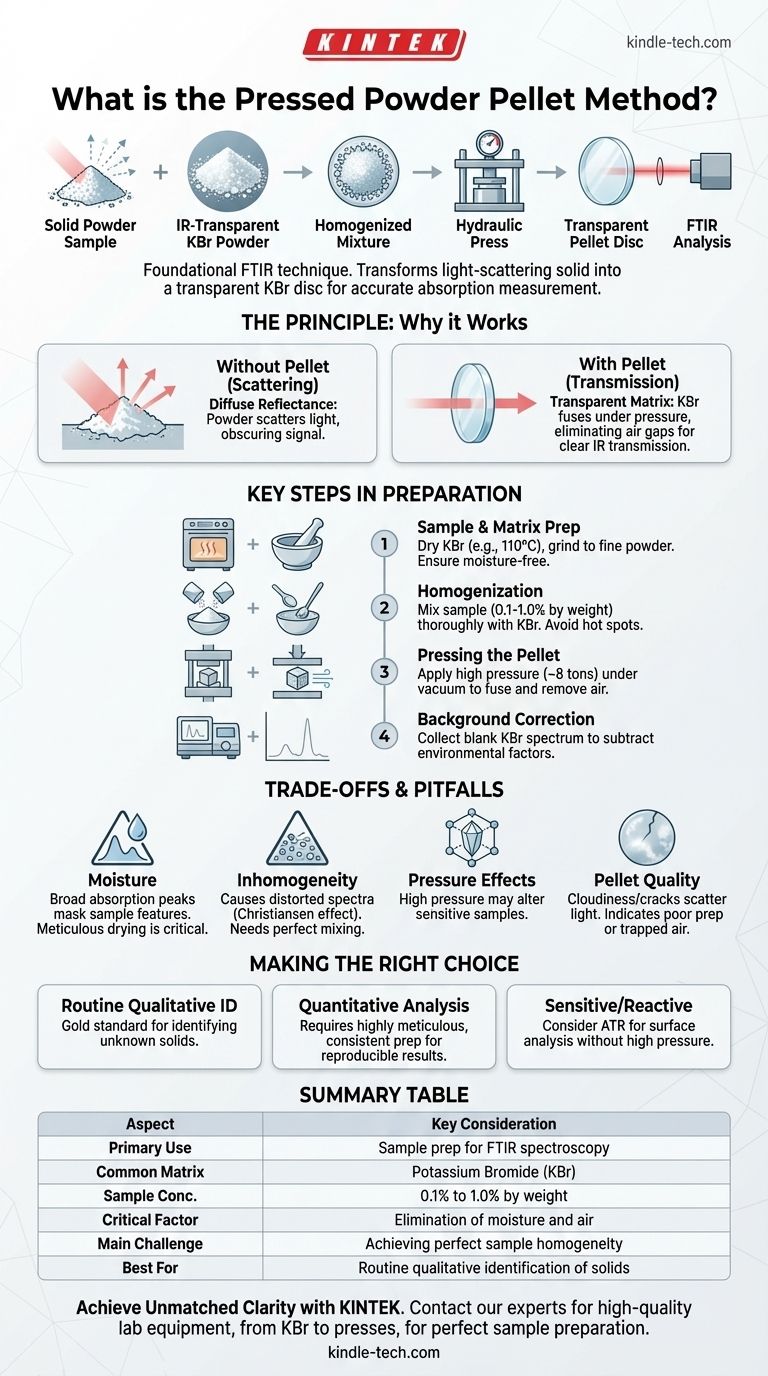
The pressed powder pellet method is a foundational technique for preparing solid samples for analysis, most commonly with Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It involves diluting a small amount of a solid sample in an infrared-transparent powder, typically potassium bromide (KBr), and compressing this mixture under immense pressure. The result is a thin, glass-like, transparent disc that allows an infrared beam to pass through it for measurement.
The ultimate goal of this method is to transform a light-scattering solid powder into a transparent medium. Success hinges on eliminating moisture and ensuring the sample is perfectly dispersed, as any imperfection will obscure the true analytical result.

The Principle Behind the Pellet Method
Infrared spectroscopy works by passing a beam of IR light through a sample and measuring what light is absorbed. For this to work with solids, the sample must be prepared in a way that minimizes light scattering and allows the beam to pass through cleanly.
Why a Pellet Is Necessary
Most solid samples, when ground into a fine powder, will scatter the vast majority of the light that hits them. This scattering effect, known as diffuse reflectance, prevents an accurate absorption measurement. The pellet method overcomes this by suspending the sample particles in a non-scattering, transparent matrix.
The Role of the Matrix Material
The choice of matrix is critical. The most common material, potassium bromide (KBr), is used because it is transparent to infrared radiation in the typical analysis range (4000 to 400 cm⁻¹) and is soft enough to deform under pressure. This means the KBr itself will not contribute any significant absorption peaks, allowing the spectrum of the diluted sample to be seen clearly.
How Pressure Creates Transparency
When the KBr and sample mixture is subjected to high pressure (often around 8 tons), the individual KBr crystals deform and fuse together. This process eliminates the tiny air gaps between particles, which are the primary cause of light scattering. The result is a solid, homogenous disc with optical properties similar to a piece of glass.
Key Steps in Pellet Preparation
Executing this technique requires precision. Each step is designed to minimize contamination and maximize the quality of the final pellet.
Step 1: Sample and Matrix Preparation
First, the matrix material (KBr) must be completely free of moisture, which strongly absorbs IR light. This is achieved by drying spectroscopic-grade KBr powder in an oven, typically at around 110°C for several hours. The KBr is also ground to a fine, consistent particle size (e.g., 200 mesh) to ensure it mixes well.
Step 2: Homogenization
The sample is added to the KBr at a very low concentration, usually 0.1% to 1.0% by weight. The two are then ground together, often with an agate mortar and pestle, until the mixture is perfectly uniform. Inadequate mixing is a common source of poor results.
Step 3: Pressing the Pellet
The homogenized powder is loaded into a specialized die set, which is placed in a hydraulic press. Pressure is applied gradually while a vacuum is often pulled on the die. The vacuum removes trapped air and any residual moisture, preventing the pellet from cracking or appearing cloudy.
Step 4: Background Correction
Before analyzing the sample pellet, a background spectrum is collected. This is done either with an empty pellet holder or, ideally, with a "blank" pellet made from pure KBr. This allows the instrument's software to subtract any spectral features from the KBr, atmospheric water vapor, or the instrument itself, isolating the sample's true absorption spectrum.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While standard practice, the method is not without challenges. Understanding these is key to producing reliable data.
The Moisture Problem
Water is the primary enemy of this technique. Its presence, even in trace amounts from the air or in the KBr, will produce large, broad absorption peaks in the spectrum that can easily mask the features of your sample. Meticulous drying and handling are non-negotiable.
The Risk of Inhomogeneity
If the sample is not ground finely or mixed thoroughly into the KBr, the resulting pellet will contain "hot spots" of concentrated sample. This leads to a distorted spectrum with incorrect peak ratios and poor reproducibility, a phenomenon known as the Christiansen effect.
Pressure-Induced Changes
The high pressures involved can sometimes alter the sample itself. Certain crystalline materials may change their polymorphic form, leading to a different spectrum than the original material. In rare cases, the sample can react with the alkali halide matrix (e.g., via ion exchange), creating spectral artifacts.
Pellet Quality Issues
A perfect pellet is crystal clear. Cloudiness indicates moisture contamination or insufficient pressure. Cracks often result from trapped air or releasing the pressure too quickly. A poor-quality pellet will scatter light and degrade the quality of the final spectrum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
The KBr pellet method is a powerful tool, but it's important to know when it is—and isn't—the best approach.
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative identification: The KBr pellet method is a robust and cost-effective gold standard for identifying unknown solid compounds.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Be aware that pellet thickness and sample homogeneity are critical variables, requiring highly meticulous and consistent preparation to achieve reproducible results.
- If you are analyzing sensitive or reactive materials: Consider alternative FTIR sampling methods like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), which analyzes the sample surface directly without high pressure or a matrix.
Ultimately, mastering the pressed pellet technique is a direct reflection of careful lab work and a clear understanding of its physical principles.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sample preparation for FTIR spectroscopy |
| Common Matrix | Potassium Bromide (KBr) |
| Sample Concentration | 0.1% to 1.0% by weight |
| Critical Factor | Elimination of moisture and air |
| Main Challenge | Achieving perfect sample homogeneity |
| Best For | Routine qualitative identification of solids |
Achieve Unmatched Clarity in Your FTIR Analysis
Mastering the pressed powder pellet technique is essential for reliable spectroscopic results. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—from spectroscopic-grade KBr to durable hydraulic presses and pellet dies—that your laboratory needs for perfect sample preparation every time.
Ensure your analyses are never compromised by poor pellet quality. Contact our experts today to find the precise tools and support that will elevate your laboratory's capabilities and data integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of mechanical presses? Choose the Right Press for Your Application
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in BZY20 cold sintering? Boost Green Density to 76%
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for solid-state battery assembly? Achieve High-Pressure Densification
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in AFLMB testing? Improve Cycle Life with Constant Pressure
- What is the primary function of a hydraulic press in SiC/Al-Zn-Mg-Cu extrusion? Mastering Material Deformation
- What happens when hydraulics overheat? Prevent Catastrophic System Failure and Costly Downtime
- Why are high-precision laboratory hydraulic presses necessary? Mastering Ceramic Membrane Green Body Manufacturing
- What is the difference between a hydraulic press and a servo press? Choosing the Right Force for Your Application



















