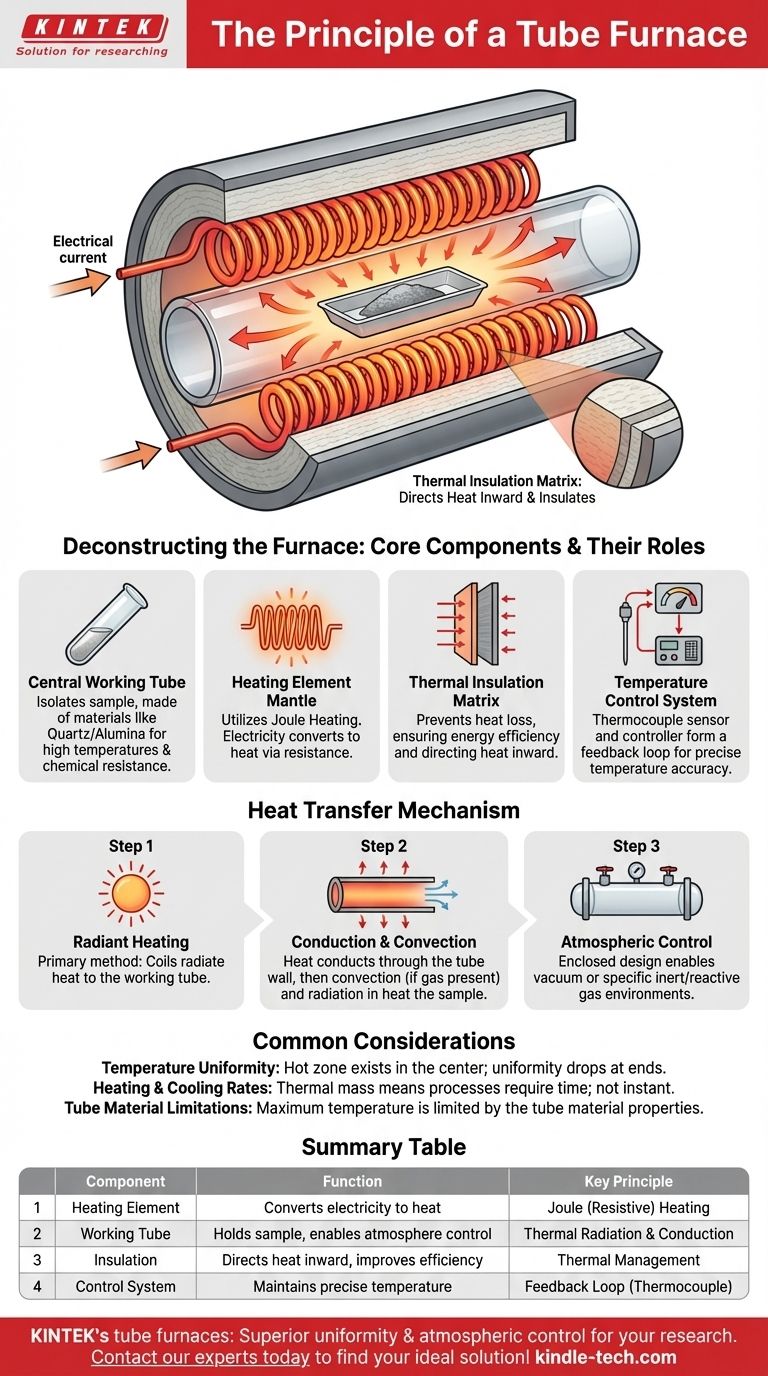
At its core, a tube furnace operates on the principle of electrical resistance heating. It uses heating elements, typically coiled wires, that surround a central tube. When an electric current is passed through these coils, their inherent resistance causes them to heat up intensely, and this heat is then radiated inward to uniformly heat the sample placed inside the tube.
The fundamental principle is the conversion of electrical energy into controlled, radiant thermal energy within an insulated cylindrical chamber. This design allows for precise temperature control over a sample in a contained, and often specific, atmospheric environment.
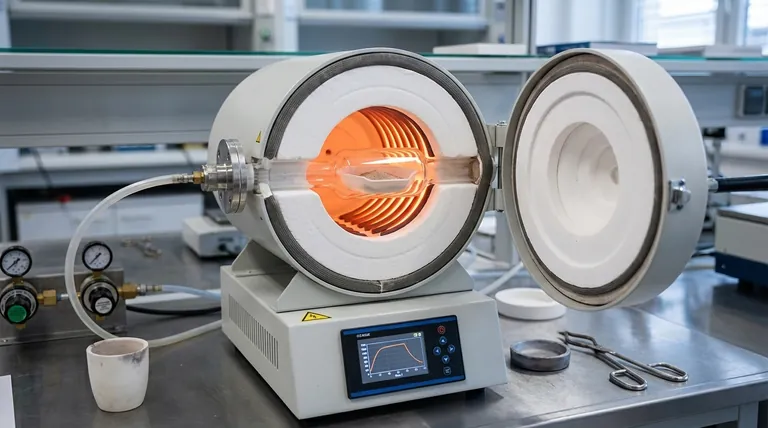

Deconstructing the Furnace: Core Components and Their Roles
To truly understand the principle, we must look at how its key components work together to generate and manage heat.
The Central Working Tube
The working tube is the heart of the furnace, acting as the primary chamber for your sample. It's a long, cylindrical vessel that isolates the sample from the heating elements.
Tubes are made from various materials like quartz, alumina, or specialized metal alloys, chosen based on the required maximum temperature, chemical compatibility, and thermal shock resistance.
The Heating Element Mantle
Surrounding the tube is a "mantle" that contains the heating coils. This is where the energy conversion happens.
The principle is Joule heating (or resistive heating). As electricity flows through the coils, resistance converts this electrical energy directly into heat. This is the same principle used in a common toaster, but engineered for much higher temperatures and precision.
The Thermal Insulation Matrix
The heating coils are not exposed; they are embedded within a thermally insulating matrix.
This insulation is critical. It serves two functions: preventing heat from escaping outward for energy efficiency and safety, and directing the generated heat inward toward the working tube, ensuring the sample receives uniform heating.
The Temperature Control System
A thermocouple, a type of temperature sensor, is placed near the heating elements or the tube.
This sensor provides real-time temperature data to a controller. The controller then modulates the electrical power sent to the coils, creating a feedback loop that maintains the desired temperature with high accuracy. This control system is fundamental to the furnace's reliable operation.
Understanding Heat Transfer and Process Control
The way heat moves from the source to the sample is key to the furnace's function. This understanding allows for precise control over material processing.
Radiant Heating is Dominant
The primary method of heat transfer is thermal radiation. The hot inner surface of the heating mantle radiates energy that is absorbed by the outer surface of the working tube.
Conduction and Convection Follow
Once the tube wall is hot, heat conducts through the tube material to its inner surface. From there, it heats the atmosphere within the tube.
Finally, a combination of radiation and convection (if a gas is present) transfers the heat from the inner tube wall to the sample, which is typically held in a ceramic or metal "boat."
Enabling Atmospheric Control
The enclosed nature of the tube is a key design principle. By fitting flanges to the ends of the tube, you can create a sealed environment.
This allows processes to be run under a vacuum or in the presence of a specific inert or reactive gas, which is impossible in an open-air furnace and critical for many advanced material applications.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, the design of a tube furnace comes with inherent operational trade-offs that must be managed for successful results.
Temperature Uniformity
While designed for uniformity, a "hot zone" exists in the center of the tube where the temperature is most stable. The temperature can drop off significantly near the ends of the tube. Accurate sample placement is critical.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The thermal insulation required for high-temperature stability also means that tube furnaces have significant thermal mass. Consequently, they cannot heat up or cool down instantly. These rates must be factored into your process timing.
Tube Material Limitations
The maximum operating temperature of the entire system is ultimately limited by the material of the working tube. Pushing a quartz tube, for example, beyond its thermal limit will cause it to deform or break.
Applying This Principle to Your Goal
Understanding how a tube furnace works allows you to select and use one effectively for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or annealing: The principle of controlled, insulated radiant heating provides the stable and uniform temperature environment you require.
- If your primary focus is processing in a specific atmosphere: The enclosed tube design is the key feature that enables you to control the environment, whether it's high vacuum or a specific process gas.
- If your primary focus is creating a thermal gradient: Multi-zone tube furnaces, which apply this same heating principle with several independent sets of coils, are the ideal choice.
By grasping the interplay between resistive heating, thermal radiation, and feedback control, you can better manage your experiments and achieve more reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Converts electricity to heat | Joule (Resistive) Heating |
| Working Tube | Holds sample, enables atmosphere control | Thermal Radiation & Conduction |
| Insulation | Directs heat inward, improves efficiency | Thermal Management |
| Control System | Maintains precise temperature | Feedback Loop (Thermocouple) |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing in your lab?
KINTEK's tube furnaces are engineered for superior temperature uniformity and atmospheric control, perfect for material synthesis, annealing, and research under specific gas or vacuum conditions. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a reliable solution tailored to your exact needs.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal tube furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the applications of tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















