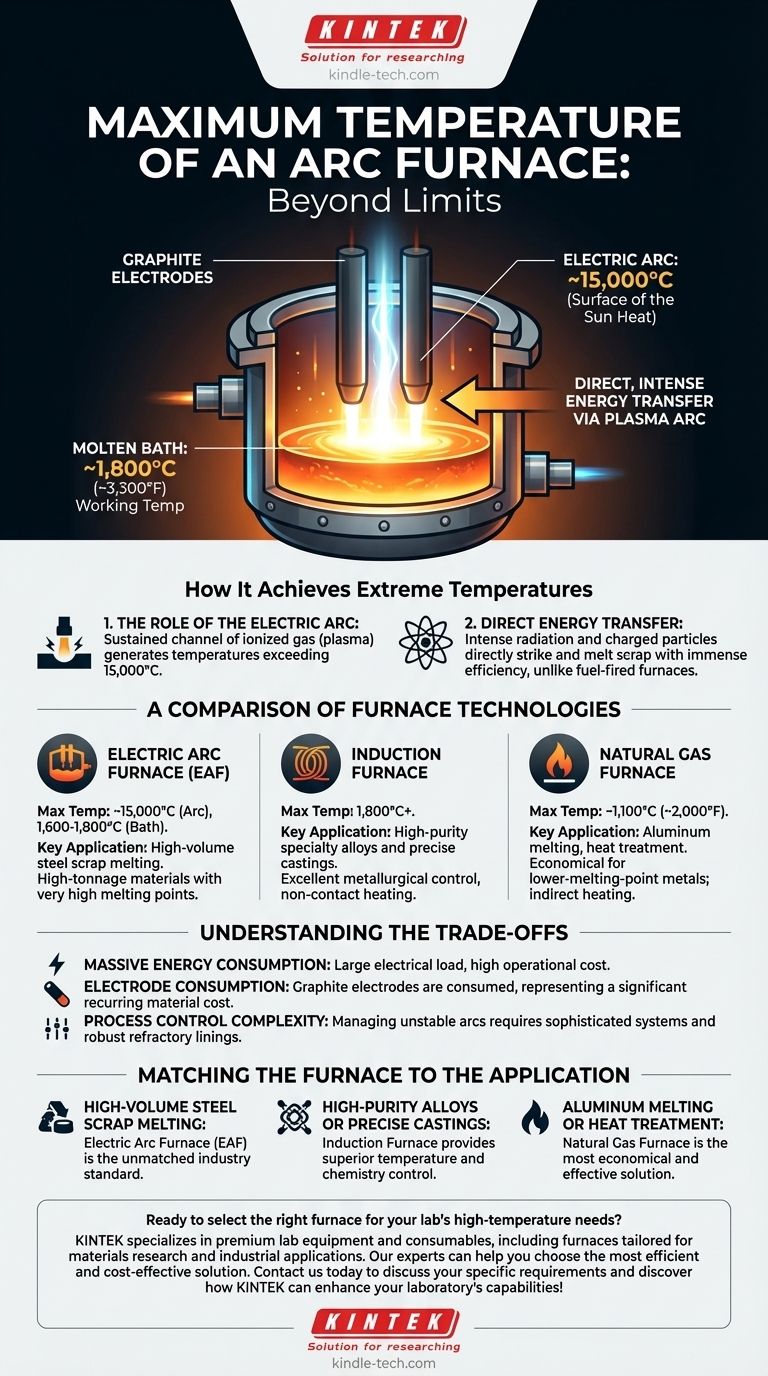
In practical terms, an electric arc furnace (EAF) operates with a molten metal bath at temperatures around 1,800°C (approximately 3,300°F). However, the electric arc itself—the source of the heat—can reach temperatures far higher, often cited as approaching the surface temperature of the sun.
The defining characteristic of an arc furnace isn't just its high operational temperature, but its method of direct, intense energy transfer via a plasma arc. This makes it uniquely suited for melting high-tonnage materials with very high melting points, such as steel scrap.
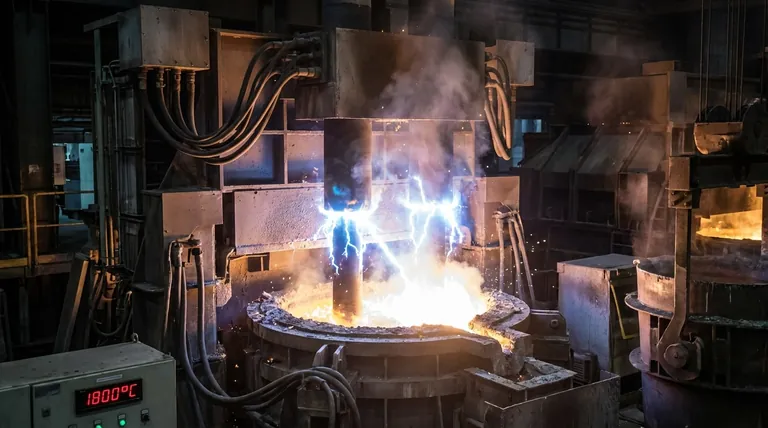

How an Arc Furnace Achieves Extreme Temperatures
Understanding the mechanism of an arc furnace reveals why it can achieve temperatures far beyond conventional combustion or induction methods.
The Role of the Electric Arc
The heart of the furnace is the high-power electric arc generated between large graphite electrodes and the metallic charge (the material to be melted).
This arc is not a simple spark; it's a sustained channel of plasma, an ionized gas that is incredibly hot. This is where the extreme temperatures, sometimes estimated in excess of 15,000°C, are generated.
Direct Energy Transfer
Unlike a fuel-fired furnace that heats the chamber's atmosphere, the arc furnace transfers energy with immense efficiency. The intense radiation and charged particles from the arc directly strike the scrap metal, causing rapid and localized melting.
Practical Operating Temperatures
While the arc itself is extraordinarily hot, the primary goal is to create a homogenous molten bath of metal. For steelmaking, this bath is controlled and maintained at a working temperature of approximately 1,600°C to 1,800°C to facilitate refining and casting.
A Comparison of Furnace Technologies
The choice of furnace technology is dictated entirely by the material and the desired outcome. The temperatures they can achieve reflect their core purpose.
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
An EAF is the workhorse for recycling steel scrap. Its ability to rapidly generate extreme heat makes it the premier choice for melting down large volumes of dense, high-melting-point material.
Induction Furnace
An induction furnace heats metal without direct contact. It uses powerful magnetic fields to induce an electric current within the charge material itself, heating it from the inside out.
As noted, these can reach 1,800°C or more. They offer excellent metallurgical control and are often preferred for producing high-purity specialty alloys and in foundries.
Natural Gas Furnace
A natural gas furnace relies on the combustion of fuel to heat a chamber. It is a form of indirect heating and is limited by the chemistry of combustion.
With maximum temperatures around 1,100°C (2,000°F), these furnaces are ideal for processing lower-melting-point metals like aluminum or for applications like heat treatment, but they cannot melt steel efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The immense power of an arc furnace comes with significant operational considerations.
Massive Energy Consumption
An EAF is one of the largest single electrical loads on any power grid. The cost of electricity is a primary factor in its operational expense.
Electrode Consumption
The graphite electrodes are not permanent. They are slowly consumed during the melting process through sublimation and breakage, representing a significant recurring material cost.
Process Control Complexity
Managing the stability of a multi-megawatt arc and protecting the furnace walls from its intense radiation requires sophisticated control systems and robust refractory linings.
Matching the Furnace to the Application
Choosing the correct heating technology is a critical engineering and financial decision based entirely on the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is high-volume steel production from scrap: The electric arc furnace is the unmatched industry standard for its raw melting power.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity specialty alloys or precise castings: An induction furnace provides superior temperature and chemistry control.
- If your primary focus is melting aluminum or performing heat treatment: A natural gas furnace is the most economical and effective solution.
Ultimately, the right technology is the one that delivers the necessary thermal energy to your material in the most controlled and cost-effective manner.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Maximum Temperature | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | ~15,000°C (Arc), 1,600-1,800°C (Bath) | High-volume steel scrap melting |
| Induction Furnace | 1,800°C+ | High-purity alloys, precise castings |
| Natural Gas Furnace | ~1,100°C | Aluminum melting, heat treatment |
Ready to select the right furnace for your lab's high-temperature needs? KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces tailored for materials research and industrial applications. Whether you're melting metals, synthesizing materials, or conducting heat treatments, our experts can help you choose the most efficient and cost-effective solution. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification



















