Microwave sintering is a high-speed thermal process that uses microwave radiation to heat and compact a powdered material into a solid mass. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside in, microwave energy penetrates the material and generates heat volumetrically, creating a rapid and uniform temperature rise from within.
The core advantage of microwave sintering over conventional methods is its ability to heat materials internally. This fundamental difference leads to dramatically faster processing times, superior temperature uniformity, and greater energy efficiency, fundamentally changing the economics and quality of material production.

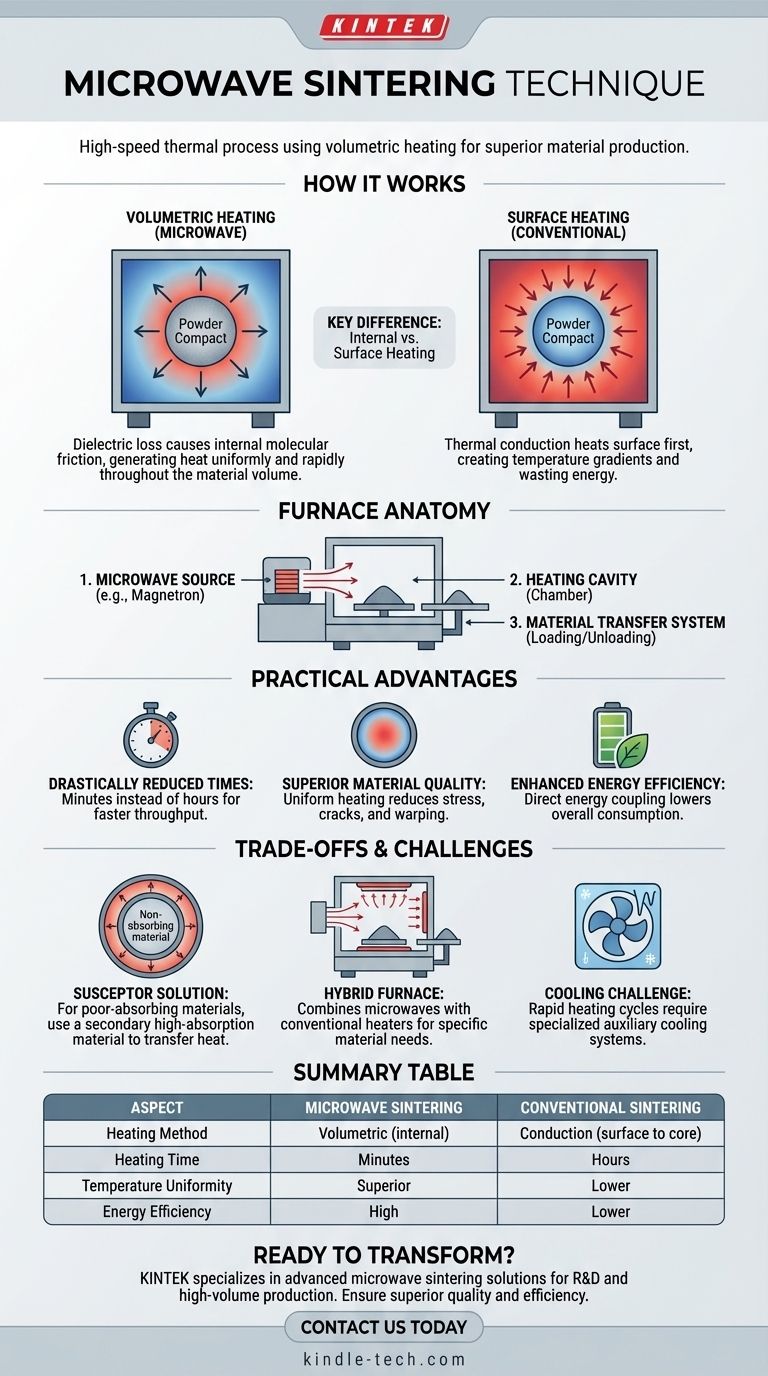
How Microwave Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering is the process of turning a powder into a solid piece using heat and pressure, all below the material's melting point. Microwave sintering achieves this with a unique heating mechanism.
From Radiation to Internal Heat
The process leverages a principle called dielectric loss. When exposed to a microwave electromagnetic field, certain materials experience friction at a molecular level as their internal structure tries to align with the rapidly changing field.
This internal friction generates heat directly and simultaneously throughout the entire volume of the material. It is the same principle that heats food in a home microwave oven, but applied with industrial precision to materials like ceramics.
The Key Difference: Volumetric vs. Surface Heating
A conventional furnace relies on thermal conduction. It heats the outer surface of the material first, and that heat must slowly travel toward the core. This creates a significant temperature gradient, is slow, and wastes energy heating the furnace chamber.
Microwave sintering provides volumetric heating. By generating heat everywhere at once, it nearly eliminates internal temperature gradients, reduces thermal stress, and shortens the heating cycle from hours to minutes.
The Anatomy of a Microwave Furnace
A typical microwave sintering furnace consists of three primary parts:
- A microwave source (like a magnetron) to generate the radiation.
- A heating cavity or chamber where the material is placed.
- A material transfer system for loading and unloading, enabling either batch or continuous processing.
These furnaces can be designed to operate under a controlled atmosphere or vacuum, depending on the material's requirements.
The Practical Advantages of Speed and Uniformity
The unique heating mechanism of microwave sintering translates directly into significant operational benefits.
Drastically Reduced Sintering Times
Because the material heats instantly from within, the time required to reach the target sintering temperature is dramatically reduced. This rapid heating rate is the most celebrated advantage, increasing production throughput significantly.
Superior Material Quality
Uniform heating minimizes the temperature difference between the surface and the core of the part. This reduces the risk of internal stresses, cracks, or warping, resulting in a more consistent and structurally sound final product.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
By delivering energy directly to the material that needs to be heated, microwave sintering is far more efficient than heating an entire conventional furnace chamber. This direct coupling of energy reduces overall consumption and lowers operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful implementation.
The Susceptor Solution for Non-Absorbing Materials
Not all materials respond effectively to microwave energy, especially at lower temperatures. A common example is monoclinic zirconia.
For these materials, a susceptor is used. A susceptor is a secondary material with high microwave absorption (like silicon carbide) that is placed in the furnace with the target material. The susceptor heats up rapidly and transfers its thermal energy to the non-absorbing material through traditional radiation and conduction.
The Hybrid Furnace Approach
Another solution for poor-absorbing materials is a hybrid furnace. This design combines microwave energy with conventional electrical heating elements. The conventional heaters raise the material's temperature to a point where it begins to absorb microwave energy effectively, at which point the microwaves take over for rapid, volumetric heating.
The Cooling Challenge
The rapid heating cycle can create a new bottleneck: cooling. The specialized equipment can become very hot, and managing this heat to allow for safe and timely removal of the sintered parts may require auxiliary cooling systems, adding complexity to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your specific material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and speed: Microwave sintering is an excellent choice due to its incredibly fast heating cycles.
- If you are working with complex geometries or materials prone to thermal stress: The uniform, internal heating of microwaves provides superior part integrity and reduces failure rates.
- If your material has low microwave absorption: You must be prepared to use a susceptor or invest in a hybrid furnace, which adds process variables and cost.
By understanding its principles and limitations, you can leverage microwave sintering to achieve superior material properties with unmatched efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Microwave Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Volumetric (internal) | Conduction (surface to core) |
| Heating Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Temperature Uniformity | Superior (reduced gradients) | Lower (significant gradients) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (direct material heating) | Lower (chamber heating required) |
Ready to transform your lab's material processing capabilities?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including microwave sintering solutions. Our furnaces are designed to deliver the rapid, uniform heating that accelerates your R&D and production while ensuring superior material quality and energy efficiency.
Whether you're working with ceramics, complex geometries, or high-volume production, KINTEK has the expertise and technology to meet your specific sintering needs.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK microwave sintering system can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and output!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of firing porcelain in a vacuum? Achieve Denser, Stronger, and More Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Why are porcelain fired under vacuum? To Eliminate Porosity for Superior Strength & Translucency
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the function of a porcelain furnace? Precision Firing for Lifelike Dental Restorations
- What are five applications of soldering? From Electronics to Art, Master Material Joining



















