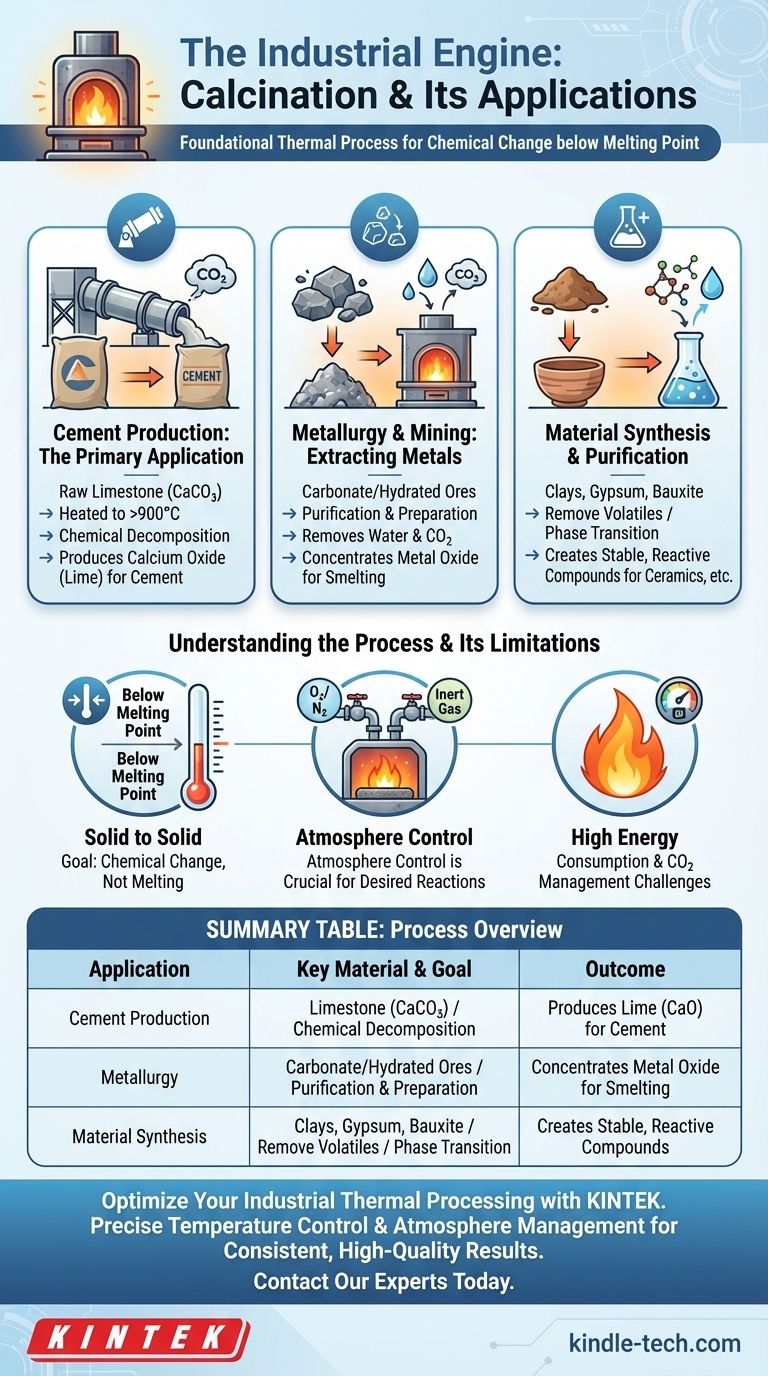
At its core, calcination is a foundational thermal process used across heavy industry to induce chemical changes in raw materials. Its most widespread industrial application is in the production of cement, where limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated in a kiln to produce lime (calcium oxide), a critical ingredient. It is also essential for extracting metals from their natural ores by removing volatile components before the final smelting stage.
The fundamental purpose of calcination is to use high heat—just below a material's melting point—to force a chemical decomposition, drive off volatile substances like water or carbon dioxide, or trigger a specific phase transition. It is a process of purification and transformation, not of melting.
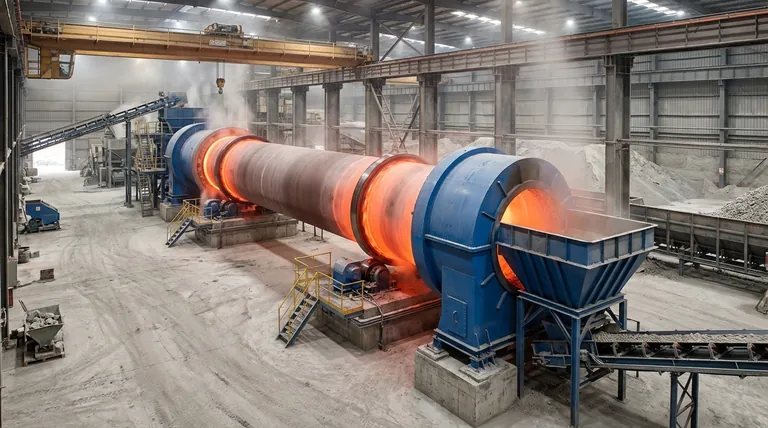

The Role of Calcination in Industrial Processes
Calcination is a form of thermal treatment. The process is conducted in a specialized furnace or reactor, often a large rotating cylinder called a calciner, which allows for precise temperature control.
The goal isn't to liquefy the material but to heat it intensely enough to break chemical bonds and fundamentally change its composition or structure.
Cement Production: The Primary Application
The most common and highest-volume use of calcination is in manufacturing Portland cement.
Raw limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is fed into a massive rotary kiln and heated to over 900°C. This heat causes a decomposition reaction, driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂) and leaving behind calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime. This lime is the primary component of cement.
Metallurgy and Mining: Extracting Metals from Ores
Calcination is a critical preparatory step in smelting and refining metals. Many metals, such as lead, zinc, and copper, are mined as carbonate or hydrated ores.
Before these ores can be smelted to extract the pure metal, they must be calcined. The process removes water from hydrated minerals and carbon dioxide from carbonate ores, concentrating the metal oxide and making the subsequent smelting process more efficient and effective.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Beyond cement and metals, calcination is used to prepare a wide range of industrial materials.
The process is used to remove volatile organic compounds from clays before firing them into ceramics. It is also used to activate materials like petroleum coke or to drive water out of substances like bauxite and gypsum to create more stable or reactive compounds for further processing.
Understanding the Process and Its Limitations
While powerful, calcination is a specific tool for a specific job. Misunderstanding its principles can lead to process failures or undesired outcomes.
The Goal: Chemical Change, Not Melting
The defining characteristic of calcination is that it occurs below the material's melting point. If the temperature is too high and the material melts, the process becomes smelting or refining, which has a different purpose and outcome.
Atmosphere Control is Crucial
The chemical result of calcination is highly dependent on the atmosphere inside the furnace. For example, heating a substance in an oxygen-rich environment can promote oxidation, which may or may not be desired. In other cases, an inert atmosphere is required to prevent unwanted side reactions.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing massive volumes of raw material to temperatures of 900°C or higher is an extremely energy-intensive process. The cost of fuel and the management of emissions (especially the CO₂ released from carbonates) are significant operational challenges in industries that rely on calcination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calcination is a versatile tool for material transformation. The key is to align the process parameters with your desired end product.
- If your primary focus is chemical decomposition: Use calcination to break down carbonate compounds into their essential oxides, as seen in cement and lime production.
- If your primary focus is material purification: Apply calcination to remove unwanted volatile substances, such as water from hydrated minerals or CO₂ from raw ores before smelting.
- If your primary focus is phase transition: Use precise temperature control during calcination to change the crystalline structure of a material, thereby altering its physical properties.
Ultimately, calcination is the industrial engine for transforming raw, earthy materials into the purified and reactive building blocks of modern manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Material | Process Goal | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement Production | Limestone (CaCO₃) | Chemical Decomposition | Produces Lime (CaO) for cement |
| Metallurgy | Carbonate/Hydrated Ores | Purification & Preparation | Concentrates metal oxide for smelting |
| Material Synthesis | Clays, Gypsum, Bauxite | Remove Volatiles / Phase Transition | Creates stable, reactive compounds |
Optimize Your Industrial Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Whether you are developing new materials, purifying ores, or producing cement, precise thermal treatment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and industrial calcination equipment that deliver the exact temperature control and atmosphere management required for your specific process goals.
Our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-quality results while managing energy consumption effectively.
Ready to enhance your calcination process? Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the right equipment for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















