The most important part of preheating is not simply reaching a specific temperature, but rather slowing the cooling rate of the entire weld area after welding is complete. While a target temperature is necessary, the ultimate goal is to reduce the thermal shock that causes cracking and brittleness, ensuring a strong and ductile final weld.
Preheating is fundamentally a process of thermal control. Its primary purpose is to prevent the formation of brittle microstructures and reduce residual stress by minimizing the temperature difference between the molten weld puddle and the surrounding base metal.

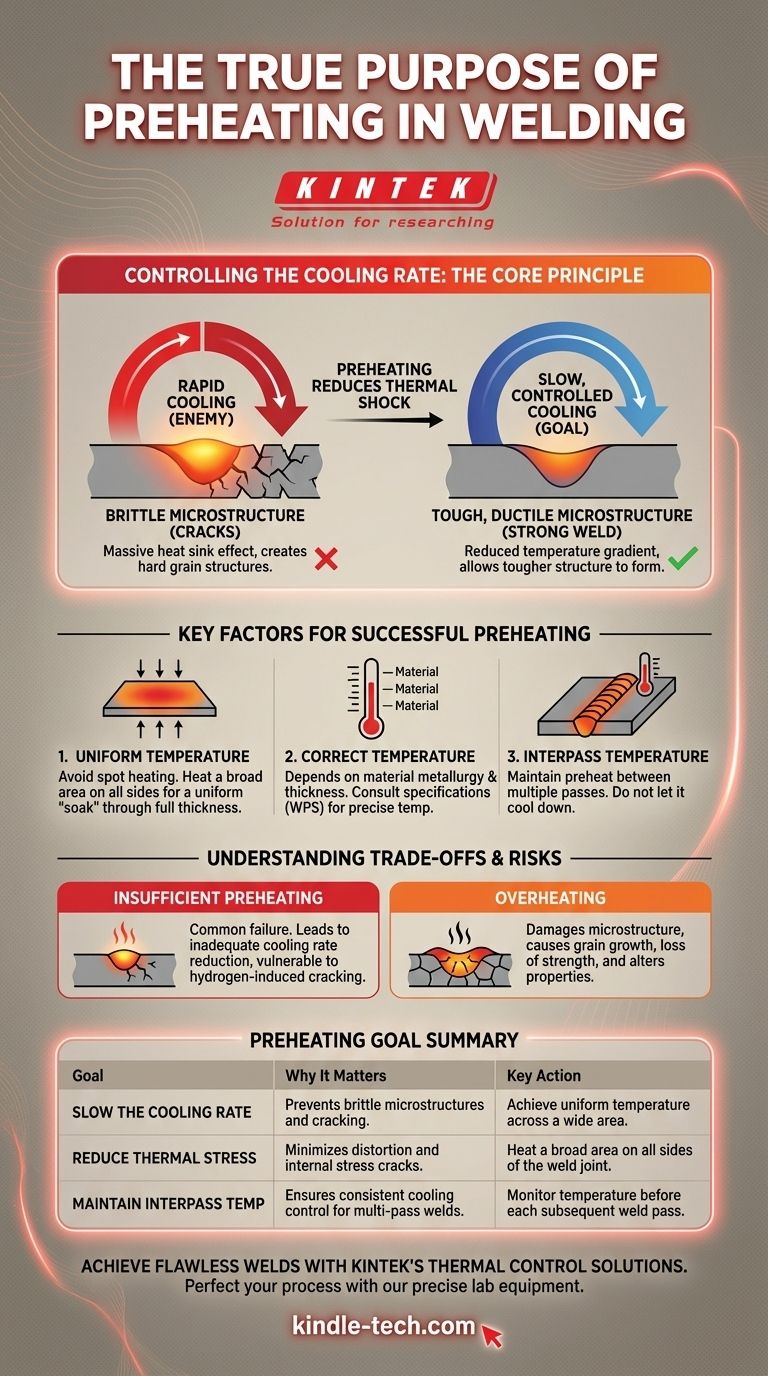
The Core Principle: Controlling the Cooling Rate
The success or failure of a weld on certain materials often comes down to the speed at which it cools. Preheating is your primary tool for controlling this speed.
Why Rapid Cooling is the Enemy
When you weld, you create an area of molten metal that is thousands of degrees hotter than the base material around it.
If the surrounding metal is cold, it acts like a massive heat sink, pulling heat away from the weld at an extremely high rate. This rapid cooling, or quenching, can create a hard and brittle grain structure (like martensite in carbon steels) that is highly susceptible to cracking.
How Preheating Slows Things Down
By heating the base metal before you begin welding, you significantly reduce the temperature difference between the weld pool and the parent material.
This smaller temperature gradient means the heat dissipates much more slowly. A slow, controlled cooling process allows a tougher, more ductile microstructure to form, dramatically reducing the risk of post-weld cracking.
Reducing Thermal Stress and Distortion
Preheating also helps manage mechanical forces. Heating a large area causes the base metal to expand before welding begins.
As the weld and the preheated zone cool together, they shrink more uniformly. This minimizes the internal stress that builds up from uneven shrinkage, which is a primary cause of both distortion and stress-related cracks.
Key Factors for Successful Preheating
Achieving the desired slow cooling rate requires more than just pointing a torch at the metal. Focus on these critical factors.
Achieving Uniform Temperature
The most common mistake is spot heating—only heating the immediate weld joint. This is ineffective and can even increase stress.
You must heat a broad area on all sides of the weld joint. The goal is a uniform "soak," where the heat penetrates through the full thickness of the material. For small parts, an oven is ideal. For larger fabrications, use a large heating torch in a constant, sweeping motion to avoid creating hot spots.
Determining the Correct Temperature
The required preheat temperature is not a single number; it depends entirely on the material's metallurgy and thickness.
Factors like the carbon content of steel, the alloy type, and the thickness of the part dictate the necessary temperature. A preheat of 120°C (250°F) might be sufficient for a piece of cast iron, while a thick section of high-strength alloy steel might require over 250°C (500°F). Always consult the material specifications or a welding procedure specification (WPS).
Maintaining Interpass Temperature
For welds that require multiple passes, the preheat temperature must be maintained. This is known as the interpass temperature.
Letting the part cool down between passes defeats the entire purpose of preheating. You must check the temperature before laying down each subsequent bead to ensure the cooling rate remains slow and controlled throughout the entire process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential, preheating must be done correctly. Improper application introduces its own set of problems.
The Danger of Insufficient Preheating
This is the most common failure. Under-heating or heating too small of an area will not slow the cooling rate enough to prevent cracking. It provides a false sense of security while leaving the weld vulnerable to failure, especially from hydrogen-induced cracking.
The Problem with Overheating
More is not always better. Exceeding the recommended preheat temperature for a given material can damage its microstructure, leading to a loss of strength or toughness. Overheating can cause excessive grain growth or alter the properties imparted by previous heat treatments.
How to Apply This to Your Weld
Focus on the underlying goal of the preheat to guide your actions.
- If your primary focus is preventing cracks in cast iron or high-carbon steel: Concentrate on achieving a slow, uniform cool-down. This may involve wrapping the part in a thermal blanket after welding to slow the cooling even further.
- If your primary focus is welding thick material sections: Ensure the heat has fully "soaked" through the entire thickness of the part to reduce internal stresses that cause cracking deep within the joint.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on a large assembly: Prioritize heating a wide, uniform area around the joint to balance the thermal expansion and subsequent contraction.
By understanding that preheating is about controlling the cooling rate, you move from simply following a rule to mastering the welding process.
Summary Table:
| Key Preheating Goal | Why It Matters | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Slow the Cooling Rate | Prevents brittle microstructures and cracking. | Achieve uniform temperature across a wide area. |
| Reduce Thermal Stress | Minimizes distortion and internal stress cracks. | Heat a broad area on all sides of the weld joint. |
| Maintain Interpass Temperature | Ensures consistent cooling control for multi-pass welds. | Monitor temperature before each subsequent weld pass. |
Achieve Flawless Welds with KINTEK's Thermal Control Solutions
Perfecting your preheating process is essential for strong, crack-free welds. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise, reliable lab equipment and consumables that support critical thermal processes like material testing and preparation.
Whether you're developing new welding procedures or ensuring material integrity, our tools help you maintain the exact temperatures needed for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your welding and material testing workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory oven in MnO2-GAC synthesis? Optimize Your Catalyst Preparation
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- Why do ceramics need to be sintered? Unlock Strength and Durability Through High-Temperature Fusion



















