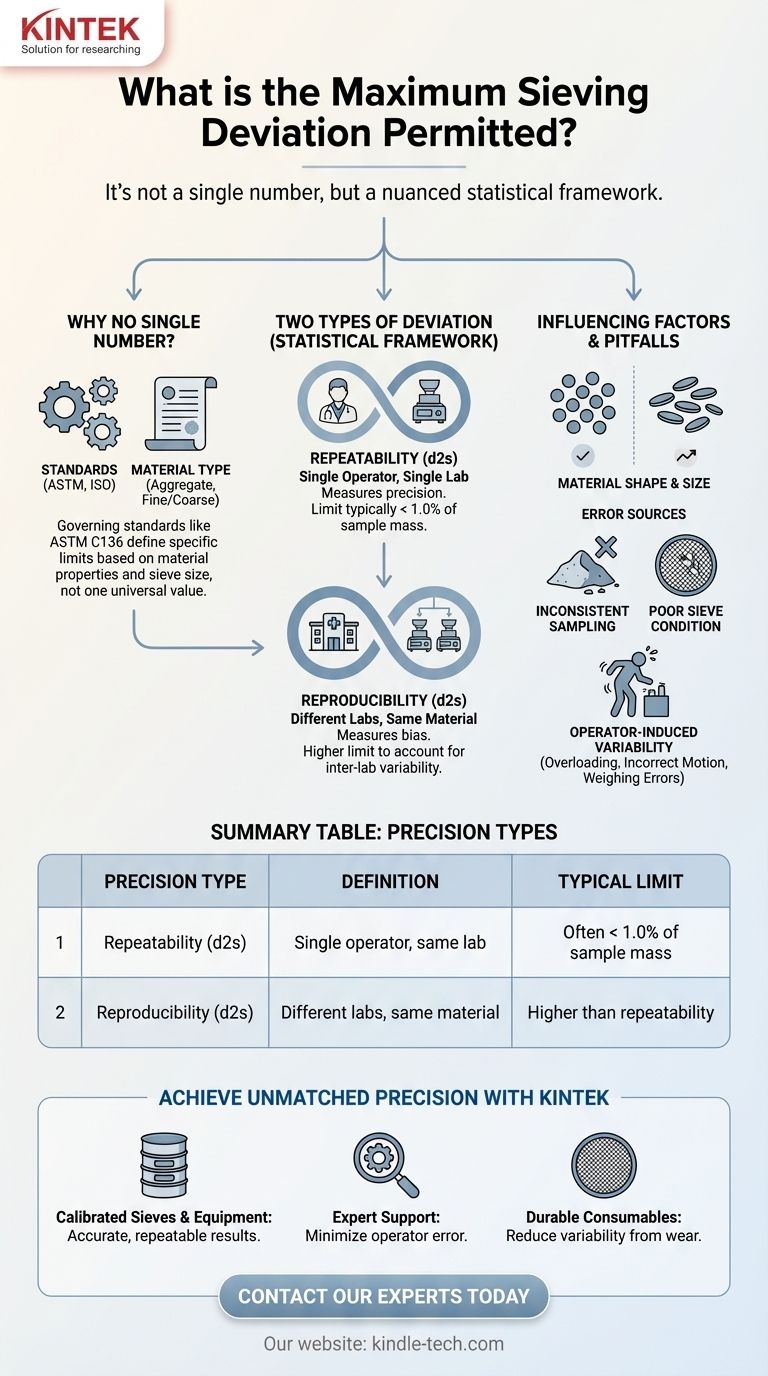
The question of a single "maximum sieving deviation" is a common one, but the answer is nuanced. There is no universal value. Instead, the permitted deviation is strictly defined by the specific testing standard you are following (such as ASTM or ISO), the type of material being tested, and whether you are comparing results from a single operator or between different laboratories.
The core takeaway is that "permitted deviation" isn't one number, but a statistical framework. It is defined by standards like ASTM C136 and is split into repeatability (for a single lab) and reproducibility (for different labs), with specific limits that change based on the material's properties and the sieve size in question.

Why "Maximum Deviation" Isn't a Single Number
To ensure test results are meaningful, we must first understand the sources of variation and how standards control for them. The idea of a single tolerance is too simplistic for a procedure sensitive to so many factors.
The Role of Governing Standards
Industry standards are the ultimate authority on this topic. Organizations like ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) publish detailed procedures that include tables of acceptable precision.
For example, ASTM C136, "Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates," is the foundational document for aggregates in many parts of the world. The values within this standard are the legal and technical limits.
Distinguishing Repeatability from Reproducibility
Standards break down "deviation" into two critical concepts:
- Repeatability: This measures precision within a single lab. It answers the question, "If the same operator tests the same material twice, how close should the results be?"
- Reproducibility: This measures bias between different labs. It answers, "If two different labs test the same material, how close should their results be?"
The acceptable limit for reproducibility is always larger than for repeatability, as it must account for variations in equipment, environment, and operator technique between facilities.
How Material Type Dictates the Limits
The physical nature of the material being sieved has a profound impact on acceptable deviation.
A sample of uniform, rounded gravel will pass through sieves very consistently. In contrast, a sample of crushed stone with flat, elongated particles may produce more variation, as a particle's orientation determines if it passes through an opening. The standards account for this by providing different limits for different material types (e.g., coarse aggregate vs. fine aggregate).
Deconstructing the Precision Statements (An ASTM C136 Example)
To make this concrete, let's examine how a standard like ASTM C136 structures its precision limits. You must always refer to the latest version of the standard for the official values.
The Single-Operator Precision (d2s) Limit
This is the repeatability limit. The (d2s) notation means "difference two-sigma." It indicates that the difference between two properly conducted tests by the same operator should not exceed this value in 95% of cases.
This limit is typically expressed as a percentage of the total sample mass. For most sieve sizes in an aggregate test, this value is often below 1.0% but can vary.
The Multi-Laboratory Precision (d2s) Limit
This is the reproducibility limit. It defines the maximum acceptable difference between test results on the same material from two different laboratories.
As expected, these values are higher than the single-operator limits to account for inter-lab variability. These are the critical numbers used to settle disputes between a material producer and a customer.
How to Interpret the Values
If the difference between your two test results (either in your own lab or compared to another) exceeds the (d2s) limit specified in the standard for a particular sieve, it is a red flag.
This doesn't automatically mean one result is "wrong," but it indicates that the variability is higher than statistically acceptable. The results should be considered suspect pending an investigation into the procedure.
Understanding Common Pitfalls and Sources of Error
Achieving results within the permitted deviation requires rigorous attention to detail. Most errors stem from a few common areas.
Inconsistent Sampling Technique
This is the single greatest source of error in sieve analysis. If the initial test sample is not a representative cross-section of the entire material stockpile, the test is invalid before it even begins. Proper quartering or splitting is non-negotiable.
Poor Sieve Condition
Sieves are precision instruments that wear out. A sieve with stretched wires, damaged mesh (denting), or clogged openings (blinding) will not provide an accurate result. Regular inspection and calibration are essential.
Operator-Induced Variability
Even with perfect equipment, the operator can introduce errors. Common mistakes include:
- Overloading sieves: Prevents particles from having a fair chance to pass through the openings.
- Incorrect shaking time or motion: Insufficient agitation leads to incomplete separation.
- Errors in weighing: Incorrectly weighing the material retained on each sieve invalidates the calculation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to managing sieving deviation should be directly tied to your objective.
- If your primary focus is internal quality control: Concentrate on repeatability. Regularly run duplicate tests to ensure your operator and equipment are producing consistent results within the single-operator (d2s) limits.
- If your primary focus is resolving a dispute with a supplier or customer: The multi-laboratory (d2s) limit for reproducibility is your guide. Ensure both parties use the exact same standard, test method, and properly calibrated equipment.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new testing procedure: Begin by acquiring the correct standard for your material. Then, perform a repeatability study to establish your lab's baseline precision and validate your process.
Understanding that permitted deviation is a statistical control, not a single number, transforms sieve analysis from a routine task into a powerful quality assurance tool.
Summary Table:
| Precision Type | Definition | Key Standard (e.g., ASTM C136) | Typical Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repeatability (d2s) | Single operator, same lab | Single-Operator Precision | Often < 1.0% of sample mass |
| Reproducibility (d2s) | Different labs, same material | Multi-Laboratory Precision | Higher than repeatability |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Sieve Analysis with KINTEK
Are inconsistent sieving results impacting your quality control or causing disputes with suppliers? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that help laboratories like yours meet stringent ASTM and ISO standards.
By choosing KINTEK, you benefit from:
- Calibrated Sieves & Equipment: Ensure your results are accurate and repeatable.
- Expert Support: Get guidance on proper testing procedures to minimize operator error.
- Durable Consumables: Reduce variability caused by worn or damaged sieves.
Don't let sieving deviation compromise your data integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can help you achieve reliable, reproducible results every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What materials are required for sieving? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is the advantage of sieving? A Simple, Reliable Method for Particle Size Analysis
- How many types of sieves are there? Choose the Right Sieve for Your Material Analysis
- Is a dry sieve analysis more accurate than a washed sieve analysis? Choosing the Right Method for Your Material
- What is the industrial use of sieve? Essential for Quality Control & Process Efficiency
- Why is a standard sieve used to screen ground powders before the hot-pressing sintering of LiTa2PO8? Achieve Peak Density
- What are the uses of sieves in the laboratory? Master Particle Size for Quality & Performance
- Which solids can be separated from a solution by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Sieving



















