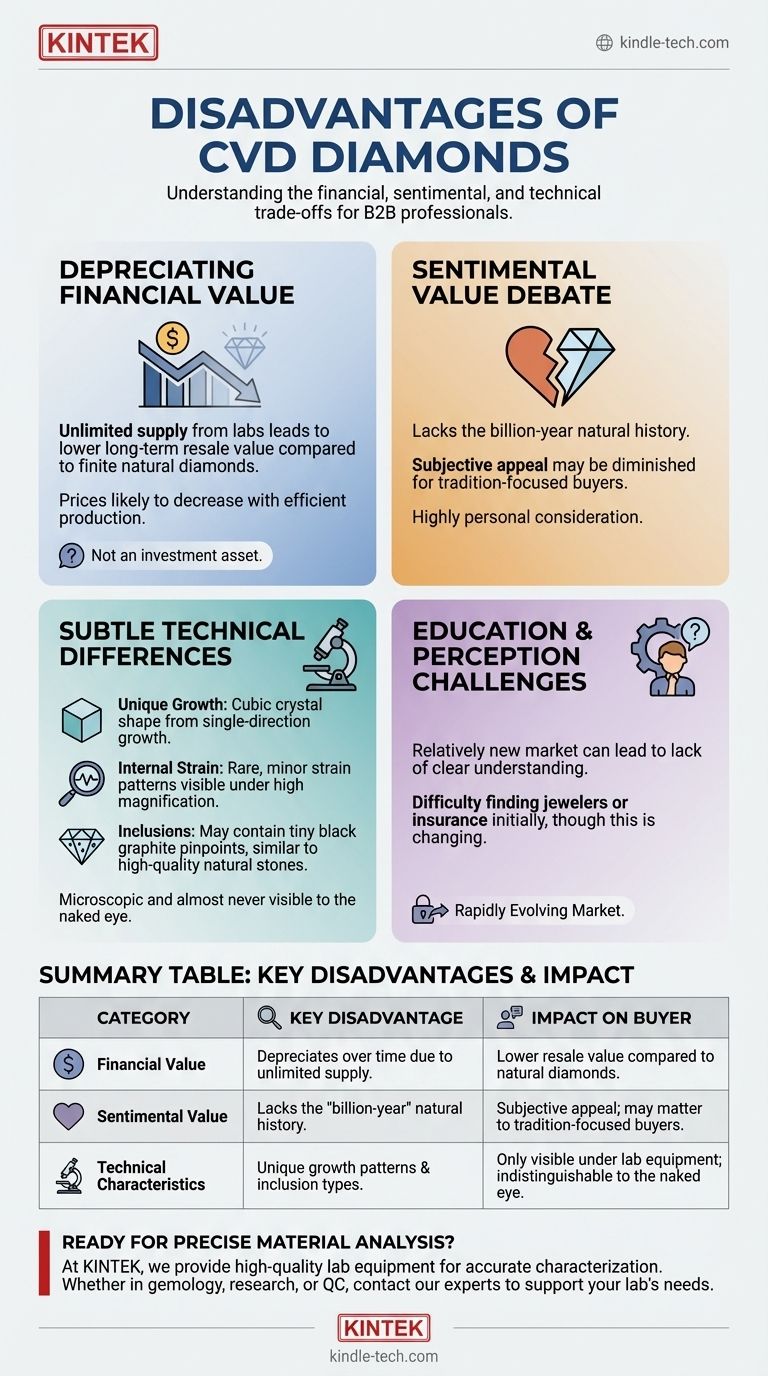
At their core, the disadvantages of CVD diamonds are not related to their beauty, chemical composition, or durability—which are identical to natural diamonds—but rather to market perception, financial value, and very subtle characteristics of their growth process. These factors primarily influence their standing as a long-term asset and their sentimental value to certain buyers.
The most significant drawbacks of a CVD diamond are its depreciating financial value and the ongoing debate around its sentimental weight compared to a natural stone. For the vast majority of observers, its physical and optical properties are indistinguishable from a mined diamond.

The Financial & Sentimental Considerations
For most potential buyers, the primary concerns are not technical but are rooted in value and tradition. These factors represent the most significant trade-offs when choosing a lab-grown diamond.
Depreciating Financial Value
Unlike natural diamonds, which are finite resources, CVD diamonds can be created in a lab with virtually no supply constraints. This fundamental difference means they do not hold resale value in the same way.
As technology improves and production becomes more efficient, the cost to create CVD diamonds is likely to continue decreasing, which will in turn lower their long-term market value.
The Debate Over Sentimental Value
A natural diamond's journey over billions of years deep within the Earth is a powerful narrative for many, symbolizing rarity and timelessness.
For some, a lab-grown diamond may lack this romantic history, which can diminish its sentimental appeal. This is, of course, a highly subjective and personal consideration.
Challenges in Education and Perception
The lab-grown diamond market is still relatively new. As a result, there can be a lack of clear understanding among both consumers and even some jewelers.
This can sometimes lead to difficulty in finding jewelers willing to work with or insure lab diamonds, although this is rapidly changing as they become more mainstream.
Subtle Physical & Technical Differences
While a CVD diamond is chemically and optically a real diamond, its unique manufacturing process can leave behind microscopic tells that distinguish it from a natural stone. These are almost never visible to the naked eye.
Unique Growth Characteristics
CVD diamonds are grown in layers in a single direction, resulting in a cubic crystal shape. Natural diamonds form under immense pressure and heat from all directions.
Potential for Internal Strain
This single-direction growth can, in rare instances, cause internal strain within the crystal lattice. However, these strain patterns are typically minor and only visible under specialized, high-magnification laboratory equipment.
Common Inclusion Types
The microscopic imperfections, or inclusions, found in CVD diamonds often differ from those in natural diamonds. CVD diamonds may contain tiny black pinpoint dots of graphite. These are similar to inclusions found in high-quality natural stones and are extremely difficult to identify without a gemologist's microscope.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Making an informed decision requires separating objective facts from market narratives and understanding the true implications of your choice.
Distinguishing Fact from Fiction
It is critical to note that some commonly cited "disadvantages" are factually incorrect. CVD diamonds have a significantly lower environmental impact and are free from the human rights concerns associated with conflict diamonds. These are two of their most significant advantages, not drawbacks.
The Critical Role of Certification
The risk of a lab-grown diamond being deceptively sold as a natural one underscores the need for certification from a reputable lab like the GIA or IGI. A certificate guarantees the diamond's origin (lab-grown or natural) and provides an objective grade of its quality, protecting you as a consumer.
Navigating Insurance
While some insurers were initially hesitant, most major providers now readily insure lab-grown diamonds. It is crucial to get an appraisal and ensure your policy covers the full replacement cost, just as you would with a natural diamond.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by your personal priorities. There is no single "best" choice, only the right choice for you.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carat size and quality for your budget: A CVD diamond is an outstanding choice, offering the exact same brilliance and fire as a natural diamond for a fraction of the cost.
- If your primary focus is long-term financial investment or tradition: A high-quality, certified natural diamond has a historical track record of holding or appreciating in value.
- If your primary focus is ethical sourcing and environmental sustainability: A CVD diamond is the superior option, as it avoids the ecological and social issues tied to mining.
Ultimately, understanding these key distinctions empowers you to choose the diamond that aligns perfectly with your values, budget, and purpose.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Disadvantage | Impact on Buyer |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Value | Depreciates over time due to unlimited supply | Lower resale value compared to natural diamonds |
| Sentimental Value | Lacks the "billion-year" natural history | Subjective appeal; may matter to tradition-focused buyers |
| Technical Characteristics | Unique growth patterns & inclusion types (e.g., graphite pinpoints) | Only visible under lab equipment; indistinguishable to the naked eye |
Still have questions about choosing the right diamond for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise material analysis. Whether you're in gemology, research, or quality control, our expertise can help you accurately characterize and verify materials like diamonds.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your laboratory's specific needs and ensure you have the right tools for informed decision-making.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the process of lab created diamonds? A Clear Guide to HPHT & CVD Methods
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses


















