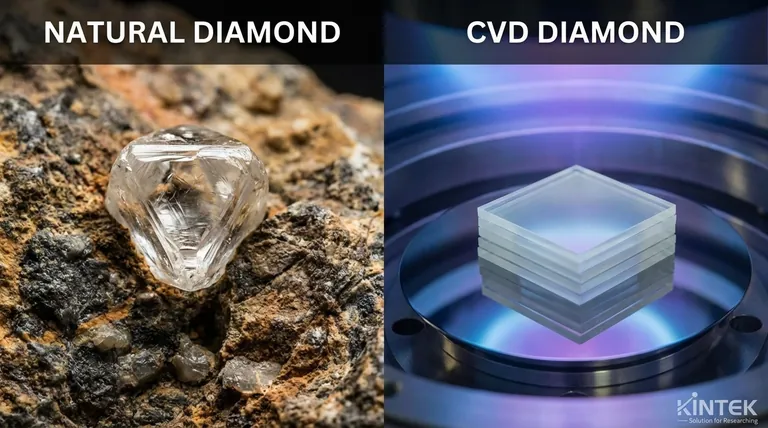
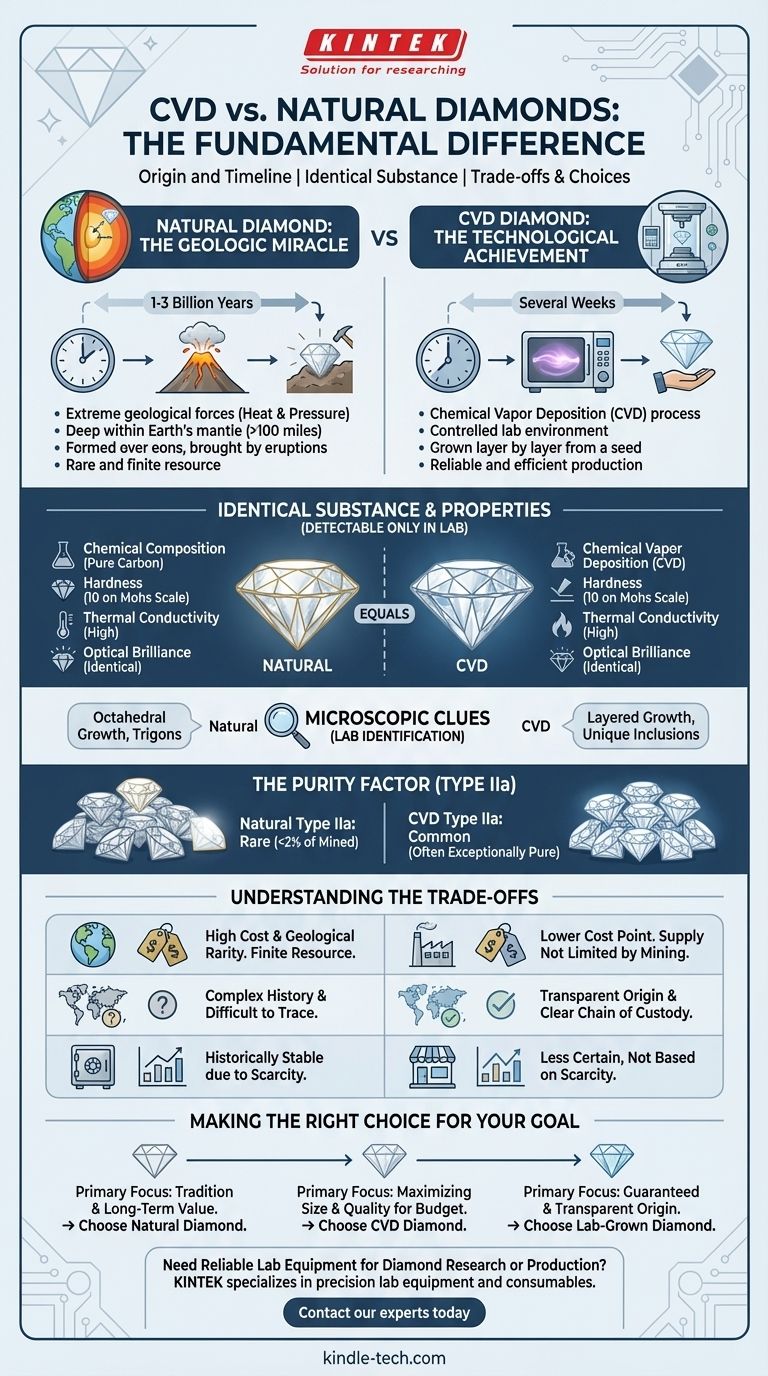
The fundamental difference between a CVD and a natural diamond is their origin. A natural diamond is formed over billions of years under immense heat and pressure deep within the Earth's mantle. A CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is grown in a laboratory over several weeks using advanced technology. Despite their vastly different creation stories, they are physically, chemically, and optically identical.
The core takeaway is this: A CVD diamond is not a "fake" diamond; it is a real diamond. The distinction lies not in the final material but in the formation process, which leaves microscopic signatures in the crystal structure that are undetectable to the naked eye but can be identified by a gemological laboratory.

The Core Distinction: Origin and Timeline
The most significant difference is how and where each diamond is made. This origin story is the foundation for all other distinctions, from rarity to price.
The Geologic Miracle (Natural Diamonds)
Natural diamonds are a product of extreme geological forces. They form from carbon atoms subjected to intense heat and pressure more than 100 miles below the Earth's surface.
This process takes between 1 and 3 billion years. The diamonds are then brought to the surface through rare volcanic eruptions, a journey that preserves their crystalline structure.
The Technological Achievement (CVD Diamonds)
CVD diamonds are created in a highly controlled laboratory environment using a method called Chemical Vapor Deposition.
The process begins with a tiny diamond "seed." This seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases like methane. Using technology like microwaves, the gas is heated, causing carbon atoms to separate and "rain" down, depositing onto the seed and growing the diamond layer by layer.
This entire process is completed in just a few weeks.
Are They Truly Identical?
While their origin is different, the end product is the same material. However, the different growth environments leave behind subtle, microscopic clues.
Identical Physical and Chemical Properties
Both natural and CVD diamonds are made of a crystalline carbon structure. This means they share the exact same chemical composition, hardness (a 10 on the Mohs scale), thermal conductivity, and optical brilliance.
For all practical intents and purposes, they are the same material with the same performance and appearance.
Microscopic Clues from Growth
The way a diamond grows leaves an imprint on its internal structure. Natural diamonds often grow in an octahedral (eight-sided) shape, and their surfaces can have unique etch marks called trigons.
CVD diamonds grow in layers, which can result in a different crystal structure. They may also contain unique inclusions not found in natural stones, such as trace amounts of non-diamond carbon, which are artifacts of the lab process.
The Purity Factor (Type IIa)
Interestingly, the controlled lab environment often produces diamonds of exceptionally high purity. Many CVD diamonds are classified as Type IIa, a category that contains almost no nitrogen impurities.
In nature, Type IIa diamonds are incredibly rare, making up less than 2% of all mined diamonds. This means the average CVD diamond is often chemically purer than the average natural diamond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The difference in origin creates a clear set of practical trade-offs for any buyer to consider.
Cost and Rarity
Natural diamonds are a finite resource recovered through expensive and labor-intensive mining operations. Their price is directly tied to their geological rarity.
CVD diamonds can be produced reliably and efficiently in a lab. Because their supply is not limited by mining, they are available at a significantly lower price point, often allowing a buyer to get a larger or higher-quality stone for the same budget.
Source and Supply Chain
The diamond mining industry has a complex history and a global supply chain that can be difficult to trace.
The lab-grown process offers a transparent and controlled origin. Buyers know exactly where their diamond was made, providing a clear chain of custody from the lab to the retailer.
Resale Value
The value of natural diamonds is supported by their centuries-long market history and their inherent rarity as a finite natural resource.
Because CVD diamonds can be manufactured, they do not possess the same scarcity. While they have value, their long-term resale value is less certain and is not based on the same principle of limited supply.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, both are genuine diamonds. The choice between them is a matter of personal priority and value.
- If your primary focus is tradition and long-term value retention: A natural diamond's geological rarity and history make it the traditional choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A CVD diamond offers the same physical material, often with higher purity, at a more accessible price.
- If your primary focus is a guaranteed and transparent origin: A lab-grown diamond provides a clear, documented creation story from a controlled environment.
The right choice is the one that best aligns with your personal values, whether you prize the miracle of geology or the marvel of modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Natural Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Formed over billions of years in Earth's mantle | Grown in a lab over several weeks |
| Primary Cost Factor | Geological rarity and mining costs | Production efficiency and technology |
| Typical Purity (Type IIa) | Rare (<2% of mined diamonds) | Common (often exceptionally pure) |
| Resale Value | Historically stable due to scarcity | Less certain, not based on scarcity |
| Supply Chain | Complex and often difficult to trace | Transparent and controlled |
Need Reliable Lab Equipment for Diamond Research or Production?
Whether you're analyzing diamond purity or developing advanced CVD processes, the right equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of gemological laboratories and materials science researchers.
We can provide the tools you need for accurate, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management












