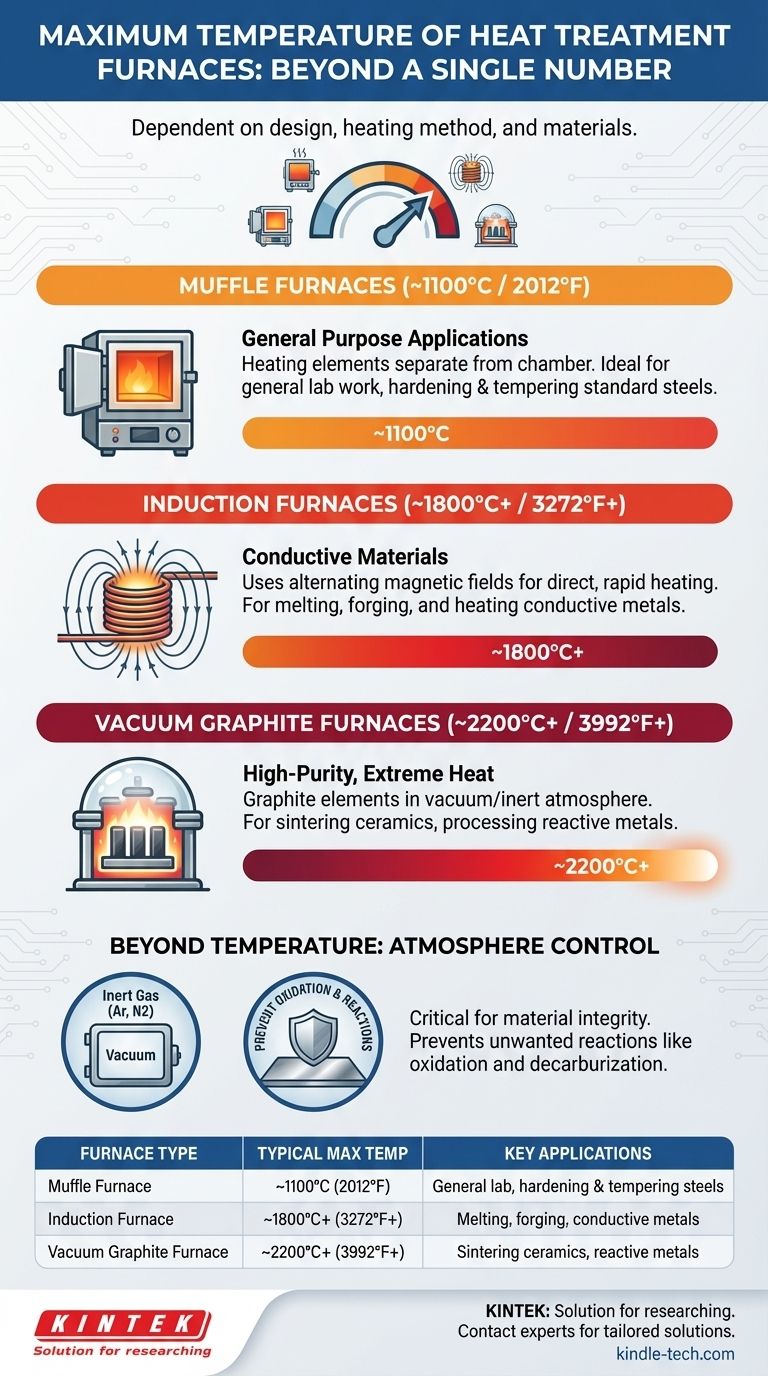
The maximum temperature of a heat treatment furnace is not a single value; it is entirely dependent on the furnace's design, heating method, and construction materials. While a standard muffle furnace may max out around 1100°C (2012°F), specialized systems like induction furnaces can exceed 1800°C (3272°F), and vacuum graphite furnaces can reach temperatures of 2200°C (3992°F) or more.
The critical insight is not to ask for a single maximum temperature, but to understand that each furnace type represents a specific technology designed to meet the temperature and atmospheric requirements of a particular material and process. The limit is defined by the tool, not by the concept of heat treatment itself.
Why Furnace Type Dictates Temperature
The maximum achievable temperature is a direct result of a furnace's fundamental design. The heating elements, insulation, and internal atmosphere are all engineered for a specific operational range. Exceeding this range leads to equipment failure and compromised results.
Muffle Furnaces: For General Purpose Applications (~1100°C)
A muffle furnace is a common, front-loading box furnace. Its heating elements are typically separate from the internal chamber (the "muffle"), which protects the workload from direct radiation and combustion byproducts.
Their construction limits them to around 1100°C, making them ideal for general-purpose lab work, hardening and tempering of standard steels, and other lower-temperature processes.
Induction Furnaces: For Conductive Materials (~1800°C+)
Induction furnaces do not use conventional heating elements. Instead, they use powerful alternating magnetic fields generated by a coil to induce an electric current directly within the metallic workpiece.
This direct heating is extremely rapid and efficient, allowing temperatures to reach 1800°C or higher. This technology is a cornerstone of the steel industry for melting, forging, and specialized heat treatments of conductive materials.
Vacuum Graphite Furnaces: For High-Purity, Extreme Heat Processes (~2200°C+)
These are highly specialized furnaces designed for the most demanding applications. They use graphite heating elements, which can withstand extreme heat without melting.
Crucially, they operate under a vacuum or a controlled inert atmosphere. This prevents the graphite elements and the workpiece from oxidizing (burning up) at extreme temperatures. This allows them to safely reach 2200°C or more, necessary for sintering advanced ceramics, processing reactive metals, and creating high-purity materials.
Beyond Temperature: The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Simply reaching a high temperature is not enough. The chemical environment inside the furnace is just as critical to the outcome of the heat treatment process.
What is Atmosphere Control?
Atmosphere control involves replacing the normal air inside a furnace with a specific gas or creating a vacuum. This is managed by a well-sealed furnace body and ventilation systems, often including water-cooled fans and safety mechanisms.
Common atmospheres include inert gases like argon or nitrogen, reactive gases for processes like carburizing, or a near-perfect vacuum to remove all reactive molecules.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with the oxygen in the air, forming a layer of oxide scale. This damages the surface finish and can alter the material's dimensions.
A controlled atmosphere prevents this oxidation, as well as other unwanted reactions like decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), ensuring the material's integrity is preserved.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment furnace involves balancing capability with practical constraints. There is no single "best" furnace, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Cost vs. Capability
Higher maximum temperatures and advanced atmosphere controls come at a significant cost. A vacuum graphite furnace can be orders of magnitude more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than a simple muffle furnace.
Heating Method vs. Material
The heating method is not universal. An induction furnace is incredibly effective for a steel shaft but is completely useless for heating a ceramic component, which is not electrically conductive.
Process Time vs. Complexity
While an induction furnace can heat a part in minutes, it may not provide the slow, uniform soak time required for relieving stress in a large, complex casting. The process dictates the required heating and cooling rates, which influences the choice of furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching your specific engineering goal to the right technology.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, annealing, or tempering common tool steels: A standard muffle furnace with a range up to 1100°C is typically the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating conductive metals for forging, melting, or surface hardening: An induction furnace capable of 1800°C or more provides the necessary speed and power.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced ceramics, refractory metals, or high-purity alloys without oxidation: A vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace reaching 2200°C or higher is essential.
Ultimately, understanding the capabilities and limitations of each furnace type empowers you to select the precise tool required for your specific material and desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | ~1100°C (2012°F) | General lab work, hardening & tempering steels |
| Induction Furnace | ~1800°C+ (3272°F+) | Melting, forging, heating conductive metals |
| Vacuum Graphite Furnace | ~2200°C+ (3992°F+) | Sintering ceramics, processing reactive metals |
Selecting the right furnace is critical for your process success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the ideal heat treatment furnace—whether it's a standard muffle furnace for general work or a high-temperature vacuum system for advanced materials—ensuring precise temperature control and the correct atmosphere for your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven for SRB regeneration? Preserve Biological Viability
- What is the difference between sintering and fusion? Solid-State vs. Liquid-Phase Processing Explained
- Why is a vacuum drying oven used for Norem02 alloy powder? Ensure Defect-Free Laser Cladding Results
- What role does a two-stage rotary vane vacuum pump play in a radio frequency (rf) plasma carbonitriding system?
- How does furnace temperature precision affect Inconel 718 grain size? Master Microstructural Control
- Does heating steel make it stronger? Unlock Maximum Strength with Controlled Heat Treatment
- What are the uses of heat treated aluminum alloys? Unlock High-Strength, Lightweight Performance
- What is the range for heat treating? The Goal-Defined Temperature Guide



















