High Density: It is one of the densest metals, nearly twice as dense as lead.
- Extreme Hardness: It is exceptionally hard and resistant to scratching and wear.
- High Tensile Strength: It resists being pulled apart, especially at high temperatures.
Common Applications
Because of this unique combination of properties, tungsten is critical for demanding industrial applications. You find it in incandescent light bulb filaments, heating elements in high-temperature furnaces, welding electrodes, and high-speed cutting tools.
Beyond Pure Metals: The Search for Even Higher Temperatures
While tungsten holds the record for a pure metal, the quest for materials that can operate in jet engines, rocket nozzles, and fusion reactors has pushed scientists to create even more resilient substances.
Advanced Alloys: Tantalum Hafnium Carbide
By combining different elements, metallurgists can create alloys with properties superior to their individual components. Tantalum hafnium carbide (Ta-Hf-C) is a metallic alloy that was long considered the material with the highest known melting point, at approximately 3,990 °C (7,214 °F).
This demonstrates a critical principle: a combination of elements can create a molecular structure with even stronger bonds and greater thermal stability than any single element can achieve on its own.
The True Record Holders: Advanced Ceramics
If we expand our definition from "metal" to "material," the current record holders are non-metallic compounds. Computer simulations and subsequent experiments have shown that materials like hafnium carbonitride (HfCN) have the highest known melting point of any substance, potentially exceeding 4,100 °C (7,400 °F).
These are not metals, but ceramics. They are valued for their thermal stability but are often extremely brittle, which limits their structural applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material for a high-temperature application is never just about finding the highest melting point. There are always critical trade-offs to consider.
The Brittleness Problem
Many materials with high melting points, including tungsten, are very brittle at room temperature. This makes them difficult and expensive to machine or form into complex shapes. They can shatter under impact rather than bending.
Extreme Density and Weight
The high density of tungsten and its alloys is a significant drawback in applications where weight is a primary concern, such as in the aerospace industry. A component made of tungsten is substantially heavier than an identical one made of steel or titanium.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
Most refractory metals perform poorly in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. Tungsten, for example, will rapidly oxidize (essentially, burn away) in open air at high heat. Therefore, it must be used in a vacuum or a protective, inert atmosphere, adding significant complexity and cost to its application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of material depends entirely on the specific balance of properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is the highest melting point for a pure, elemental metal: Tungsten is your definitive answer.
- If your goal is absolute maximum temperature resistance, regardless of material type: You must look beyond pure metals to engineered alloys and advanced ceramics like hafnfium carbonitride.
- If you need to balance heat resistance with workability and lower density: Consider other refractory metals like molybdenum or tantalum, which offer slightly lower melting points but are often easier to machine and less dense than tungsten.
Understanding these distinctions is the key to selecting a material that doesn't just survive extreme heat, but performs reliably within it.

Summary Table:
| Material | Type | Melting Point (°C) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten (W) | Pure Metal | 3,422 °C | Highest melting pure metal; dense and brittle |
| Tantalum Hafnium Carbide (Ta-Hf-C) | Alloy | ~3,990 °C | Alloy with superior thermal stability |
| Hafnium Carbonitride (HfCN) | Ceramic | >4,100 °C | Highest known melting point; non-metallic and brittle |
Ready to find the right high-temperature material for your application?
Navigating the trade-offs between melting point, density, and workability is complex. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables for testing and processing these advanced materials. Whether your project involves refractory metals, alloys, or ceramics, we can help you select the right tools for your research and production needs.
Contact our technical team today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature material challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a quartz tube facilitate fractional condensation in a horizontal tube vacuum gasification furnace? Expert Guide
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















