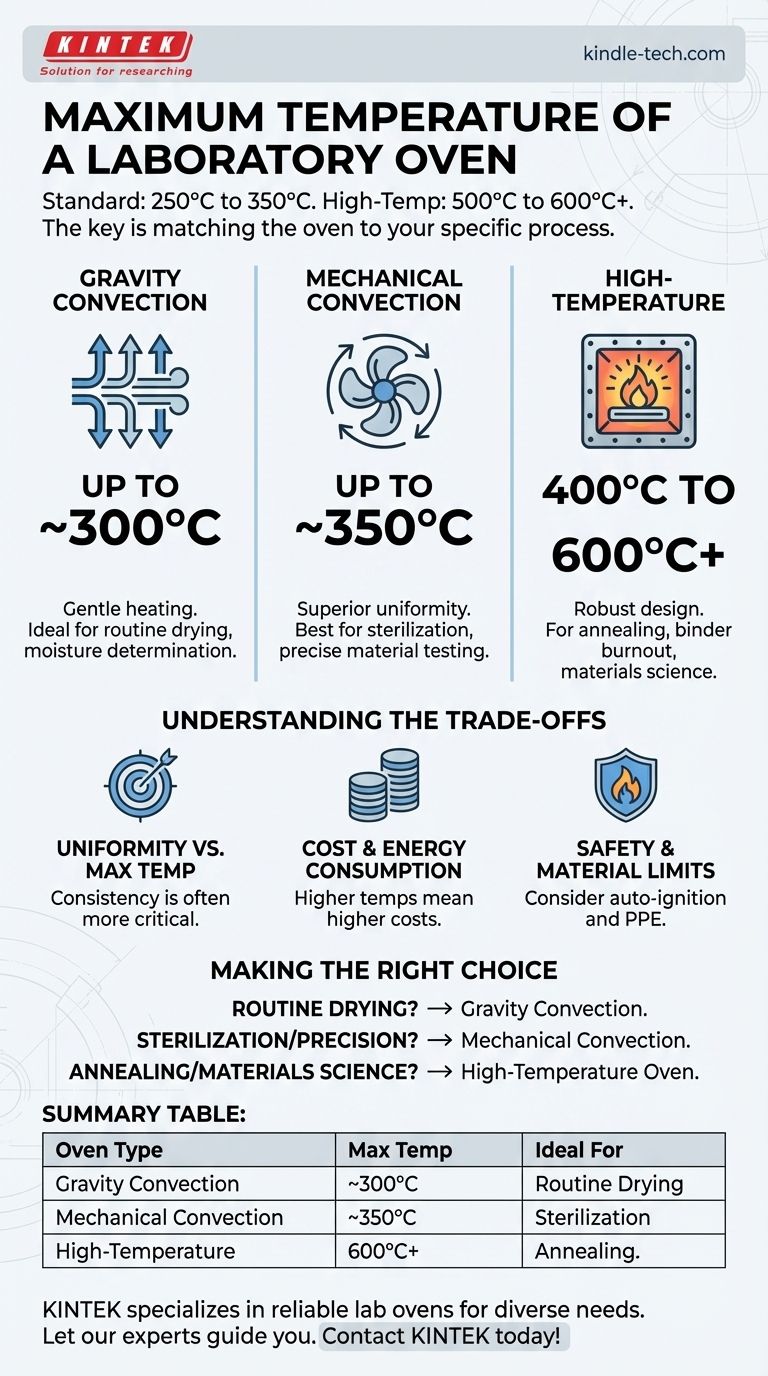
In short, most standard laboratory ovens operate up to a maximum temperature of 250°C to 350°C (482°F to 662°F). However, specialized high-temperature models are designed to reach 500°C to 600°C or even higher, depending entirely on their construction and intended application.
The concept of a single "maximum temperature" for a laboratory oven is misleading. The crucial factor is not the highest number an oven can reach, but matching the oven's specific type, heating mechanism, and performance characteristics to your scientific process.

Why Oven Type Dictates Temperature Limits
The maximum temperature is a direct result of an oven's design, from its heating elements and insulation to its method of air circulation. Understanding these categories is key to selecting the right instrument.
General Purpose & Gravity Convection Ovens (Up to ~300°C)
These are the most common ovens found in a laboratory. They rely on natural convection, where hot air rises and cooler air sinks, to circulate heat.
This gentle airflow makes them ideal for simple heating and drying processes, such as drying glassware or performing moisture determination tests where disturbing the sample is a concern. Their simpler design limits their upper temperature and temperature uniformity.
Mechanical (Forced-Air) Convection Ovens (Up to ~350°C)
These ovens use an internal fan to actively circulate hot air throughout the chamber. This forced convection results in far superior temperature uniformity and stability compared to gravity models.
The consistent internal environment is critical for applications like sterilization, material testing, and certain curing processes that require a precise, repeatable temperature across the entire sample.
High-Temperature Ovens (400°C to 600°C+)
When processes like annealing, binder burnout, or advanced materials testing are required, a high-temperature oven is necessary. These are built for extreme heat.
They feature robust insulation, high-wattage heating elements, and reinforced chamber construction to safely and consistently maintain temperatures that would damage a standard oven. These are specialized instruments for demanding industrial and research applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an oven based on its maximum temperature alone can lead to inefficient or inaccurate results. Several factors must be balanced.
Uniformity vs. Max Temperature
An oven that can reach 350°C but has a temperature uniformity of ±15°C is far less useful for sensitive work than an oven that maxes out at 300°C with a uniformity of ±1.5°C. Uniformity—the temperature consistency across different points in the chamber—is often more critical than the peak temperature.
Cost and Energy Consumption
Higher maximum temperatures require more advanced insulation, more powerful heating elements, and more sophisticated controllers. This directly translates to a significantly higher purchase price and greater ongoing energy consumption.
Safety and Material Limits
Operating at high temperatures introduces significant safety risks. You must consider the auto-ignition temperature of any materials placed inside the oven. High-temperature applications often require specific ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) to manage fumes and prevent burns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should always be dictated by the demands of your specific application, not by a simple temperature rating.
- If your primary focus is routine drying or gentle warming: A standard gravity convection oven provides the necessary performance at the lowest cost.
- If your primary focus is sterilization, component testing, or any process needing high precision: A mechanical convection oven is the correct choice for its superior temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is materials science, annealing, or heat-treating: You must invest in a purpose-built high-temperature oven designed for these extremes.
Ultimately, defining your required temperature range, uniformity, and process sensitivity will guide you to the correct instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Oven Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity Convection | Up to ~300°C | Natural air circulation, gentle heating | Routine drying, moisture determination |
| Mechanical Convection | Up to ~350°C | Fan-forced air, superior temperature uniformity | Sterilization, precise material testing |
| High-Temperature | 400°C to 600°C+ | Robust insulation, high-wattage elements | Annealing, binder burnout, materials testing |
Need the Right Laboratory Oven for Your Application?
Choosing the correct oven is critical for the accuracy, safety, and efficiency of your work. The maximum temperature is just one factor; temperature uniformity, construction, and intended use are equally important.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including a full range of laboratory ovens tailored to diverse needs. Whether you require a standard model for drying or a high-temperature oven for advanced materials testing, we can help you select the ideal instrument for your specific process requirements.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide



















