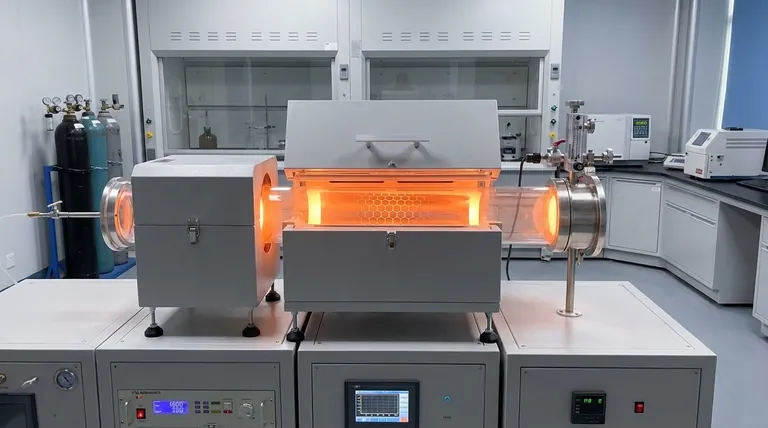
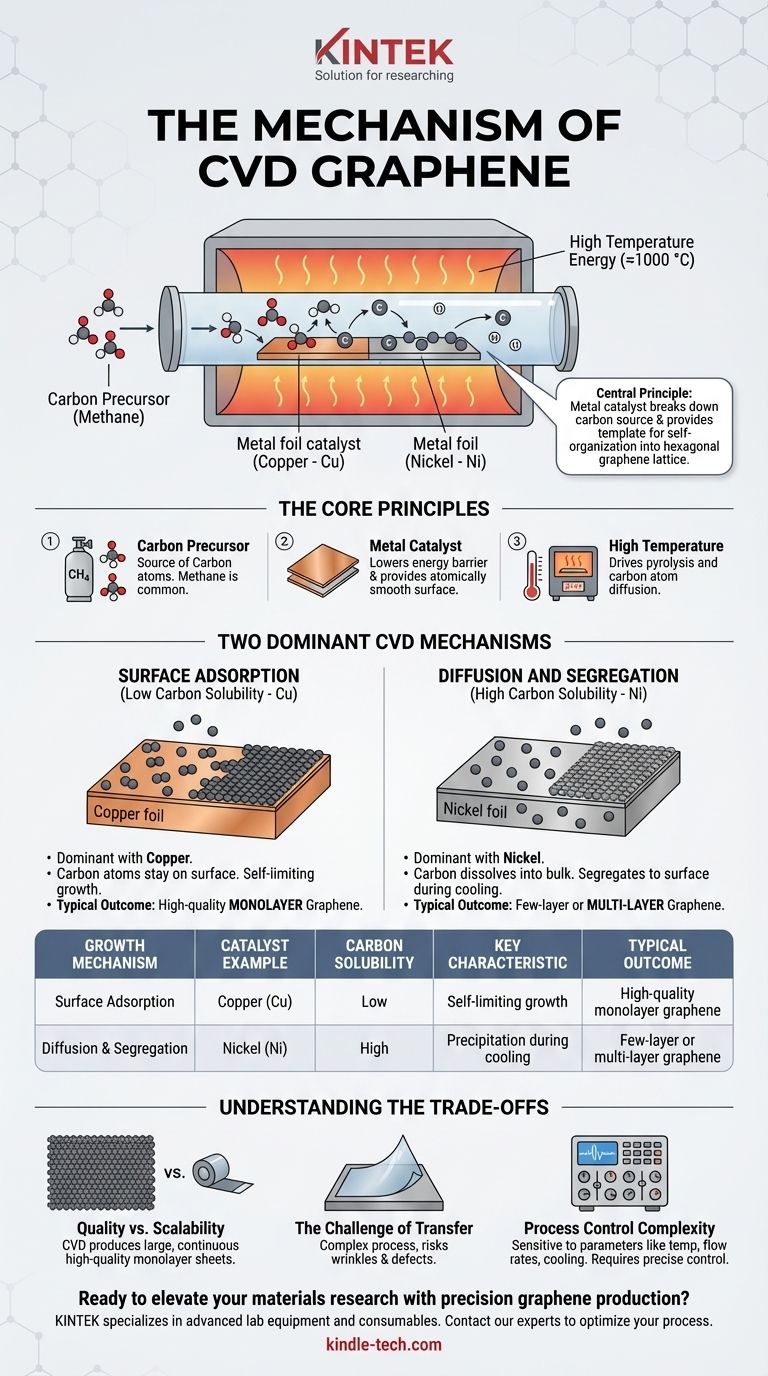
At its core, the mechanism of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for graphene is a controlled, high-temperature process that "assembles" a single layer of carbon atoms onto a catalytic metal surface. A carbon-containing gas, such as methane, is introduced into a furnace where it decomposes on a heated metal foil, typically copper. These individual carbon atoms then diffuse across the metal surface, linking together to form a continuous, one-atom-thick sheet of graphene.
The central principle of graphene CVD is using a metal catalyst to accomplish two tasks simultaneously: breaking down a carbon source gas and providing an atomically flat template on which the resulting carbon atoms can self-organize into the hexagonal graphene lattice. The choice of metal fundamentally dictates the growth mechanism and the final quality of the film.

The Core Principles of Graphene CVD
To understand the mechanism, it's essential to break the process down into its three critical components: the precursor, the catalyst, and the energy source.
The Role of the Carbon Precursor
The process begins with a carbon-containing gas, known as a precursor. Methane (CH₄) is the most common choice.
This gas is pumped into a vacuum chamber, acting as the raw material from which the carbon atoms are harvested.
The Function of the Metal Catalyst
A metal foil, most often copper (Cu) or sometimes nickel (Ni), serves as the substrate and catalyst. Its role is twofold.
First, it dramatically lowers the energy barrier required to break the chemical bonds of the precursor gas. This allows the gas to decompose and release its carbon atoms at manageable temperatures (around 1000 °C).
Second, it provides an atomically smooth surface for the carbon atoms to move across and arrange themselves into the stable, hexagonal structure of graphene.
The Importance of High Temperature
Heat is the engine that drives the entire reaction. The high temperature inside the furnace provides the necessary thermal energy for two key steps.
It facilitates the pyrolysis, or thermal decomposition, of the precursor gas on the catalyst's surface. It also gives the carbon atoms enough kinetic energy to diffuse freely across the metal surface and find the most energetically favorable positions to form the graphene lattice.
Two Dominant CVD Mechanisms
The specific type of metal catalyst used determines which of two primary growth mechanisms will occur. This choice is based on the metal's carbon solubility—its ability to absorb carbon atoms into its bulk structure.
Surface Adsorption (Low Carbon Solubility)
This is the dominant mechanism when using copper (Cu), which has very low carbon solubility.
In this process, carbon atoms stay exclusively on the surface of the copper foil. They adsorb, diffuse, and nucleate into small graphene "islands." These islands grow outwards as more carbon atoms attach to their edges until they merge into a complete sheet.
Because carbon cannot dissolve into the copper, the process is self-limiting. Once a full layer of graphene covers the surface, it prevents the catalyst from decomposing more methane, effectively stopping the growth. This makes copper the ideal catalyst for producing high-quality, large-area monolayer graphene.
Diffusion and Segregation (High Carbon Solubility)
This mechanism occurs when using catalysts like nickel (Ni), which has a high solubility for carbon at elevated temperatures.
Here, carbon atoms from the precursor gas first dissolve into the bulk nickel, much like sugar dissolving in hot water. The graphene does not form immediately.
Instead, formation happens during the cooling phase. As the nickel cools, its ability to hold carbon decreases, and the dissolved carbon atoms "precipitate" or segregate back to the surface, where they crystallize into graphene layers. This method is harder to control and often results in multiple or non-uniform layers of graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While CVD is the most promising method for industrial-scale graphene production, it is not without its challenges.
Quality vs. Scalability
The primary advantage of CVD is its ability to produce large, continuous sheets of high-quality monolayer graphene, far surpassing the size limitations of methods like mechanical exfoliation (the "Scotch tape" method).
The Challenge of Transfer
Graphene grown via CVD is formed on a metal foil and is almost always intended for use on a different substrate, such as a silicon wafer. This requires a complex transfer process to move the fragile, one-atom-thick film, which can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination that degrade its properties.
Process Control Complexity
The final quality of the graphene is extremely sensitive to process parameters. Minor variations in temperature, gas flow rates, pressure, and cooling rates can significantly impact the uniformity, domain size, and defect density of the final film. Achieving consistent, high-quality results requires precise control over the entire environment.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your reason for investigating the CVD mechanism will determine which aspects are most important to you.
- If your primary focus is large-area, high-quality monolayer graphene for electronics: The self-limiting surface adsorption mechanism on copper is the industry-standard method you need to master.
- If your primary focus is producing few-layer or multi-layer graphene directly: The diffusion and segregation mechanism on nickel is a potential route, but be aware of the inherent challenges in controlling layer thickness.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Understanding how catalyst carbon solubility dictates the growth mechanism is the key to experimenting with new alloy catalysts or alternative substrates.
Ultimately, mastering CVD graphene production is a matter of precisely controlling the surface chemistry and thermodynamics of the catalyst system.
Summary Table:
| Growth Mechanism | Catalyst Example | Carbon Solubility | Key Characteristic | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Adsorption | Copper (Cu) | Low | Self-limiting growth | High-quality monolayer graphene |
| Diffusion & Segregation | Nickel (Ni) | High | Precipitation during cooling | Few-layer or multi-layer graphene |
Ready to elevate your materials research with precision graphene production?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge laboratory applications. Whether you are developing next-generation electronics or conducting surface chemistry research, our CVD systems and expert support can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our solutions can optimize your graphene synthesis process and accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















