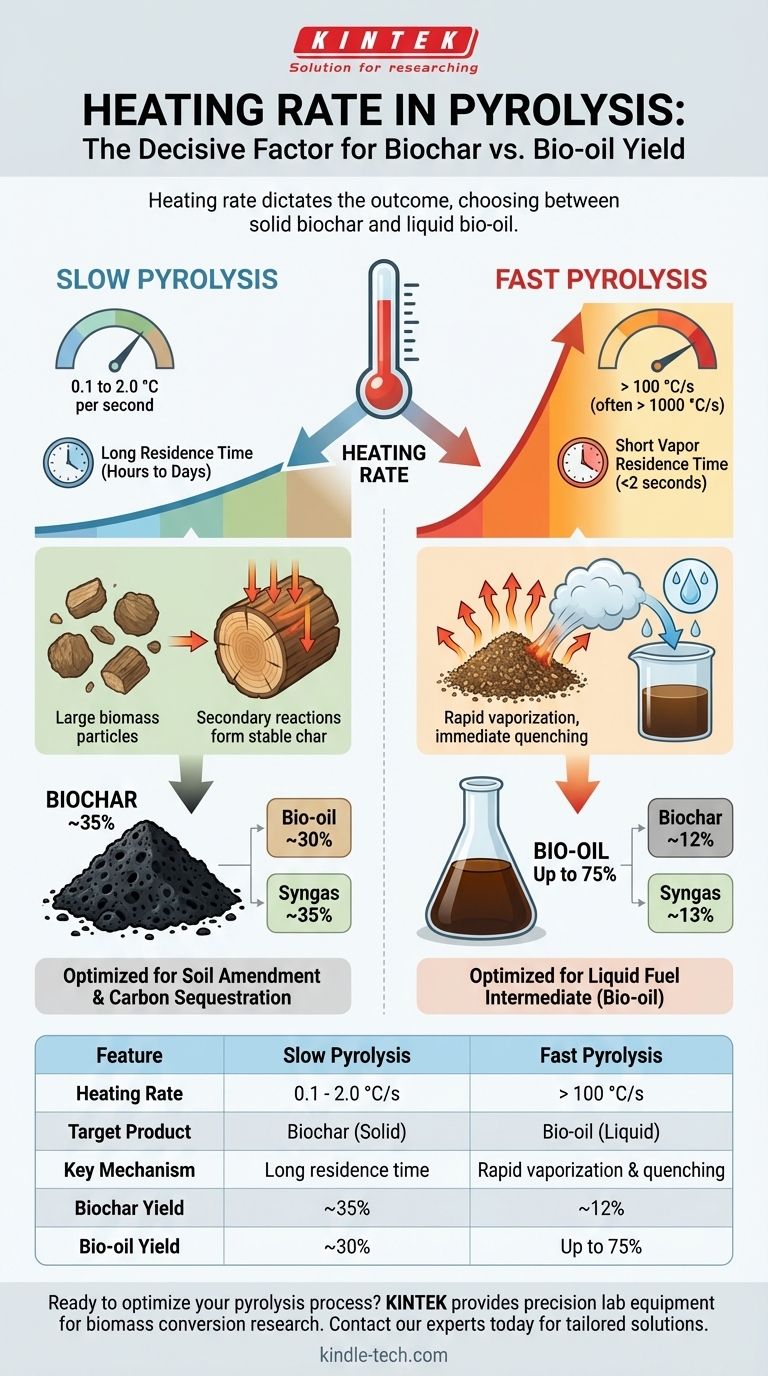
The heating rate is the single most decisive factor in determining the outcome of pyrolysis, dictating whether the process yields primarily solid biochar or liquid bio-oil. For slow pyrolysis, the heating rate is very low, typically in the range of 0.1 to 2.0 °C per second. In stark contrast, fast pyrolysis employs extremely high heating rates, usually greater than 100 °C per second and often reaching over 1000 °C per second in specialized reactors.
The fundamental difference is a strategic choice of what product to favor. Slow heating provides the time necessary for secondary reactions that form stable, solid biochar. Fast heating is engineered to vaporize biomass and immediately remove those vapors before they can react further, maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil.

The Role of Heating Rate in Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of a material, such as biomass, at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen. The speed at which you apply this heat—the heating rate—fundamentally alters the chemical reaction pathways.
Heat Transfer vs. Reaction Time
Think of the heating rate as a race between heat transfer into a biomass particle and the time the resulting vapors spend in the hot zone.
In slow pyrolysis, the slow heating allows heat to penetrate deep into the biomass particle. This provides a long residence time for both the solids and the initial vapors, promoting secondary reactions where vapors crack and repolymerize on the surface of the hot solids to form additional, stable char.
In fast pyrolysis, the goal is the opposite. Extremely rapid heating focuses on the surface of the biomass particle, causing it to quickly decompose and vaporize. These vapors are then removed from the reactor in less than two seconds to be rapidly cooled (quenched), preventing those secondary char-forming reactions.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis is a long-established process, historically used for charcoal production. It prioritizes the creation of a solid, carbon-rich product.
The Target Heating Rate and Temperature
The process uses very low heating rates, typically 0.1 to 2.0 °C/s, to reach a moderate peak temperature of around 400 to 600 °C. The total time for the process can range from several hours to days.
The Underlying Mechanism
The long residence time of solids and vapors is key. As primary vapors are slowly released, they interact with the hot char bed, leading to cracking and repolymerization reactions that increase the overall char yield and its stability.
Typical Product Yields
Slow pyrolysis provides a balanced distribution of products, with a clear emphasis on the solid fraction.
- Biochar: ~35%
- Bio-oil (tar/pyroligneous acid): ~30%
- Syngas: ~35%
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Bio-oil
Fast pyrolysis is a more modern technology developed to convert biomass into a liquid fuel intermediate, often called bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
The Target Heating Rate and Temperature
This process requires extremely high heating rates, starting at 100 °C/s and often exceeding 1000 °C/s. It targets a similar peak temperature of 450 to 600 °C but reaches it almost instantaneously.
The Underlying Mechanism
Success depends on three conditions: very high heating rates, short vapor residence times (<2 seconds), and rapid quenching of the products. This combination maximizes the production of primary vapors and prevents them from breaking down into non-condensable gases or forming secondary char.
Typical Product Yields
Fast pyrolysis is engineered to shift the product balance dramatically toward the liquid fraction.
- Bio-oil: Up to 75%
- Biochar: ~12%
- Syngas: ~13%
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating rate is not just about product yield; it involves significant operational and economic trade-offs.
Process Complexity and Cost
Slow pyrolysis can be achieved with relatively simple and robust equipment, such as kilns or retort reactors. Fast pyrolysis requires much more sophisticated and expensive systems, like circulating fluidized bed or ablative reactors, to achieve the necessary heat transfer rates.
Feedstock Requirements
Fast pyrolysis demands finely ground feedstock (typically <2 mm) with low moisture content to ensure rapid and uniform heating. Slow pyrolysis is far more forgiving and can process larger chunks of biomass with higher moisture content.
Product Quality and Stability
The bio-oil produced from fast pyrolysis is acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable, often requiring immediate upgrading to be used as a fuel. In contrast, the biochar from slow pyrolysis is a highly stable and valuable product with direct applications in agriculture (soil amendment) and carbon sequestration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal heating rate is determined entirely by your desired end-product and operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Use slow pyrolysis with low heating rates (0.1-2.0 °C/s) and long residence times.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (bio-oil) for energy or chemical production: Use fast pyrolysis with very high heating rates (>100 °C/s) and rapid vapor quenching.
- If your primary focus is a balanced output or processing varied feedstock with simpler equipment: Consider intermediate pyrolysis, which operates with moderate heating rates (around 10-100 °C/s) and offers a flexible balance between char and oil yields.
Ultimately, mastering the heating rate gives you direct control over the transformation of biomass into valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Heating Rate | Target Product | Key Mechanism | Typical Biochar Yield | Typical Bio-oil Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | 0.1 - 2.0 °C/s | Biochar (Solid) | Long residence time for vapor-solid reactions | ~35% | ~30% |
| Fast Pyrolysis | >100 °C/s (often >1000 °C/s) | Bio-oil (Liquid) | Rapid vaporization & immediate quenching | ~12% | Up to 75% |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum biochar or bio-oil yield? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research. Whether you're developing slow pyrolysis for sustainable biochar or fast pyrolysis for liquid biofuels, our reactors and temperature control systems deliver the accuracy and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's pyrolysis projects with tailored solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















