In materials science, cryomilling is a high-energy mechanical milling process performed at cryogenic temperatures, typically using liquid nitrogen. It is used to grind powders into extremely fine particles, often on the nanometer scale. By making materials brittle and absorbing the heat of the milling process, cryomilling creates unique nanocrystalline structures that significantly enhance material strength and performance.
The core purpose of cryomilling is not simply to make powders smaller. It is a sophisticated technique to precisely control a material's internal grain structure at the nanoscale, creating advanced materials with properties that are impossible to achieve with traditional milling methods.
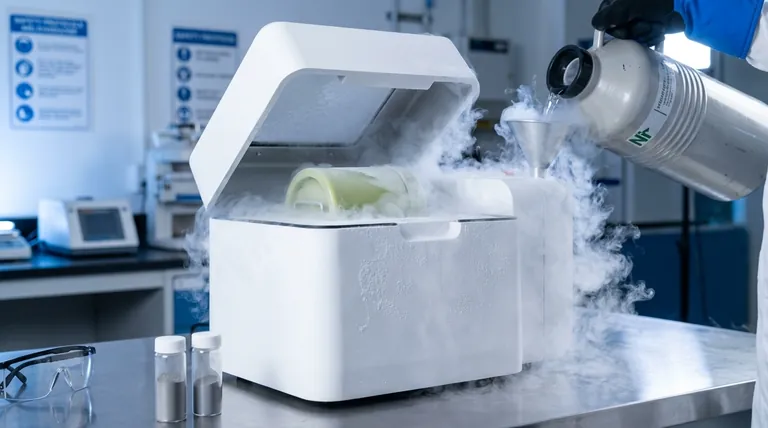

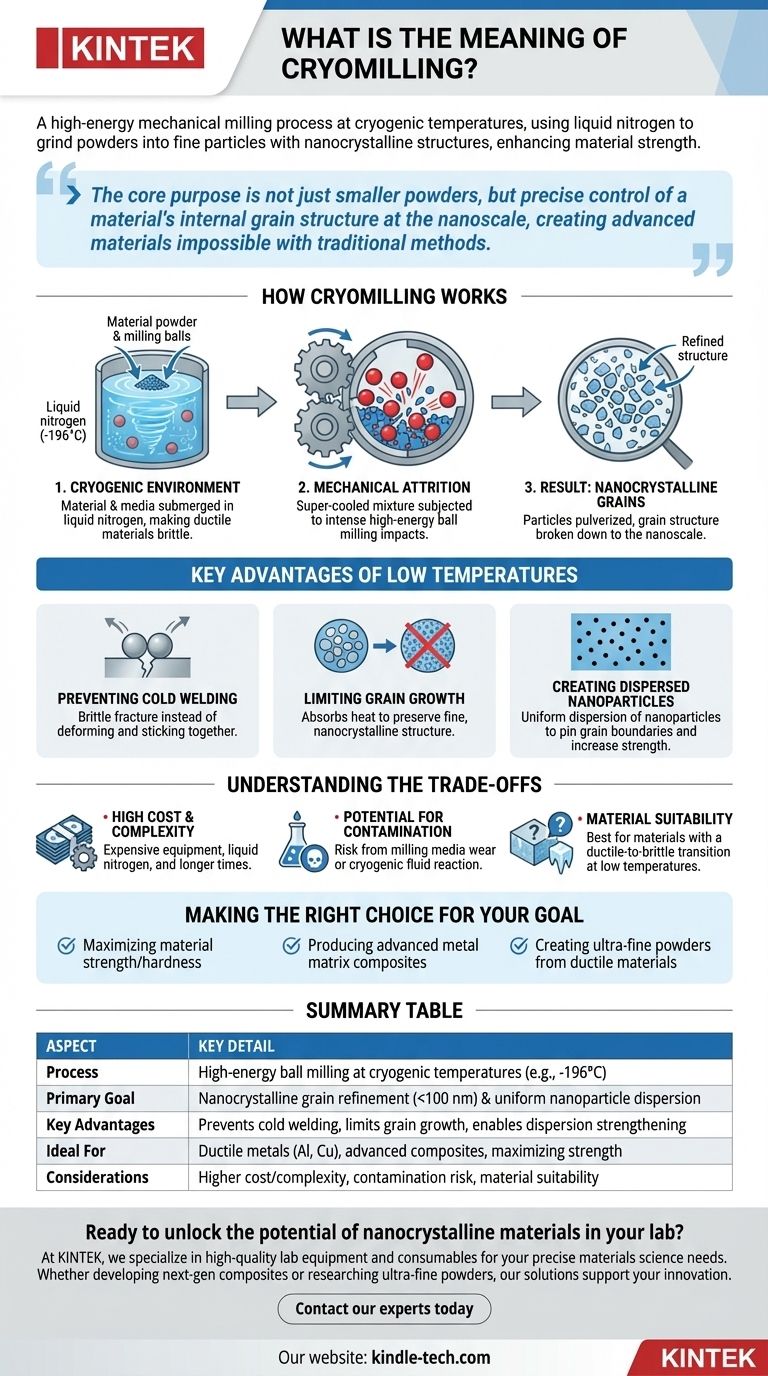
How Cryomilling Works
Cryomilling combines two distinct processes—mechanical attrition and a cryogenic environment—to achieve its unique results. Understanding each component reveals why the technique is so effective.
The Cryogenic Environment
The process begins by immersing the material powder and the milling media (typically steel or tungsten carbide balls) in a cryogenic fluid, most commonly liquid nitrogen (-196°C or -321°F). This extreme cold is critical, as it makes ductile materials brittle and easy to fracture.
The Mechanical Attrition
Inside a sealed, insulated vial, the super-cooled mixture is subjected to intense mechanical attrition, usually in a high-energy ball mill. The milling media repeatedly collide with the material powder, fracturing the particles with tremendous force.
The Result: Nanocrystalline Grains
The combination of embrittlement and high-energy impacts pulverizes the material. More importantly, it breaks down the internal crystal grain structure of the particles, refining them to a nanocrystalline scale (typically under 100 nanometers).
The Key Advantages of Low Temperatures
Performing the milling process at cryogenic temperatures is what separates cryomilling from conventional methods. This environment solves several fundamental problems that occur during room-temperature milling.
Preventing Cold Welding
Ductile metals, like aluminum or copper, tend to flatten and weld together under the pressure of milling. The cryogenic temperatures make these metals brittle, causing them to fracture cleanly instead of deforming and sticking together.
Limiting Grain Growth
Standard milling generates significant localized heat, which can cause the newly formed nanograins to immediately grow larger, a process called recrystallization. The liquid nitrogen bath constantly absorbs this heat, preserving the fine, nanocrystalline structure that gives the material its enhanced strength.
Creating Dispersed Nanoparticles
Cryomilling also allows for the uniform dispersion of nanometer-scale particles throughout a material, a technique known as dispersion strengthening. These particles, which can be oxides or nitrides formed in-situ or other added compounds, pin the grain boundaries and further increase the material's strength and stability at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, cryomilling is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not a universal solution for all powder processing needs.
High Cost and Complexity
The use of liquid nitrogen, insulated milling equipment, and longer processing times makes cryomilling significantly more expensive and complex than conventional milling.
Potential for Contamination
There is a risk of contamination from two sources. The milling media can wear down and introduce impurities, while the cryogenic fluid itself can react with some materials (e.g., forming nitrides from liquid nitrogen).
Material Suitability
The technique is most effective for materials that exhibit a distinct ductile-to-brittle transition at low temperatures. While applicable to many metals, polymers, and ceramics, its benefits may be less pronounced for materials that are already inherently brittle at room temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Cryomilling is chosen when the goal is to fundamentally alter a material's microstructure for superior performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material strength and hardness: Cryomilling is the premier method for achieving grain size refinement down to the nanoscale, which dramatically improves mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced metal matrix composites: The process excels at uniformly dispersing secondary strengthening particles (like oxides or carbides) within a metal powder.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-fine powders from ductile materials: The cryogenic embrittlement effect is essential for preventing agglomeration and achieving nanometer-scale particle sizes that are otherwise impossible.
Ultimately, cryomilling empowers engineers to create a new class of materials by precisely manipulating their structure at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-energy ball milling at cryogenic temperatures (e.g., -196°C with liquid nitrogen) |
| Primary Goal | Nanocrystalline grain refinement (<100 nm) and uniform nanoparticle dispersion |
| Key Advantages | Prevents cold welding, limits grain growth, enables dispersion strengthening |
| Ideal For | Ductile metals (Al, Cu), creating advanced metal matrix composites, maximizing strength/hardness |
| Considerations | Higher cost/complexity, potential for contamination, material suitability |
Ready to unlock the potential of nanocrystalline materials in your lab?
Cryomilling is a sophisticated technique for creating advanced materials with enhanced strength and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your precise materials science needs. Whether you are developing next-generation metal matrix composites or researching ultra-fine powders, our solutions are designed to support your innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can help you achieve superior results with cryomilling and other advanced processing techniques.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is cool grinding technology? Unlock Efficient Milling for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What role does a grinder play in the preparation of ultra-fine tungsten trioxide powder? Ensure Material Uniformity
- Why is a cryogenic grinder required for cured alkyd resin HRMAS NMR? Ensure Structural Integrity & Sample Precision
- What is cryogenic grinding of cardamom? Preserve Flavor, Aroma & Color with Extreme Cold
- What is the process of cryogenic milling? Achieve Fine Powders from Tough Materials
- What is the process of cryogenic ball milling? Achieve Superior Nanomaterial Synthesis
- What is the role of cryogenic grinding equipment in the pre-treatment of PTFE binders for dry electrode production?
- What food is cryogenic grinding? The Ultimate Guide to Preserving Flavor & Aroma



















