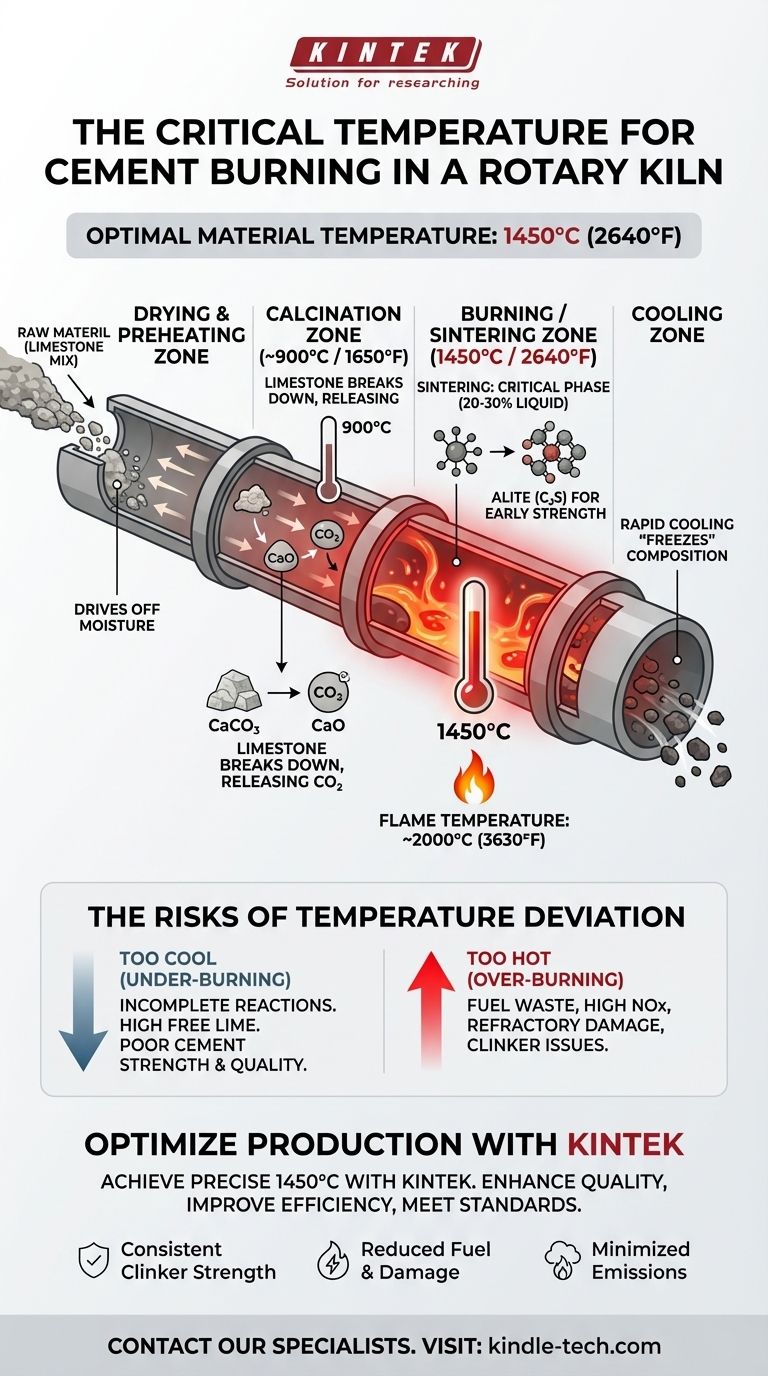
In cement manufacturing, the most suitable temperature for the burning process is a material temperature of approximately 1450°C (2640°F) within the rotary kiln's sintering zone. This specific temperature is not arbitrary; it is the critical point required to transform the raw mix into high-quality cement clinker through a process called sintering, where the material becomes partially liquid to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions.
The goal is not simply to heat the material, but to achieve a precise thermal profile. The critical material temperature of 1450°C in the burning zone ensures the formation of essential strength-giving compounds, while temperatures that are too high or too low will compromise the final product's quality and the kiln's operational stability.
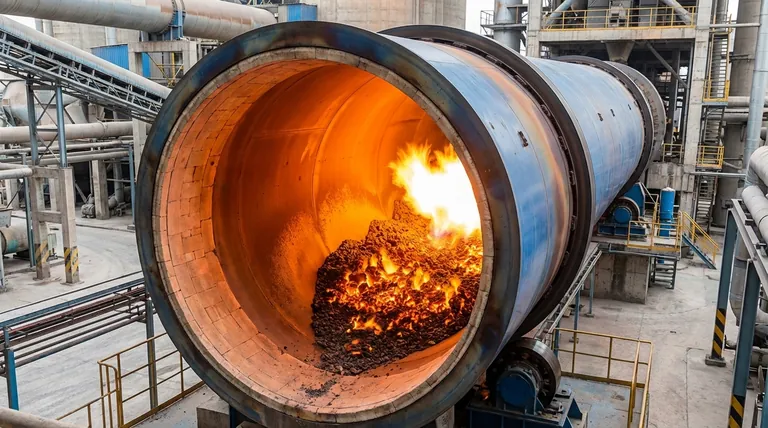

The Journey Through the Kiln: A Process of Transformation
A rotary kiln is not a simple furnace with one temperature. It's a long, rotating cylinder with a carefully controlled temperature gradient that guides the raw material through several distinct chemical transformations.
The Drying and Preheating Zone
As the raw mix enters the upper end of the kiln, it first encounters temperatures that drive off any free water. In modern systems with preheaters, this stage happens before the material even enters the kiln, significantly improving efficiency.
The Calcination Zone (Approx. 900°C)
This is the first major chemical event. Around 900°C (1650°F), the limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) in the raw mix undergoes calcination, breaking down into calcium oxide (CaO), also known as free lime, and releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO₂).
The Burning (Sintering) Zone (Approx. 1450°C)
This is the heart of the process and the hottest part of the kiln. The material temperature must reach approximately 1450°C. At this point, the material is not fully melted but enters a state of sintering, where about 20-30% of it becomes a liquid phase. This liquid acts as a solvent, facilitating the reaction between the calcium oxide (CaO) and other components (silica, alumina, iron oxide) to form the essential clinker minerals.
The Cooling Zone
After exiting the burning zone, the newly formed clinker is cooled rapidly. This rapid cooling is crucial to "freeze" the clinker's mineral composition, particularly preserving the highly reactive form of its primary strength-giving compound.
Why 1450°C is the Critical Target
Achieving this specific temperature is a matter of fundamental chemistry and process engineering. It directly impacts product quality, operational cost, and equipment longevity.
Achieving the Right Chemistry: Forming Alite (C₃S)
The primary goal of the burning zone is to form Alite (Tricalcium Silicate, C₃S). This mineral is the main driver of cement's early strength development. Its formation requires the high energy provided by temperatures around 1450°C.
The Role of the Liquid Phase
Without the partial liquid phase that forms at these high temperatures, the chemical reactions would be impractically slow. The liquid allows ions to move freely and combine efficiently into the desired clinker minerals.
Flame Temperature vs. Material Temperature
It is important to distinguish between the material temperature (1450°C) and the flame temperature. To transfer enough energy to heat the material to 1450°C, the gas flame from the burner at the kiln's discharge end must be significantly hotter, often reaching 2000°C (3630°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Risks of Temperature Deviation
Maintaining a stable temperature in the burning zone is paramount. Deviations in either direction have serious consequences.
The Problem with Burning Too Cool (Under-burning)
If the material temperature fails to consistently reach 1450°C, the chemical reactions will be incomplete. This results in high levels of unreacted free lime in the clinker, which leads to poor quality cement with low strength and potential long-term instability (unsoundness).
The Dangers of Burning Too Hot (Over-burning)
Exceeding the target temperature is equally problematic. It wastes a significant amount of fuel, increases the production of harmful NOx emissions, and can cause severe damage to the kiln's protective refractory lining, leading to costly downtime and repairs. Over-burning can also create large, less-reactive clinker crystals and operational issues like ring formation inside the kiln.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "suitable" temperature is ultimately a function of balancing quality, cost, and stability. Kiln operators constantly monitor variables to maintain this balance.
- If your primary focus is product quality and strength: Ensure the material temperature profile is stable and consistently reaches 1450°C to minimize free lime and maximize Alite formation.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and cost reduction: Avoid over-burning to save fuel and protect the refractory lining. Implement advanced process controls to stabilize kiln operation and prevent temperature fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Tightly control the peak flame temperature and ensure stable, efficient combustion to minimize the formation of thermal NOx.
Ultimately, mastering the cement kiln is about maintaining that critical 1450°C material temperature with unwavering stability.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Zone | Key Temperature | Primary Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination Zone | ~900°C (1650°F) | Decomposition of limestone (CaCO₃) | Release of CO₂; formation of free lime (CaO) |
| Burning/Sintering Zone | 1450°C (2640°F) | Sintering (20-30% liquid phase) | Formation of Alite (C₃S) and other clinker minerals |
| Flame Temperature | ~2000°C (3630°F) | Heat transfer to material | Enables material to reach 1450°C |
Optimize Your Cement Production with KINTEK
Achieving and maintaining the precise 1450°C temperature is critical for high-quality clinker, but it requires reliable equipment and expert support. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for the cement industry, helping you monitor, control, and perfect your thermal processes.
- Enhance Product Quality: Ensure consistent clinker strength by accurately monitoring kiln temperatures.
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Reduce fuel costs and prevent refractory damage with precise thermal management.
- Meet Environmental Standards: Minimize emissions through stable and efficient combustion control.
Let our expertise support your laboratory and production needs. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can help you achieve optimal kiln performance and superior cement quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















