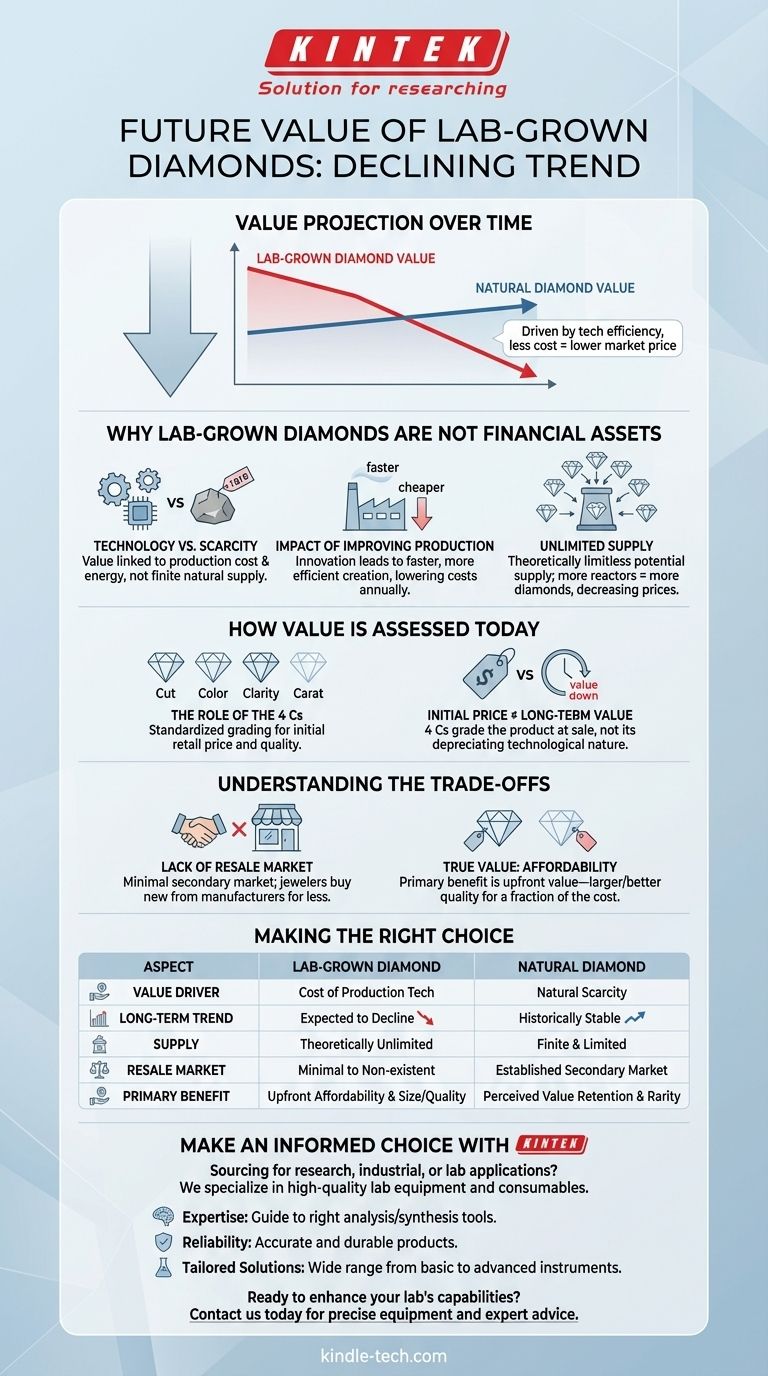
In short, the future financial value of a lab-grown diamond is expected to decline over time. Because they are a product of technology, their creation will become more efficient and less expensive. This continuous improvement in production methods will lead to lower market prices, making them unsuitable as a financial investment.
A lab-grown diamond's value is tied to the technology used to create it, not to natural scarcity. As that technology inevitably improves, the cost to produce them will fall, meaning their long-term resale value is likely to be very low.

Why Lab-Grown Diamonds Are Not Financial Assets
The Economics of Technology vs. Scarcity
Natural diamonds derive their value from being a finite, mined resource. Their supply is limited by what can be found and extracted from the earth.
Lab-grown diamonds, while physically and chemically identical, are a manufactured product. Their value is therefore linked to the cost of the technology and energy required to create them.
The Impact of Improving Production
As with any technology, the processes for creating diamonds in a lab are constantly improving.
Researchers and companies are focused on making production faster, more energy-efficient, and capable of producing higher-quality stones. This innovation directly lowers the cost of production year over year.
A Market of Unlimited Supply
The supply of lab-grown diamonds is theoretically limitless. As demand grows, more reactors can be built to create more diamonds.
This fundamental difference—unlimited potential supply versus finite natural supply—is the primary reason lab-grown diamond prices will continue to decrease.
How Value is Assessed Today
The Role of the 4 Cs
Currently, lab-grown diamonds are graded and priced using the same "4 Cs" (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) as natural diamonds.
This system provides a standardized way to assess the quality and determine the initial retail price of the stone.
Confusing Initial Price with Long-Term Value
It is critical not to confuse this initial purchase price with long-term, retained value.
The 4 Cs grade the quality of the manufactured product at the time of sale, but they do not alter its underlying nature as a piece of technology with a depreciating value.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Lack of a Resale Market
A key consideration is the absence of a significant secondary or resale market for lab-grown diamonds.
Most jewelers will not buy back lab-grown diamonds because they can acquire new ones from a manufacturer for a continuously decreasing price. This leaves private sales as the only, and often difficult, option for resale.
The True Value Proposition: Affordability
The primary benefit of a lab-grown diamond is not investment potential but upfront value.
You can acquire a physically identical diamond that is often larger or of higher quality (better color or clarity) for a significantly lower price than a natural stone of equivalent grade.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing between a lab-grown and a natural diamond depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond is the logical choice, offering the exact same physical and aesthetic properties for a fraction of the cost.
- If your primary focus is the potential for value retention: A natural diamond is the conventional option, though it should still be viewed as a luxury purchase, not a guaranteed financial investment.
Understand that a lab-grown diamond's value is realized in its beauty and affordability at the time of purchase, not in its future financial worth.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Value Driver | Cost of production technology | Natural scarcity and finite supply |
| Long-Term Value Trend | Expected to decline | Historically more stable |
| Supply | Theoretically unlimited | Finite and limited by mining |
| Resale Market | Minimal to non-existent | Established secondary market |
| Primary Benefit | Upfront affordability and size/quality for budget | Perceived value retention and rarity |
Make an Informed Choice with KINTEK
Whether you're sourcing diamonds for research, industrial applications, or specialized lab equipment, understanding material properties and market trends is crucial. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your precise needs.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expertise: We understand the science behind materials like lab-grown diamonds and can guide you to the right tools for analysis, synthesis, or quality control.
- Reliability: Our products are built for accuracy and durability, ensuring your lab operations run smoothly.
- Tailored Solutions: We serve a wide range of laboratory needs, from basic consumables to advanced analytical instruments.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact us today via our form to discuss how KINTEK can support your projects with precision equipment and expert advice.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose



















