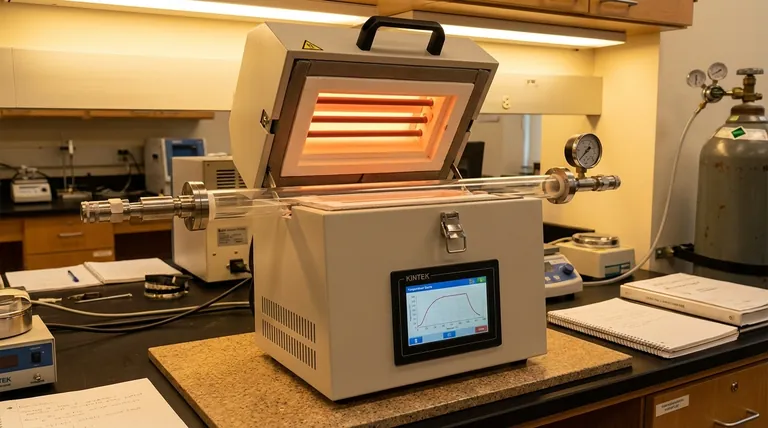
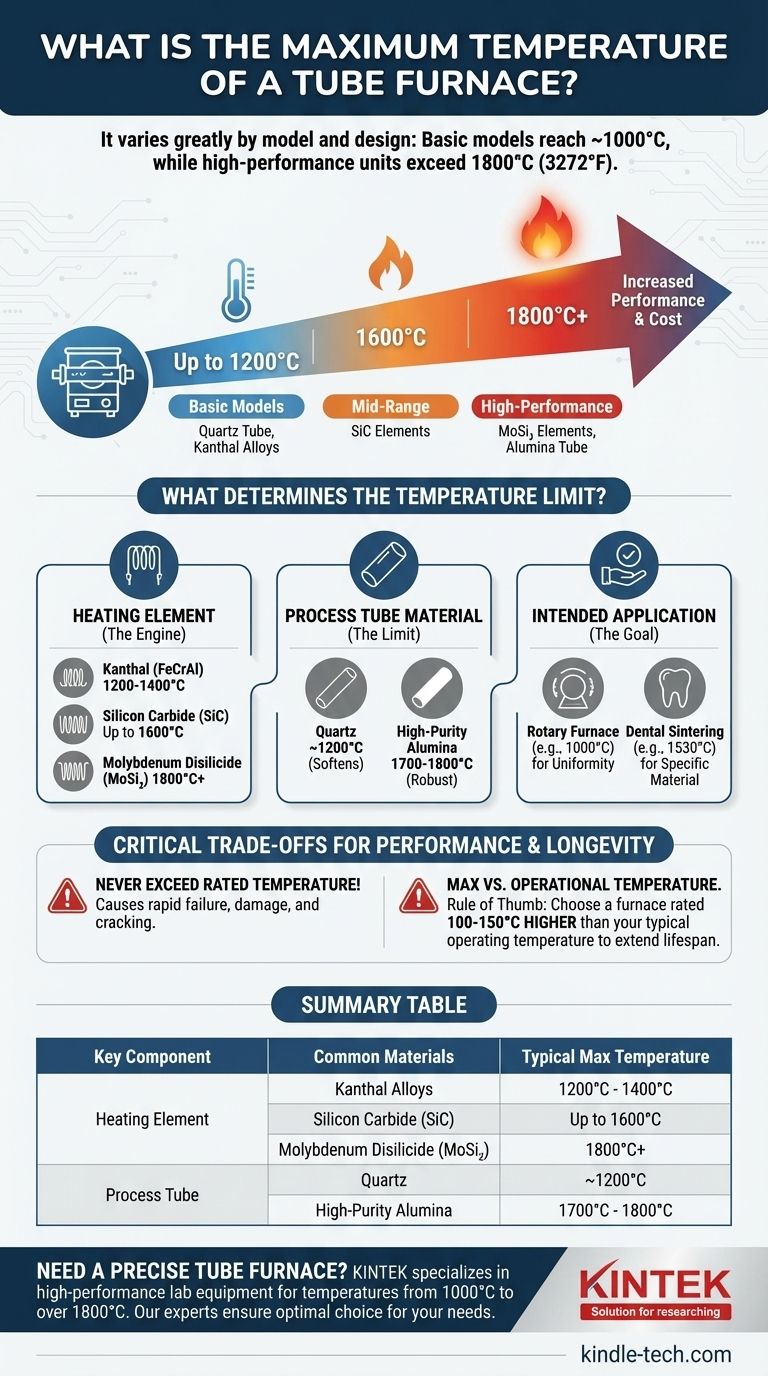
There is no single maximum temperature for a tube furnace; the value is determined entirely by the furnace's specific model, construction, and components. While some basic models operate up to 1000°C or 1200°C, high-performance laboratory tube furnaces can reliably reach 1800°C (3272°F) or even higher, depending on their design.
The question should not be "what is the high temperature of a tube furnace," but rather, "what factors determine a furnace's temperature limit, and which model meets my specific needs?" The maximum temperature is a direct result of the heating elements used, the material of the process tube, and the furnace's overall construction.

What Determines a Tube Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The "maximum temperature" listed for a furnace is a specification defined by its weakest component. Understanding these key components is essential to grasping why temperature ratings vary so widely.
The Critical Role of the Heating Element
The engine of the furnace is its heating element. Different materials have vastly different operational limits, and this is often the primary factor in a furnace's temperature rating.
- Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys: These are common and cost-effective, typically used for temperatures up to 1200°C to 1400°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): For higher temperatures, SiC elements are used. They can operate reliably up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): These are the standard for very high-temperature applications, capable of reaching 1800°C or more.
The Process Tube Material Limit
The material being heated is placed inside a tube, which must withstand the extreme temperatures. The tube itself often becomes the limiting factor.
- Quartz Tubes: A very common choice due to its properties, but it generally cannot be used above ~1200°C. It will soften and deform at higher temperatures.
- Alumina Tubes: For high-temperature work, high-purity alumina ceramic tubes are required. These can withstand sustained temperatures of 1700°C to 1800°C.
The Furnace's Intended Application
A furnace is a tool designed for a specific job. A rotary tube furnace, for example, may only be rated to 1000°C because its purpose is to tumble and process powders uniformly, not to achieve maximum heat.
In contrast, a dental furnace for sintering zirconia is specifically designed to reach temperatures like 1530°C, as that is what the material requires.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply buying the furnace with the highest temperature rating is often a mistake. There are critical trade-offs to consider for performance and longevity.
Never Exceed the Rated Temperature
The most important rule is to operate the furnace within its designed limits. Attempting to push a 1200°C furnace to 1300°C will lead to rapid failure of the heating elements, damage the insulation, and can even crack the process tube.
Maximum Temperature vs. Operational Temperature
A furnace rated for 1800°C should not be run at 1800°C continuously. Running any furnace at its absolute maximum will drastically shorten the lifespan of its heating elements. A good rule of thumb is to choose a furnace with a maximum rating at least 100-150°C higher than your typical operating temperature.
Temperature Uniformity
The "maximum temperature" is typically measured at the very center of the heating zone. The temperature will be lower toward the ends of the tube. For processes that require high precision, understanding the length of the "uniform zone" is more important than the peak temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace is about matching the equipment's capabilities to your scientific or production goals.
- If your primary focus is processing below 1200°C: A standard furnace with Kanthal elements and a quartz tube is the most cost-effective and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is working under a controlled atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas): A tube furnace is essential, and your maximum temperature will be dictated by whether you can use a quartz tube (<1200°C) or need a more expensive alumina tube (>1200°C).
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures of 1500°C or higher: You must select a furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements and a high-purity alumina process tube.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of your material, atmosphere, and temperature requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Common Materials | Typical Max Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Kanthal Alloys | 1200°C - 1400°C |
| Heating Element | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C |
| Heating Element | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1800°C+ |
| Process Tube | Quartz | ~1200°C |
| Process Tube | High-Purity Alumina | 1700°C - 1800°C |
Need a tube furnace that precisely matches your temperature and application requirements? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, offering a wide range of tube furnaces with heating elements and tube materials designed for temperatures from 1000°C to over 1800°C. Our experts will help you select the ideal model for your materials, atmosphere, and operational needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















