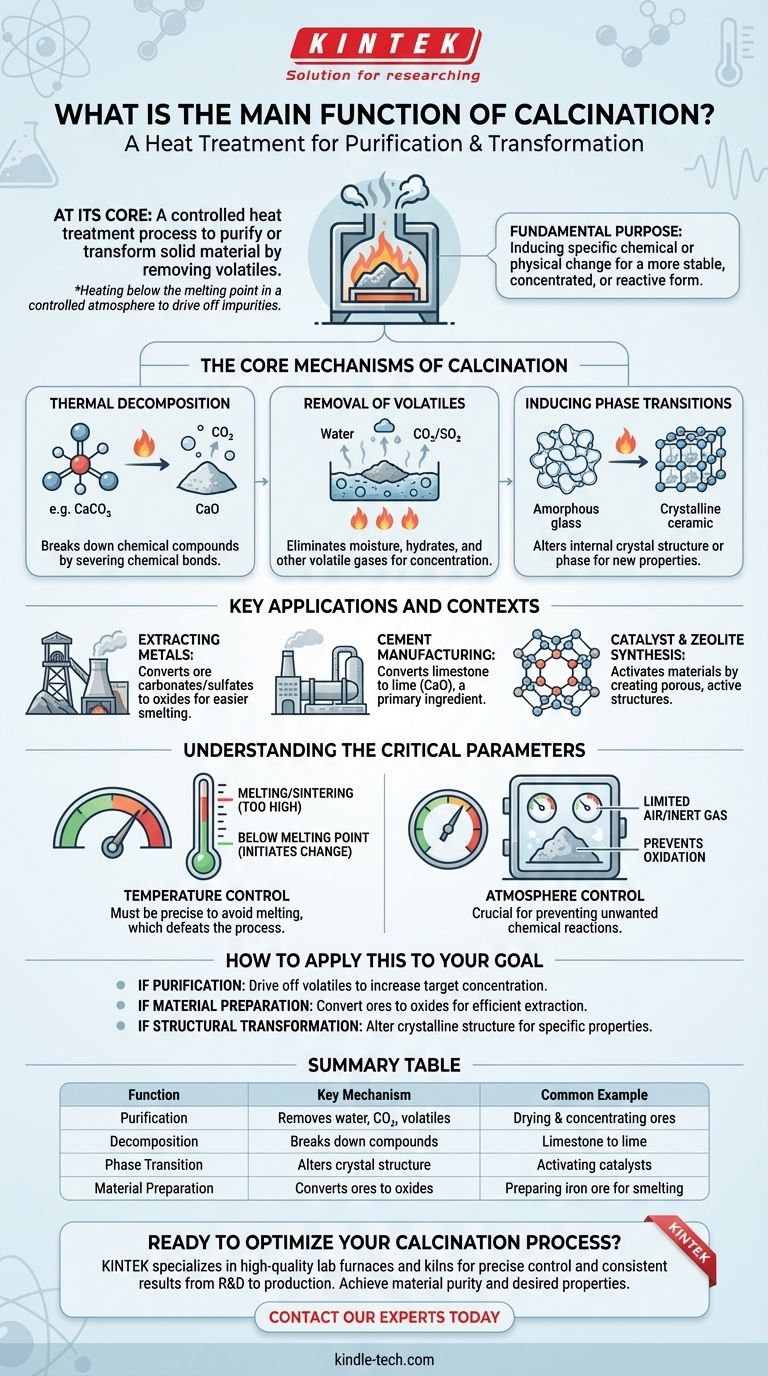
At its core, calcination is a heat treatment process designed to purify or transform a solid material by removing volatile substances. It involves heating the material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in a controlled atmosphere with limited or no air to drive off impurities like water, carbon dioxide, or sulfur.
The fundamental purpose of calcination is not just to heat a substance, but to induce a specific chemical or physical change—transforming it into a more stable, concentrated, or reactive form for subsequent processing.
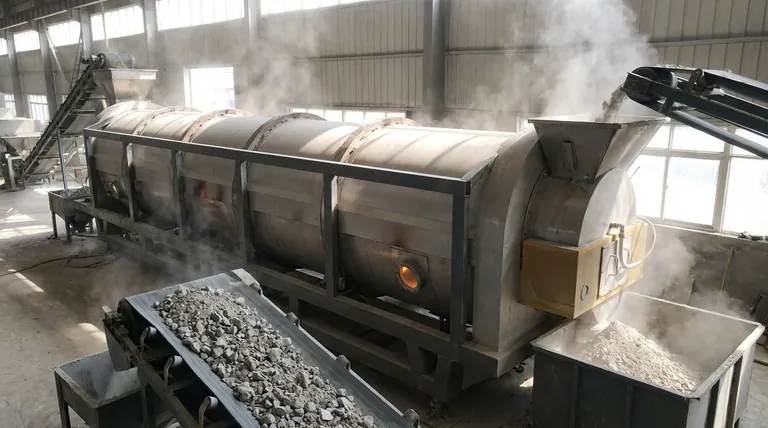

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
Calcination achieves its results through several key thermal effects. Understanding these mechanisms reveals why it is such a foundational process in materials science and metallurgy.
Thermal Decomposition
The most common function is to break down chemical compounds. By applying heat, calcination provides the energy needed to sever chemical bonds, causing a substance to decompose into simpler components.
A classic example is the breakdown of metal carbonates, like limestone (calcium carbonate), into a metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas, which is then driven off.
Removal of Volatiles
This process is highly effective at removing any substance that can be vaporized. This includes physically absorbed moisture from the surface of a material.
It also removes chemically bound water (hydrates) and other volatile gases like carbon dioxide or sulfur dioxide, leaving behind a more concentrated and purified solid.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Beyond purification, calcination can be used to alter the internal structure of a material. The controlled application of heat can cause a substance to change its crystal structure or phase.
For example, it is used in the devitrification of glass, intentionally converting the amorphous, non-crystalline glass into a crystalline ceramic with different properties.
Key Applications and Contexts
Calcination is not an obscure laboratory technique; it is a critical step in many large-scale industrial processes.
Extracting Metals from Ores
This is the most well-known application. Ores are often mined as carbonates or sulfates. Calcination converts these ores into metal oxides, which are much easier to chemically reduce into pure metal during a later smelting stage.
Cement Manufacturing
The production of cement relies heavily on calcination. Limestone (CaCO3) is heated in a kiln to produce lime (CaO), a primary ingredient in cement. This single application represents one of the largest uses of the calcination process globally.
Catalyst and Zeolite Synthesis
In the chemical industry, calcination is used to activate materials. For instance, in the synthesis of zeolites (used as catalysts and adsorbents), calcination removes placeholder ions like ammonium, creating the porous, chemically active structure the material is known for.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
The success of calcination depends on precise control over two main factors. Getting these wrong can ruin the material or render the process ineffective.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The temperature must be carefully calibrated. It needs to be high enough to initiate the desired decomposition or phase change but must remain below the material's melting point.
If the temperature is too high, the material can melt or sinter (fuse into a solid mass), which prevents the removal of volatiles and defeats the purpose of the process.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Calcination is typically performed in the absence or limited supply of air. This is crucial for preventing unwanted chemical reactions, most notably oxidation.
In some specialized cases, a controlled amount of air is introduced to achieve a specific, partial oxidation, but the atmosphere is always a deliberately managed parameter, not an afterthought.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The objective of your calcination process will determine your operational focus.
- If your primary focus is purification: Your main goal is to drive off water, carbonates, or other volatile impurities to increase the concentration of your target compound.
- If your primary focus is material preparation: Calcination is your essential first step to convert ores into oxides, making them chemically ready for efficient reduction into metal.
- If your primary focus is structural transformation: Use calcination to precisely alter the crystalline structure of a material, such as in activating a catalyst or creating glass-ceramics.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational thermal process used to precisely control the chemical and physical state of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Mechanism | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purification | Removes water, CO₂, and other volatiles | Drying and concentrating ores |
| Decomposition | Breaks down compounds (e.g., carbonates) | Converting limestone (CaCO₃) to lime (CaO) |
| Phase Transition | Alters crystal structure | Activating catalysts or creating glass-ceramics |
| Material Preparation | Converts ores to oxides for metal extraction | Preparing iron ore for smelting |
Ready to Optimize Your Calcination Process?
Calcination is a critical step for achieving material purity and desired properties. Whether you are developing new catalysts, processing ores, or manufacturing advanced ceramics, the right equipment is essential for precise temperature and atmosphere control.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and kilns designed for reliable and efficient calcination. Our solutions help you:
- Achieve consistent results with precise temperature control.
- Ensure process integrity with controlled atmosphere options.
- Scale your operations from R&D to production.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect calcination solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions



















